What Is Blue Light?
Blue light, also known as high-energy visible (HEV) light, is a color in the visible light spectrum that can be seen by human eyes. These wavelengths of visible and non-visible light are measured in nanometers (nm), and, in general, the shorter the wavelength, the higher the energy. Blue light is a short wavelength, which means it produces higher amounts of energy.
Unlike other forms of light, the eyes cannot effectively filter blue light, so more can pass through the eye to the retina. Blue light produces both benefits and concerns for our eyes and overall health.

Where Are You Exposed To Blue Light?
The largest source of blue light is sunlight. In addition, there are many other sources:
- Fluorescent light
- Fluorescent light bulbs
- LED light
- Flat screen LED televisions
- Computer monitors, smart phones, and tablet screens
Blue light exposure you receive from screens is small compared to the amount of exposure from the sun. And yet, there is concern over the long-term effects of screen exposure because of the close proximity of the screens and the length of time spent looking at them. According to an NEI-funded study, children’s eyes absorb more blue light than adults from digital device screens.
Benefits of Blue Light?
Moderate amounts of blue light are essential for good health.
- Promotes alertness
- Boosts memory and cognitive function
- Elevates mood
- Regulates circadian rhythm
Blue Light and Digital Eyestrain
Using digital devices up close or for long periods can lead to digital eyestrain.
Research has shown that when people use computers, laptops, and other digital devices, they tend to blink less often than normal. Fewer blinks can mean less moisture.
Digital eyestrain means different things to different people, but is generally related to the focusing system of the eyes.
When your eyes are strained from staring at a blue-light-emitting screen, you might notice:
- dry eyes
- sore or irritated eyes
- tired eyes
- headaches
- facial muscles fatigued by squinting
Blue light scatters more easily than most other visible light. This may make it difficult for your eye to focus when receiving blue light. Instead, your eye may digest blue light as poorly focused visual static. This reduction in contrast may make it more difficult for your eye to process blue light, potentially contributing to eyestrain.
Still, there isn’t enough evidence to confirm that blue light directly leads to eyestrain. More high-quality studies are needed.
How to Limit Blue Light Exposure
The American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO) recommends that you take the steps below to reduce digital eyestrain.
1. Practice the 20/20/20 strategy
- While you’re using a device that emits blue light, stop every 20 minutes to focus on objects that are around 20 feet away. Study those objects for 20 seconds before you return to your up-close viewing.
- Keep your eyes moist
- Eye drops, such as artificial tears, and room humidifiers are all good ways to keep your eyes from becoming too dry and irritated while you’re using blue-light-emitting devices.
2. Use eyeglasses with the right prescription
Squinting at screens for long periods isn’t recommended for the overall health of your eyes. If you wear prescription eyeglasses to correct your vision, make sure you’re wearing a prescription intended for the distance between your eyes and your screen — ideally an arm’s length away. Most glasses are formulated for longer distances.
3. Adjust the blue light on your screen
To lower the risk of eyestrain and sleep disturbance, you may want to set your screens to a “night shift” setting with warmer tones. You can also purchase blue-light-filtering screens to slip over your computer screen when you’re working at night. The filter could cut the glare of your screen.
And a 2020 research study shows that they block 30 to 60 percent of blue light, though it isn’t clear whether blocking the blue will help preserve the sleep-wake cycle for those who use backlit screens before bedtime.


 Make sure they take frequent screen breaks. Instead of focusing directly on the screen, encourage your child to look around the room every now and then, or take some time to stare out the window (at least 20 seconds is recommended by the American Optometric Association). You can even remind them to blink.
Make sure they take frequent screen breaks. Instead of focusing directly on the screen, encourage your child to look around the room every now and then, or take some time to stare out the window (at least 20 seconds is recommended by the American Optometric Association). You can even remind them to blink. It’s easy for us to forget about our eyes let alone our child’s, but it is very important to get your child’s eyes checked regularly.
