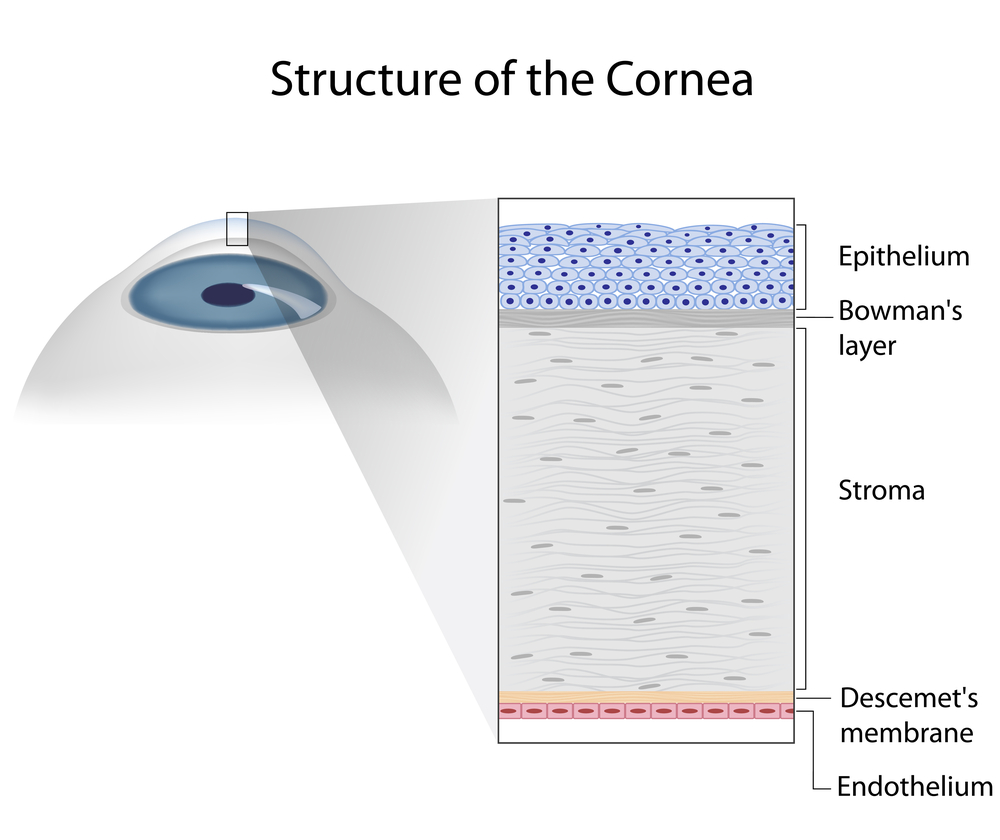
“You’ve got the macular? I’ve got some but my sister, she’s got all kinds!” Even as the word retina has become commonplace, the macula and its diseases are often feared and misunderstood. The retina is the light-sensitive layer of cells that line the inside of the eye. The many layers of the retina work together to convert what we see into an exquisitely coded signal that travels to the brain. There the message is decoded and directs us to take action – “that’s a fine looking piece of pie!”
The macula is the part of the retina that helps us see fine detail, far away objects, and color. It’s packed with more photoreceptors than any TV or monitor which is why it is prized real estate. It is the small, central area of the retina that’s worth the most – the bullseye of sight. When things happen to the macula, it gets an “r”. Macular edema, macular degeneration, macular hole, pucker, drusen, scar, fibrosis, hemorrhage, and vitreomacular traction are common conditions that involve the macula. When present, distorted vision (metamorphopsia), blank spots (scotoma), and blurred vision are common symptoms.
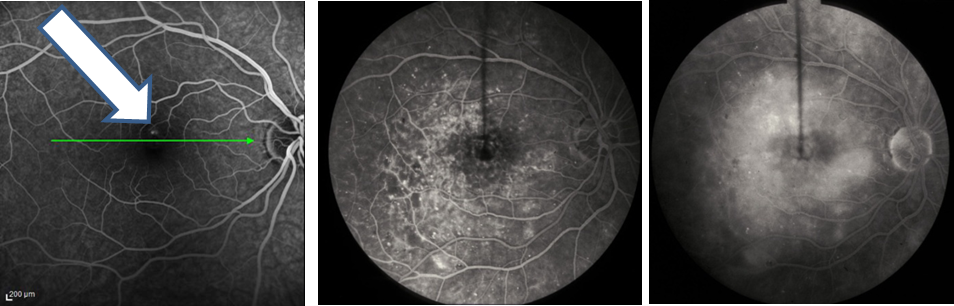
Macular edema refers to an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the layers of the macula. From the side, it looks like the snake that ate the pig. Like a droplet of water on your computer screen, images are distorted by the swollen retina – making it more difficult to see clearly. The more widespread, thicker, and severe the swelling becomes, more likely one will notice visual symptoms. If untreated, chronic macular edema can lead to irreversible damage to the macula and permanent vision loss.
