Your eyes are delicate and constantly at work, yet many everyday habits can unknowingly contribute to long-term damage to our vision. Here are 10 everyday habits that might be harming your eyes without you even realizing it:
Your eyes are delicate and constantly at work, yet many everyday habits can unknowingly contribute to long-term damage to our vision. Here are 10 everyday habits that might be harming your eyes without you even realizing it:
- Rubbing your eyes – This can damage the delicate tissues around the eyes and increase the risk of keratoconus in susceptible people. It also spreads germs, raising the chance of infections like conjunctivitis.
Better habit: Use a clean tissue or wash your face if your eyes are irritated.
- Staring at screens for too long – Spending hours on phones, computers, or tablets without breaks can cause digital eye strain. Symptoms include dryness, blurred vision, headaches, and eye fatigue.
Better habit: Follow the 20-20-20 rule — every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds.
- Sleeping in contact lenses – Wearing contacts overnight (unless specifically approved) can cut off oxygen to your corneas and increase the risk of corneal ulcer.
Better habit: Always remove and clean contacts before bed.
- Skipping sunglasses – Not wearing sunglasses exposes your eyes to harmful UV rays, increasing the risk of cataract and macular degeneration over time.
Better habit: Wear sunglasses that block 100% of UVA and UVB rays, even on cloudy days.
- Ignoring dryness or irritation – Eye dryness can lead to chronic discomfort or damage to the corneal surface if left untreated. It may be linked to dry eye syndrome.
Better habit: Use preservative-free artificial tears and blink more often, especially when using screens. If persists, see your eye care practitioner.
- Not removing makeup properly – Sleeping in eye makeup can block oil glands, causing irritation or infection.
Better habit: Gently remove makeup each night with a clean cloth or wipes designed for the eye area.
- Using expired eye makeup – Old makeup can harbor bacteria, leading to eye infections.
Better habit: Replace mascara every 3 months and avoid sharing makeup to reduce the risk of contamination.
- Poor Contact Lens Hygiene – Not cleaning your contact lenses properly or using tap water to rinse them can lead to infections.
Better habit: Always follow your eye doctor’s care instructions, use fresh solution, and wash your hands before handling lenses.
- Reading in Poor Lighting – Though it won’t permanently damage your eyes, reading in dim light can cause eye strain and discomfort.
Better habit: Read or do close up work with adequate lighting.
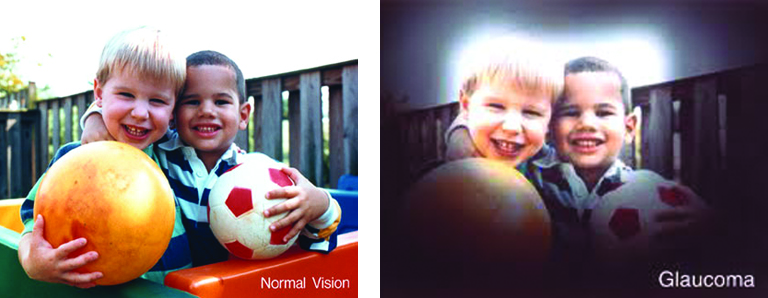
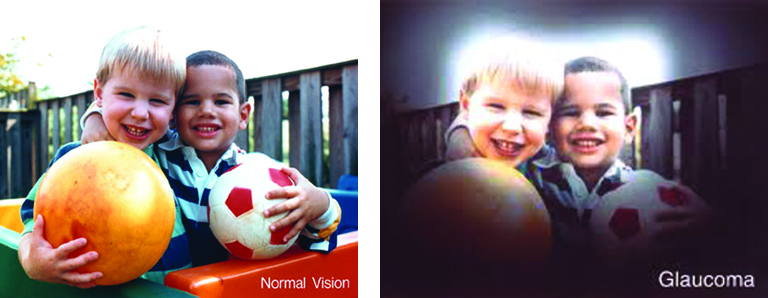
- Skipping regular eye exams – Some serious eye diseases, like glaucoma, can develop without noticeable symptoms.
