Healthy Aging Month is an annual health observance designed to focus national attention on the positive aspects of growing older. Aging is a process that brings many changes. Vision loss and blindness, however, do not have to be one of them. There are several simple steps you can take to help keep your eyes healthy for the rest of your life.
Healthy Aging Month is an annual health observance designed to focus national attention on the positive aspects of growing older. Aging is a process that brings many changes. Vision loss and blindness, however, do not have to be one of them. There are several simple steps you can take to help keep your eyes healthy for the rest of your life.
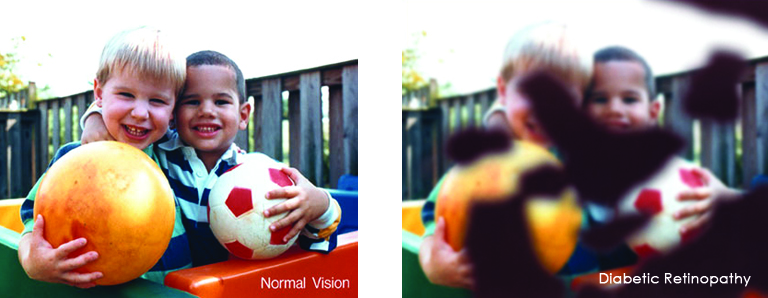
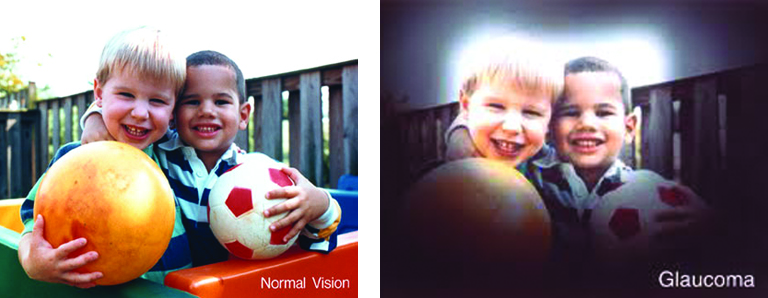
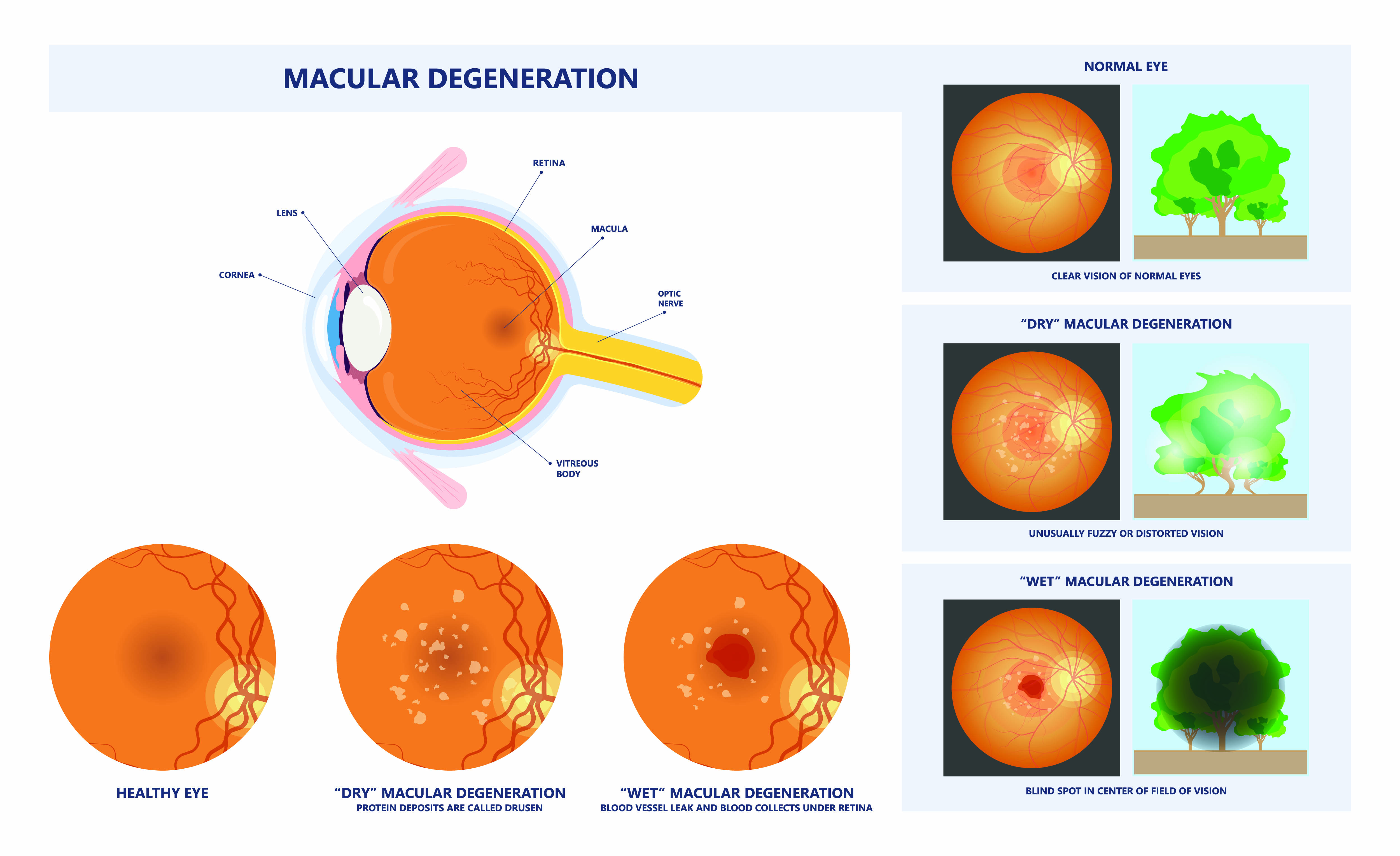
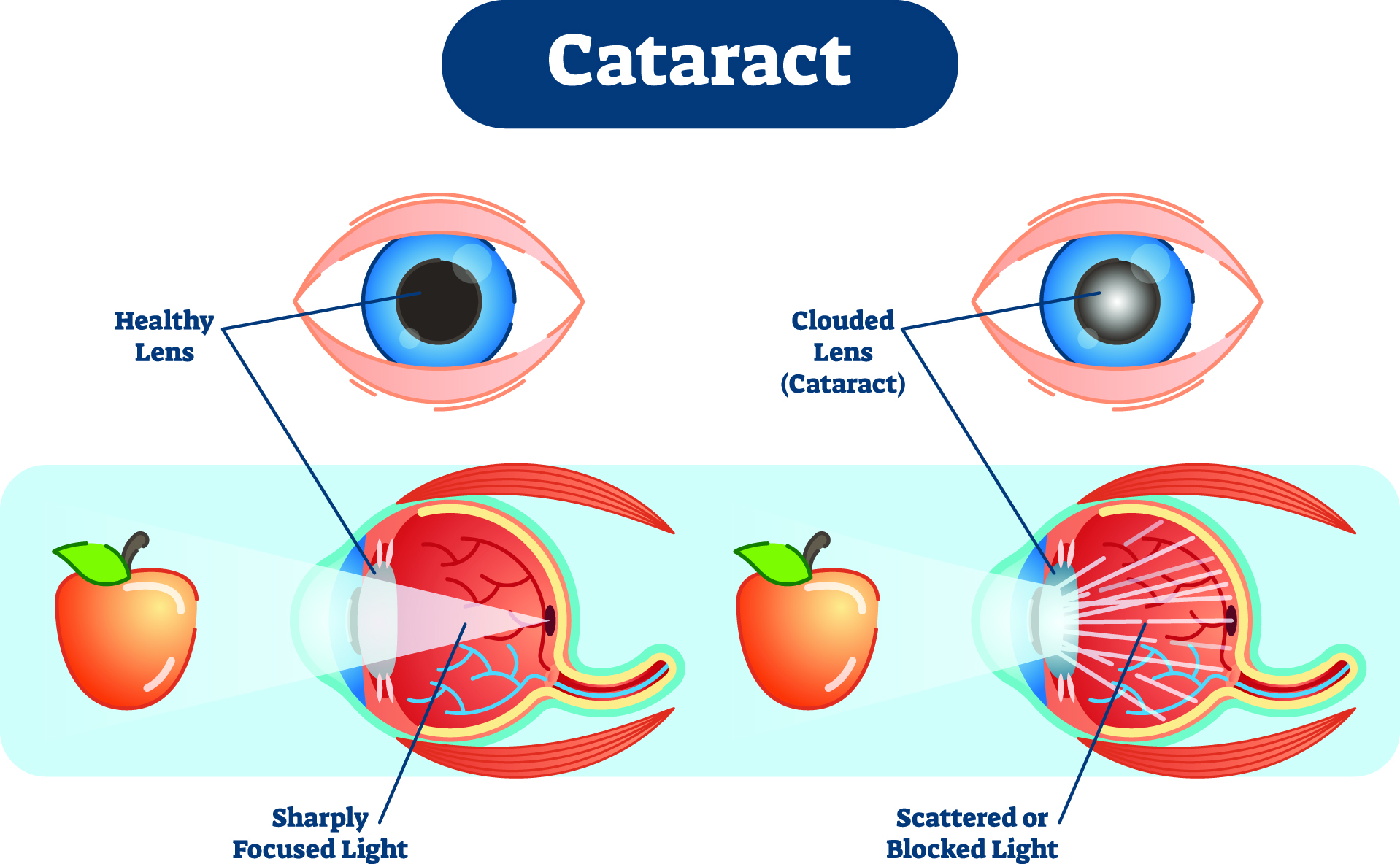
Eye diseases often have no early symptoms, but can be detected during a comprehensive dilated eye exam. A comprehensive dilated eye exam is different from the basic eye exam or screening you have for glasses or contacts. By dilating the pupils and examining the back of the eyes, your eye care professional can detect eye diseases in their early stages, before vision loss occurs. By performing a comprehensive eye exam, your eye care professional can check for early signs of –
Here are some other tips to maintain healthy vision now and as you age:

- Eat a healthy, balanced diet. Fruits and vegetables can help keep your eyes healthy. Visit our website for healthy eye recipes, click here Eye Cook.
 Maintain a healthy weight. Being overweight increases your risk for diabetes. By exercising regularly, you can help keep your body healthy and prevent vision loss.
Maintain a healthy weight. Being overweight increases your risk for diabetes. By exercising regularly, you can help keep your body healthy and prevent vision loss.
