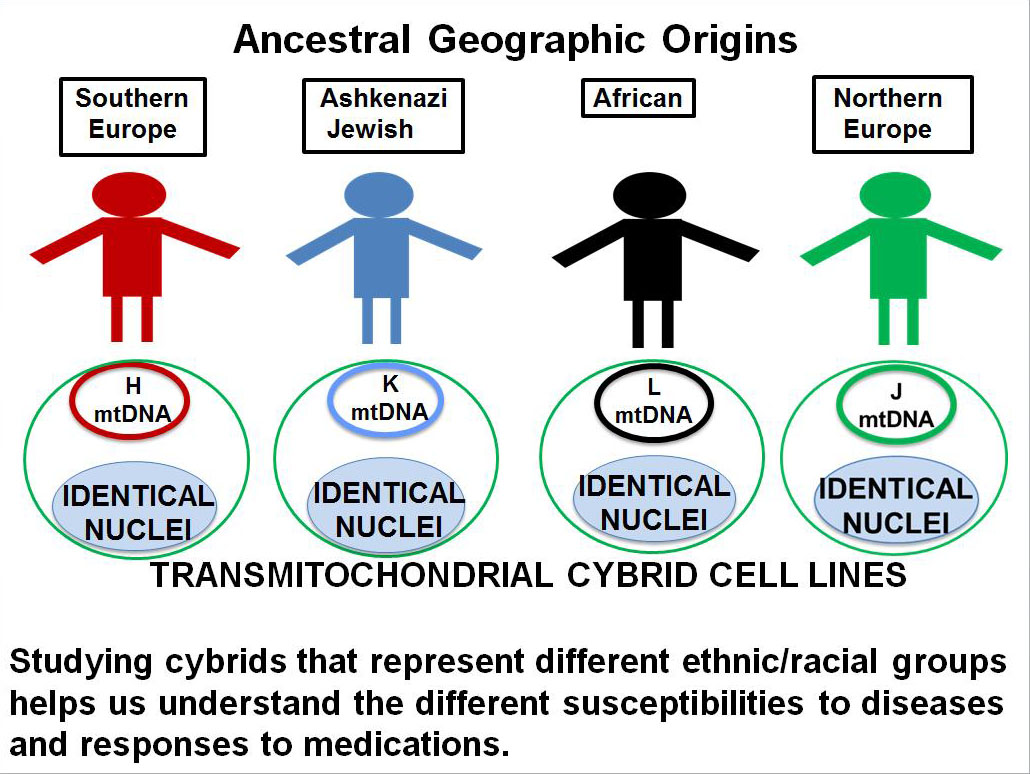
DEF Research Director Dr. M. Cristina Kenney’s research has shown that the mitochondrial DNA from different ethnic/racial populations may play a key role in determining that population’s resistance or susceptibility to disease (see previous article on 11/12/15 – Mitochondria and Age-Related Macular Degeneration). In order to study these effects, Kenney has developed the cybrid model using mitochondria from subjects of different ethnic/racial groups (Figure 1). The comparison of an individual’s mitochondria with that from other ethnic/racial groups (African, European, Asian or Ashkenazi Jewish) allows us to determine if their mitochondria determine that population’s susceptibility or resistance to disease and to response to drugs.
Personalized cybrids
Kenney’s cybrids are made with mitochondria from the blood taken from individual living donors. Looked at individually they are all really “personalized cybrids” because each cybrid test system has the mitochondria from the original donor and reflects the responses of that donor.
Using Cybrids to Study Age-Related Diseases
How is Kenney using these personalized cybrids?
Kenney is partnering with Dr. Pinchas Cohen, dean of the University of Southern California, Leonard Davis School of Gerontology, to explore how novel, small proteins produced from mitochondria might be used to treat a variety of age-related diseases such as age-related macular degeneration, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, stroke and cholesterol. Cohen’s laboratory has discovered and characterized many of these new, small proteins called “mitochondrial derived peptides” (MDPs). His work has shown that these MDPs can protect brain cells from damage and early death, such as occurs in Alzheimer’s disease. Cohen and Kenney are now testing these MDPs in the K and H cybrids to assess their protective effects to stop retinal cell death, such as seen in AMD.
Kenney explains her approach:
“Our cybrid system represents a very powerful technique. We are now using the Ashkenazi Jewish population as an excellent model to learn how the mitochondria, with their unique mtDNA, influence the risk factors for AMD. We plan to extend the study to investigate Ashkenazi Jewish people’s susceptibility to Alzheimer’s disease, heart disease and stroke. Eventually, we believe the findings for the K haplogroup mitochondrial DNA will be applicable to other groups, as well.”
11/17/15
 Anthony B. Nesburn, MD, FASC
Anthony B. Nesburn, MD, FASC
President/Medical Director
Discovery Eye Foundation