It’s easy for us to forget about our eyes let alone our child’s, but it is very important to get your child’s eyes checked regularly.
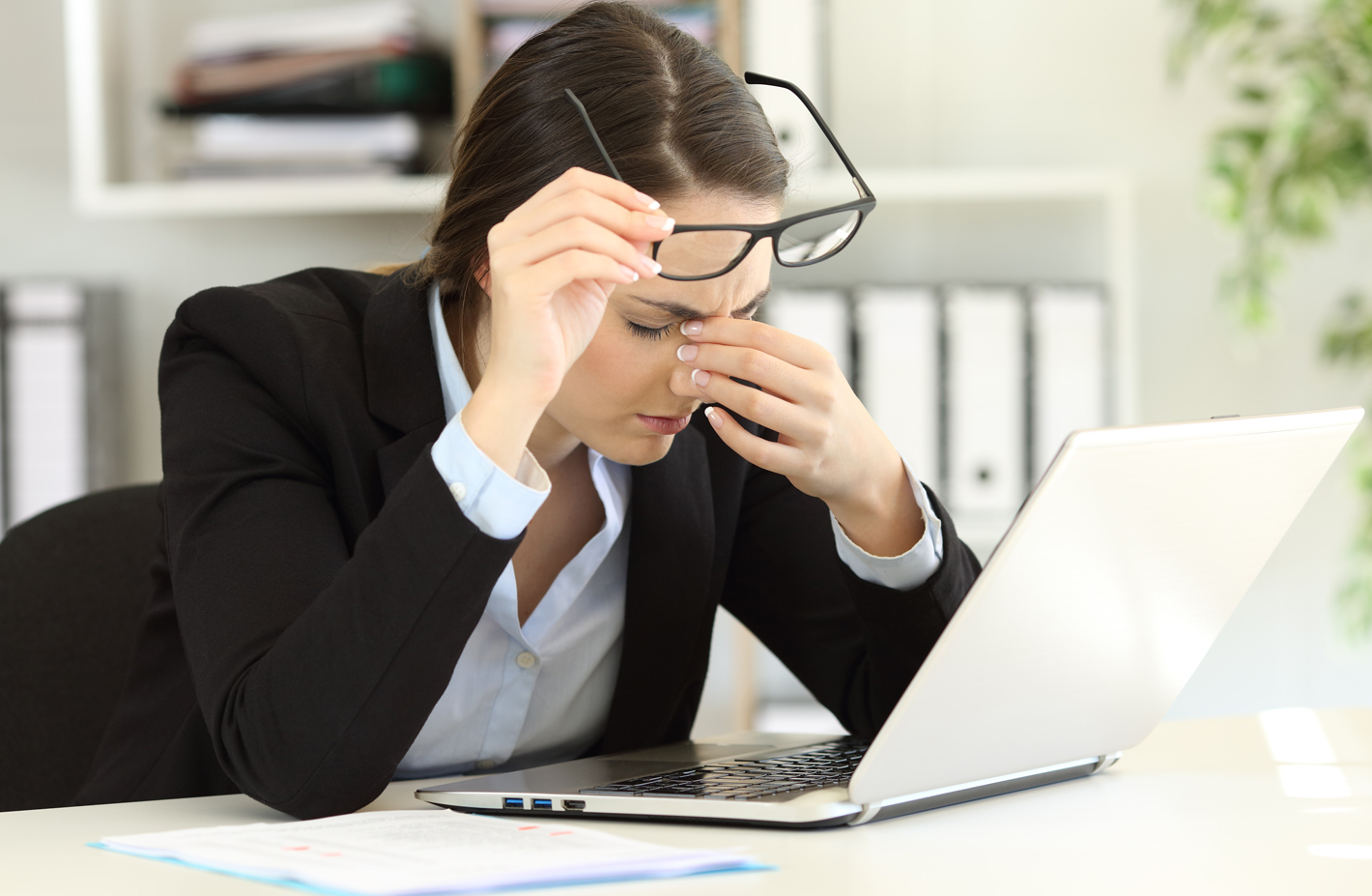



 Rest and blink your eyes – Researchers found that over 30% of people using digital devices rarely take time to rest their eyes. Just over 10% say they never take a break, even when working from home. The eye muscles get overworked and don’t get a chance to relax and recover. Experts suggest the 20-20-20 rule; every 20 minutes, focus your eyes and attention on something 20 feet away for 20 seconds. You can also get up and walk around for a few minutes.