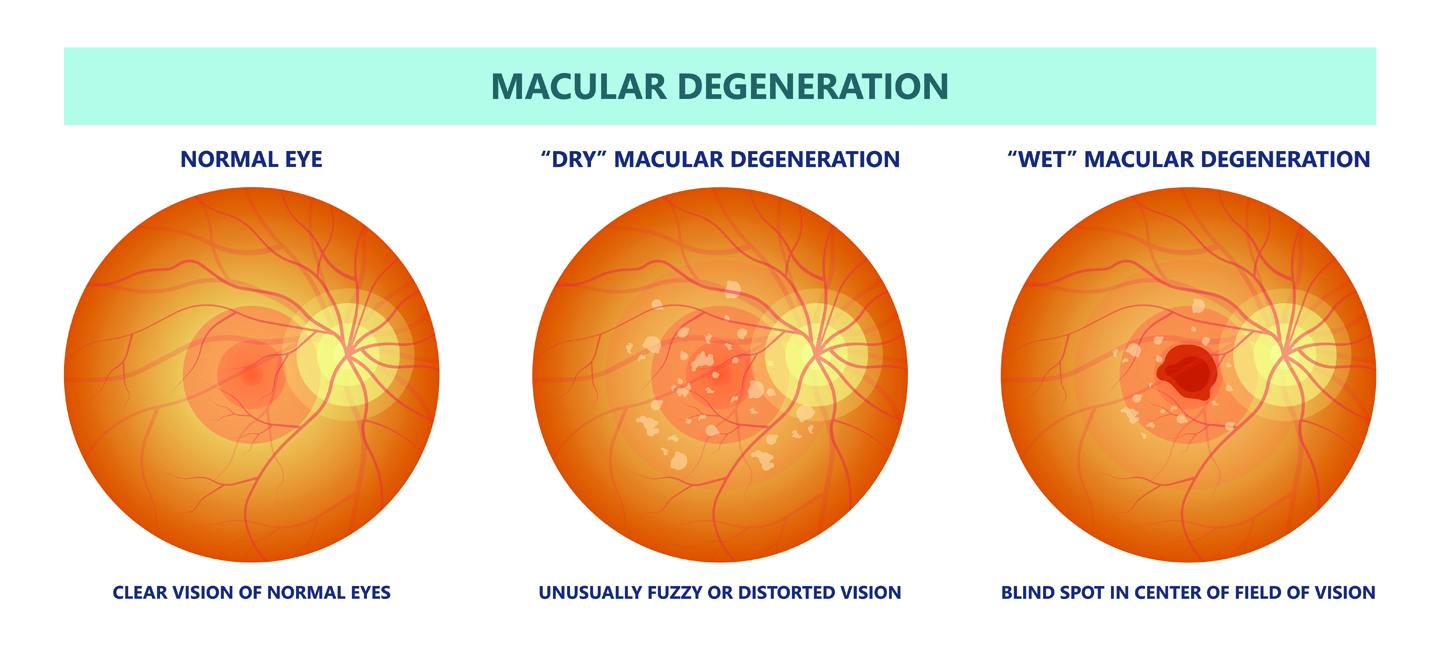
 Don’t smoke. Smoking increases your risk for age-related macular degeneration, cataract, and other eye diseases and conditions that can damage the optic nerve.
Don’t smoke. Smoking increases your risk for age-related macular degeneration, cataract, and other eye diseases and conditions that can damage the optic nerve.
 Wear protective eyewear when outdoors. Protecting your eyes from the sun’s ultraviolet rays when you are outdoors is vital for your eye health. Wearing sunglasses that block 99 to 100 percent of both UV-A and UV-B radiation.
Wear protective eyewear when outdoors. Protecting your eyes from the sun’s ultraviolet rays when you are outdoors is vital for your eye health. Wearing sunglasses that block 99 to 100 percent of both UV-A and UV-B radiation.
 Know your family history. Talk to your family members about their eye health history. It’s important to know if anyone has been diagnosed with a disease or condition since many are hereditary, such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetes . This will help determine if you are at higher risk for developing an eye disease or condition.
Know your family history. Talk to your family members about their eye health history. It’s important to know if anyone has been diagnosed with a disease or condition since many are hereditary, such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetes . This will help determine if you are at higher risk for developing an eye disease or condition.
 Consider a multivitamin. Vitamins C, E and the mineral zinc have been shown to promote eye health. Vitamins with Lutein and Zeaxanthin have been known to help patients with moderate to severe age-related macular degeneration.
Consider a multivitamin. Vitamins C, E and the mineral zinc have been shown to promote eye health. Vitamins with Lutein and Zeaxanthin have been known to help patients with moderate to severe age-related macular degeneration.