Better habit: Get a comprehensive eye exam every 1–2 years (or as recommended by your eye doctor).
Taking care of your eyes is just as important as caring for the rest of your body. Breaking bad habits and staying on top of regular eye exams can help keep your vision strong for years. If you have any concerns about your eye health, consult your eye care professional for advice.






 Low vision affects millions of Americans — including many older adults. People with low vision aren’t blind, but because of their vision loss, they may not be able to do everyday tasks like driving or reading even with glasses.
Low vision affects millions of Americans — including many older adults. People with low vision aren’t blind, but because of their vision loss, they may not be able to do everyday tasks like driving or reading even with glasses.




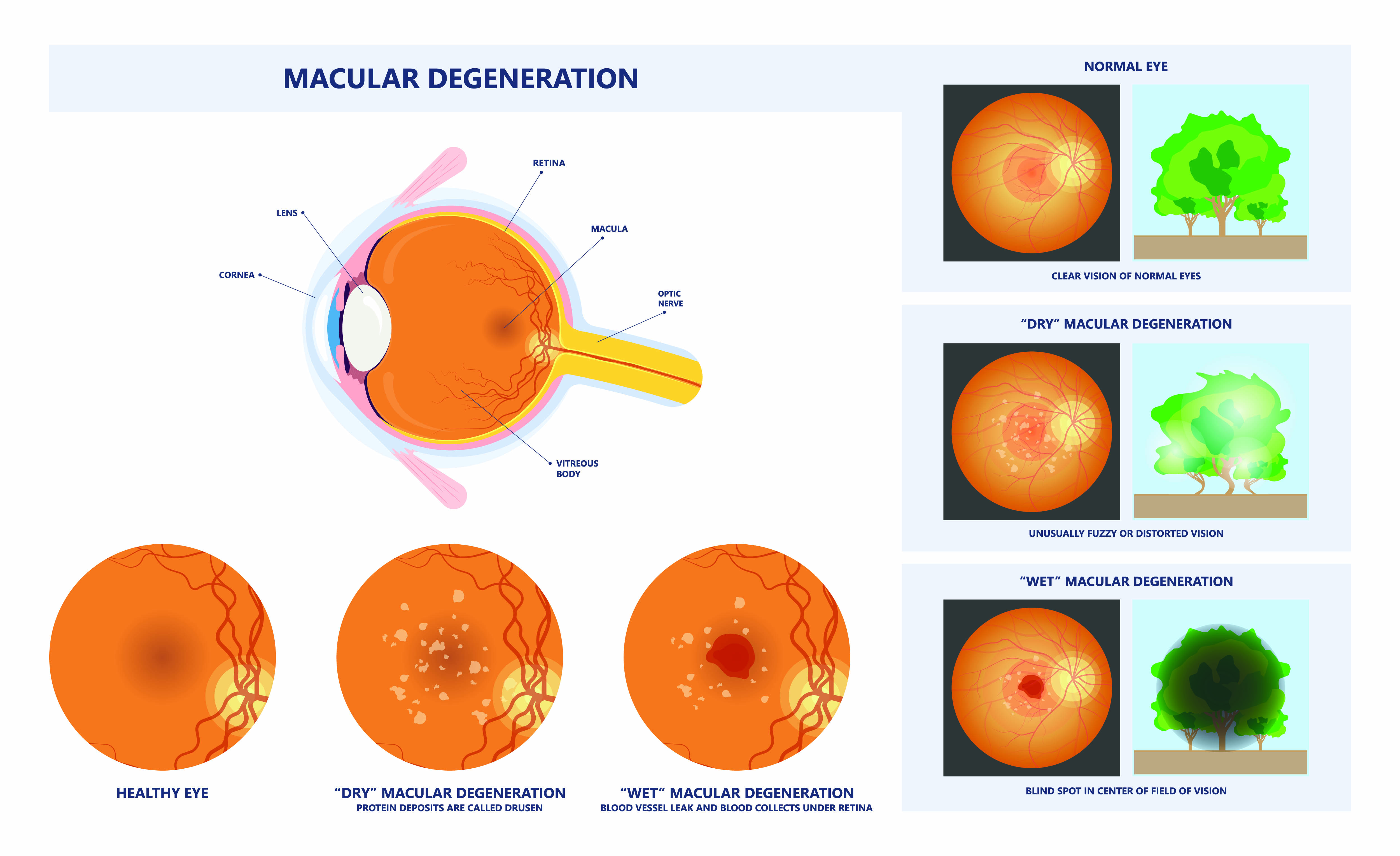
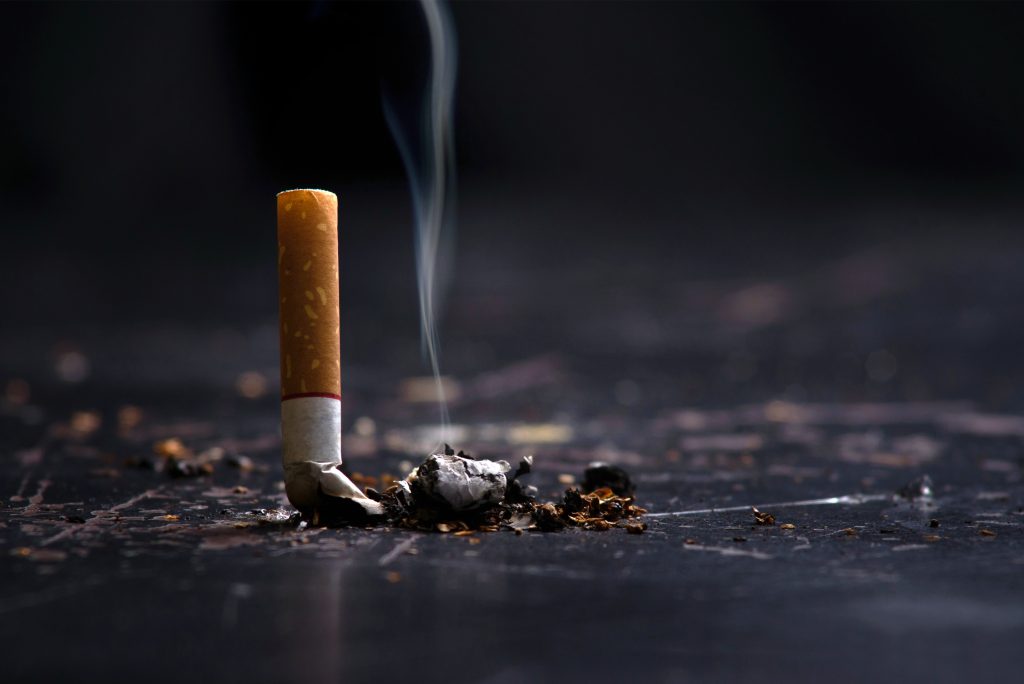
 Don’t smoke. Smoking increases your risk for age-related macular degeneration, cataract, and other eye diseases and conditions that can damage the optic nerve.
Don’t smoke. Smoking increases your risk for age-related macular degeneration, cataract, and other eye diseases and conditions that can damage the optic nerve. Wear protective eyewear when outdoors. Protecting your eyes from the sun’s ultraviolet rays when you are outdoors is vital for your eye health. Wearing sunglasses that block 99 to 100 percent of both UV-A and UV-B radiation.