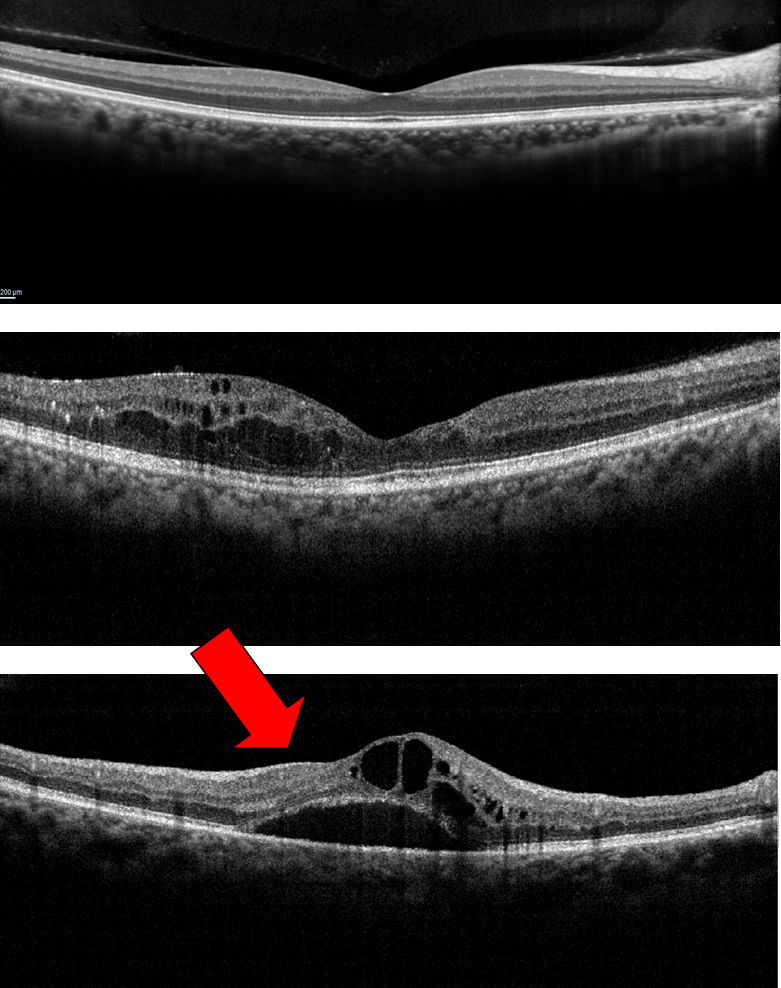
-The top image has is normal. Note the even layers and gently sloping dip of the macula called the fovea. This eye has excellent vision.
– The middle OCT has ME, black-appearing cysts (arrows) which threaten the normal fovea. This eye also has good vision.
– The bottom OCT shows ME involving the macula. Because ME involves the macular center (the fovea), vision is poor (large red arrow).
Macular edema is not a disease but the result of one. As with other conditions where abnormal fluid accumulates (leg swelling, pulmonary edema, hives, and allergy), macular edema can be caused by many conditions including metabolic (diabetes), aging (macular degeneration), hereditary (retinitis pigmentosa), inflammatory (sarcoidosis, uveitis), toxic, neoplastic (eye tumors), traumatic, surgical, and unknown causes (idiopathic, macular hole, macular pucker, vitreomacular traction). Macular edema occurs when the retina’s ability to keep fluid out of the retina is overwhelmed by the fluid leaking into it. (If more rain falls on the lawn than it can handle, you get puddles of fluid. In the retina, blisters of fluid form and swell the retina – this is macular edema. Fluorescein angiography (Figure 1) and optical coherence tomography (Figure 2) are two common tests to evaluate macular edema.
Macular edema is typically caused by increased leakage or growth of abnormal blood vessels. The most effective treatment strategies address the underlying cause (diabetes, blood vessel occlusion, neovascularization, inflammation, etc) as well as the hyperpermeability of the capillaries in and around the macula. Eye drops, laser, placement of long-acting medication implants, and surgery are effective in many diseases but the mainstay of treatment is now intravitreal injections (IVI). The IVI is an office procedure painlessly performed under topical anesthesia in which medication is placed inside the eye by a very small needle. IVI should be performed by a trained retina specialist with meticulous monitoring of treatment efficacy and of extremely rare but potentially serious complications. IVI is considered one of the most commonly performed procedure in the world.
Lucentis, Eyelea, and Ozurdex are the trade names of the three most common FDA-approved medications for the treatment of the common conditions causing macular edema. Avastin is not FDA approved but has also been extensively studied in large, well-designed, federally-funded clinical trials and is felt to have efficacy and safety no less than any of the other available options. Each option has a considerable track record of success and works by decreasing the amount of fluid leaking from abnormal blood vessels.
Macular edema is a common finding in many diseases of the retina, most which can be treated to improve vision. The physician’s therapeutic armamentarium continues to expand. There has never been a more successful time in the treatment of macular edema and macular disease. While much has been discovered, many promising therapies await.
3/5/15
 Suber S. Huang, MD, MBA
Suber S. Huang, MD, MBA
Chair, National Eye Health Education Program
Philip F. and Elizabeth G. Searle – Suber Huang MD Professor
Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine
Past-President American Society of Retina Specialists
CEO, Retina Center of Ohio