 Give your eyes a rest. If you spend a lot of time at the computer or focusing at any one distance, you sometimes forget to blink, resulting in dryness and eye fatigue. Every 20 minutes, look away about 20 feet in front of you for 20 seconds. This can help reduce eyestrain. Consider using a lubricant eye drop during long periods of intense eye use and rest your eyes for 5 minutes.
Give your eyes a rest. If you spend a lot of time at the computer or focusing at any one distance, you sometimes forget to blink, resulting in dryness and eye fatigue. Every 20 minutes, look away about 20 feet in front of you for 20 seconds. This can help reduce eyestrain. Consider using a lubricant eye drop during long periods of intense eye use and rest your eyes for 5 minutes.
You can’t stop time, but you can take care of your eyes so that they remain healthy as you age. Having a healthy vision can be possible at any age! Even if you are not experiencing vision problems, visiting an eye care professional regularly for a comprehensive dilated eye exam is the most important thing you can do to reduce your risk of vision loss as you age.
Download “Everyone’s vision can change with age”
A handout with explanation on how vision can change with age.
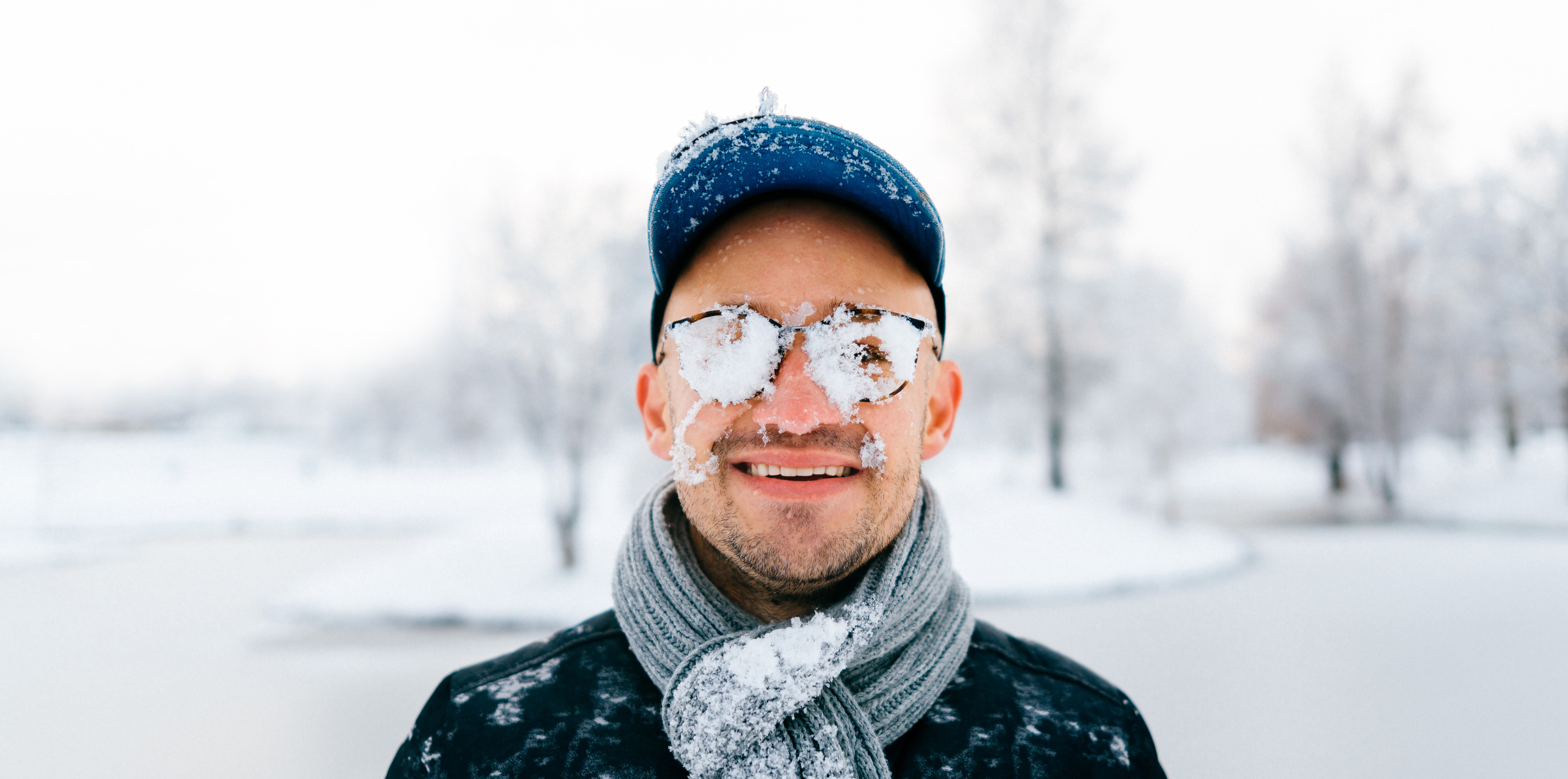








 Harsh weather conditions can reduce the natural moisture in your eyes and the irritation usually results in a burning or itching sensation that often leads to rubbing or scratching your eyes which can worsen the symptoms. Sometimes it feels like there is a foreign object in your eye and for some, dry eyes can even cause excessive tearing, as your eyes try to overcompensate for their lack of protective tears. Prolonged, untreated dry eyes can lead to blurred vision as well. Between the harsh winter winds outside and the dry heat radiating inside, our eyes are very quickly irritated and dried in the winter months. The result is itchy, dry eyes that may cause pain, blurred vision, a burning sensation, or even watery vision as our eyes try to compensate for the dryness.