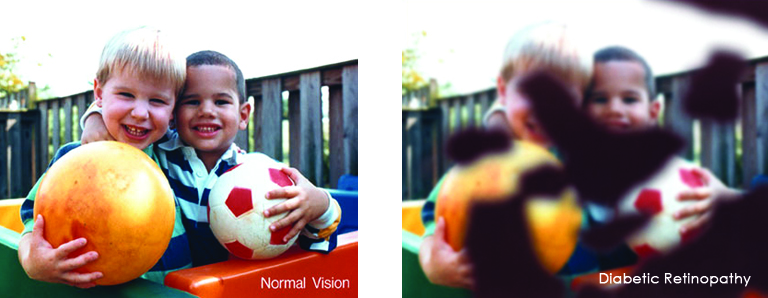
Wear protective eyewear when outdoors. Protecting your eyes from the sun’s ultraviolet rays when you are outdoors is vital for your eye health. Wearing sunglasses that block 99 to 100 percent of both UV-A and UV-B radiation. Know your family history. Talk to your family members about their eye health history. It’s important to know if anyone has been diagnosed with a disease or condition since many are hereditary, such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetes . This will help determine if you are at higher risk for developing an eye disease or condition.
Know your family history. Talk to your family members about their eye health history. It’s important to know if anyone has been diagnosed with a disease or condition since many are hereditary, such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetes . This will help determine if you are at higher risk for developing an eye disease or condition. Consider a multivitamin. Vitamins C, E and the mineral zinc have been shown to promote eye health. Vitamins with Lutein and Zeaxanthin have been known to help patients with moderate to severe age-related macular degeneration.
Consider a multivitamin. Vitamins C, E and the mineral zinc have been shown to promote eye health. Vitamins with Lutein and Zeaxanthin have been known to help patients with moderate to severe age-related macular degeneration.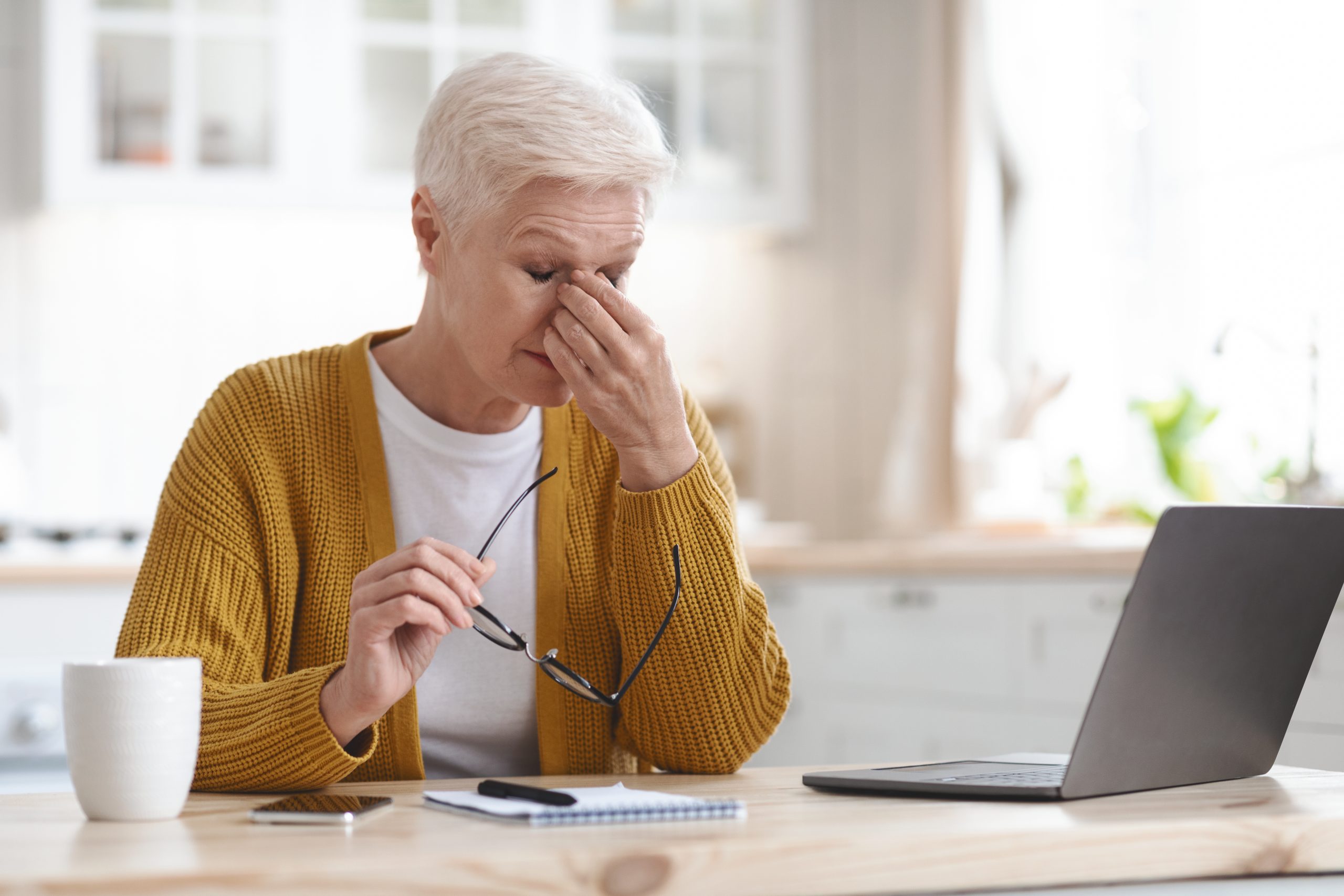 Give your eyes a rest. If you spend a lot of time at the computer or focusing at any one distance, you sometimes forget to blink, resulting in dryness and eye fatigue. Every 20 minutes, look away about 20 feet in front of you for 20 seconds. This can help reduce eyestrain. Consider using a lubricant eye drop during long periods of intense eye use and rest your eyes for 5 minutes.