Rest and blink your eyes – Researchers found that over 30% of people using digital devices rarely take time to rest their eyes. Just over 10% say they never take a break, even when working from home. The eye muscles get overworked and don’t get a chance to relax and recover. Experts suggest the 20-20-20 rule; every 20 minutes, focus your eyes and attention on something 20 feet away for 20 seconds. You can also get up and walk around for a few minutes. Reduce exposure to blue light – In the spectrum of light, blue is more high energy and close to ultraviolet light. So, if you use screens throughout the day, ask your eye doctor about the value of computer glasses that block blue light. Reducing exposure to blue light may help lessen vision problems. At home, using digital devices until bedtime can overstimulate your brain and make it more difficult to fall asleep. Eye doctors recommend no screen time at least one to two hours before going to sleep.
Reduce exposure to blue light – In the spectrum of light, blue is more high energy and close to ultraviolet light. So, if you use screens throughout the day, ask your eye doctor about the value of computer glasses that block blue light. Reducing exposure to blue light may help lessen vision problems. At home, using digital devices until bedtime can overstimulate your brain and make it more difficult to fall asleep. Eye doctors recommend no screen time at least one to two hours before going to sleep.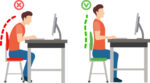 Sit up straight – Proper posture is important. Your back should be straight and your feet on the floor while you work. Elevate your wrists slightly instead of resting them on the keyboard.
Sit up straight – Proper posture is important. Your back should be straight and your feet on the floor while you work. Elevate your wrists slightly instead of resting them on the keyboard. Set up monitor properly – Make sure your computer screen is about 25 inches, or an arm’s length, away from your face. The center of the screen should be about 10-15 degrees below eye level. Cut glare by using a matte screen filter. You can find them for all types of computers, phones, and tablets. Increase font size or set the magnification of the documents you are reading to a comfortable size.
Set up monitor properly – Make sure your computer screen is about 25 inches, or an arm’s length, away from your face. The center of the screen should be about 10-15 degrees below eye level. Cut glare by using a matte screen filter. You can find them for all types of computers, phones, and tablets. Increase font size or set the magnification of the documents you are reading to a comfortable size. Consider computer glasses –For the greatest comfort at your computer, you might benefit from having your eye doctor modify your eyeglasses prescription to create customized computer glasses. This is especially true if you normally wear distance contact lenses, which may also become dry and uncomfortable during extended screen time. Computer glasses also are a good choice if you wear bifocals or progressive lenses, because these lenses generally are not optimal for the distance to your computer screen.
Consider computer glasses –For the greatest comfort at your computer, you might benefit from having your eye doctor modify your eyeglasses prescription to create customized computer glasses. This is especially true if you normally wear distance contact lenses, which may also become dry and uncomfortable during extended screen time. Computer glasses also are a good choice if you wear bifocals or progressive lenses, because these lenses generally are not optimal for the distance to your computer screen. Get an Eye Exam – If you have tried all these tips and eye strain is still an issue, it might be time to see an eye care professional to schedule an eye exam. The exam may even detect underlying issues before they becomes worse.
Get an Eye Exam – If you have tried all these tips and eye strain is still an issue, it might be time to see an eye care professional to schedule an eye exam. The exam may even detect underlying issues before they becomes worse.




 Bezalel Schendowich, OD
Bezalel Schendowich, OD