Harsh weather conditions can reduce the natural moisture in your eyes and the irritation usually results in a burning or itching sensation that often leads to rubbing or scratching your eyes which can worsen the symptoms. Sometimes it feels like there is a foreign object in your eye and for some, dry eyes can even cause excessive tearing, as your eyes try to overcompensate for their lack of protective tears. Prolonged, untreated dry eyes can lead to blurred vision as well. Between the harsh winter winds outside and the dry heat radiating inside, our eyes are very quickly irritated and dried in the winter months. The result is itchy, dry eyes that may cause pain, blurred vision, a burning sensation, or even watery vision as our eyes try to compensate for the dryness.
 Make sure they take frequent screen breaks. Instead of focusing directly on the screen, encourage your child to look around the room every now and then, or take some time to stare out the window (at least 20 seconds is recommended by the American Optometric Association). You can even remind them to blink.
Make sure they take frequent screen breaks. Instead of focusing directly on the screen, encourage your child to look around the room every now and then, or take some time to stare out the window (at least 20 seconds is recommended by the American Optometric Association). You can even remind them to blink. It’s easy for us to forget about our eyes let alone our child’s, but it is very important to get your child’s eyes checked regularly.
It’s easy for us to forget about our eyes let alone our child’s, but it is very important to get your child’s eyes checked regularly. Most people have eye problems at one time or another. Some are minor and will go away on their own, or are easy to treat at home. Others need a specialist’s care. Some eye issues come with age while others may be a serious condition.
Most people have eye problems at one time or another. Some are minor and will go away on their own, or are easy to treat at home. Others need a specialist’s care. Some eye issues come with age while others may be a serious condition. Dry eye is a common condition that occurs when your tears aren’t able to provide adequate lubrication for your eyes. Tears can be inadequate for many reasons. For example, dry eyes may occur if you don’t produce enough tears or if you produce poor-quality tears. Dry eyes can also feel very uncomfortable.
Dry eye is a common condition that occurs when your tears aren’t able to provide adequate lubrication for your eyes. Tears can be inadequate for many reasons. For example, dry eyes may occur if you don’t produce enough tears or if you produce poor-quality tears. Dry eyes can also feel very uncomfortable.