Give your eyes a rest. If you spend a lot of time at the computer or focusing at any one distance, you sometimes forget to blink, resulting in dryness and eye fatigue. Every 20 minutes, look away about 20 feet in front of you for 20 seconds. This can help reduce eyestrain. Consider using a lubricant eye drop during long periods of intense eye use and rest your eyes for 5 minutes.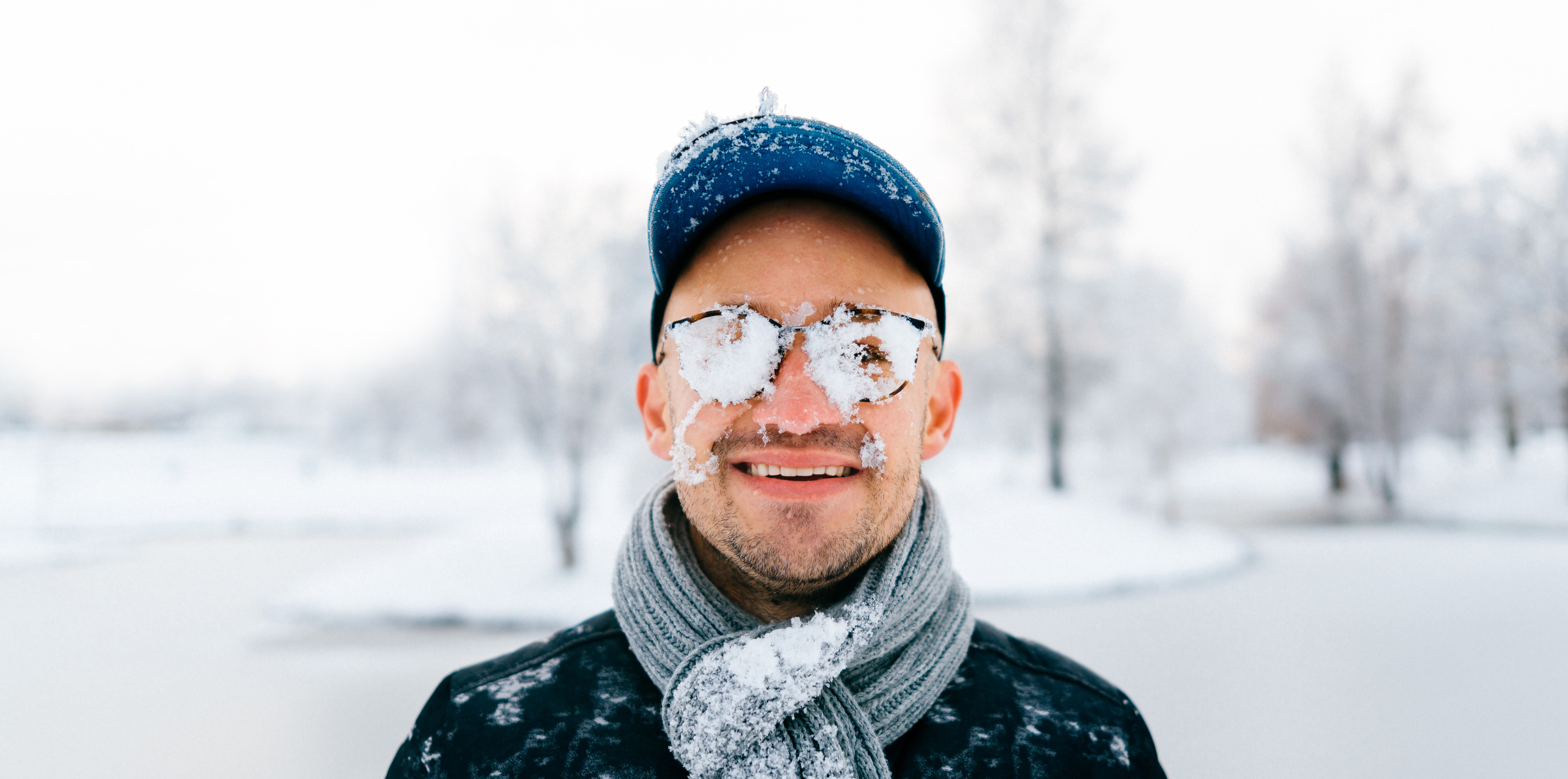 Harsh weather conditions can reduce the natural moisture in your eyes and the irritation usually results in a burning or itching sensation that often leads to rubbing or scratching your eyes which can worsen the symptoms. Sometimes it feels like there is a foreign object in your eye and for some, dry eyes can even cause excessive tearing, as your eyes try to overcompensate for their lack of protective tears. Prolonged, untreated dry eyes can lead to blurred vision as well. Between the harsh winter winds outside and the dry heat radiating inside, our eyes are very quickly irritated and dried in the winter months. The result is itchy, dry eyes that may cause pain, blurred vision, a burning sensation, or even watery vision as our eyes try to compensate for the dryness.
Harsh weather conditions can reduce the natural moisture in your eyes and the irritation usually results in a burning or itching sensation that often leads to rubbing or scratching your eyes which can worsen the symptoms. Sometimes it feels like there is a foreign object in your eye and for some, dry eyes can even cause excessive tearing, as your eyes try to overcompensate for their lack of protective tears. Prolonged, untreated dry eyes can lead to blurred vision as well. Between the harsh winter winds outside and the dry heat radiating inside, our eyes are very quickly irritated and dried in the winter months. The result is itchy, dry eyes that may cause pain, blurred vision, a burning sensation, or even watery vision as our eyes try to compensate for the dryness. Most people have eye problems at one time or another. Some are minor and will go away on their own, or are easy to treat at home. Others need a specialist’s care. Some eye issues come with age while others may be a serious condition.
Most people have eye problems at one time or another. Some are minor and will go away on their own, or are easy to treat at home. Others need a specialist’s care. Some eye issues come with age while others may be a serious condition. Dry eye is a common condition that occurs when your tears aren’t able to provide adequate lubrication for your eyes. Tears can be inadequate for many reasons. For example, dry eyes may occur if you don’t produce enough tears or if you produce poor-quality tears. Dry eyes can also feel very uncomfortable.
Dry eye is a common condition that occurs when your tears aren’t able to provide adequate lubrication for your eyes. Tears can be inadequate for many reasons. For example, dry eyes may occur if you don’t produce enough tears or if you produce poor-quality tears. Dry eyes can also feel very uncomfortable.