A common misconception is that all you need to have a successful blog or website is good content. While content people want to read is important, if you can’t see it, or it is difficult to read, very few people are going to take the time to try. There is lots of good content to choose from.
Making your content easy to scan and read and using great graphics that can tell a story are just as important. Especially if you want to reach the millions of potential readers that are blind or visually impaired.
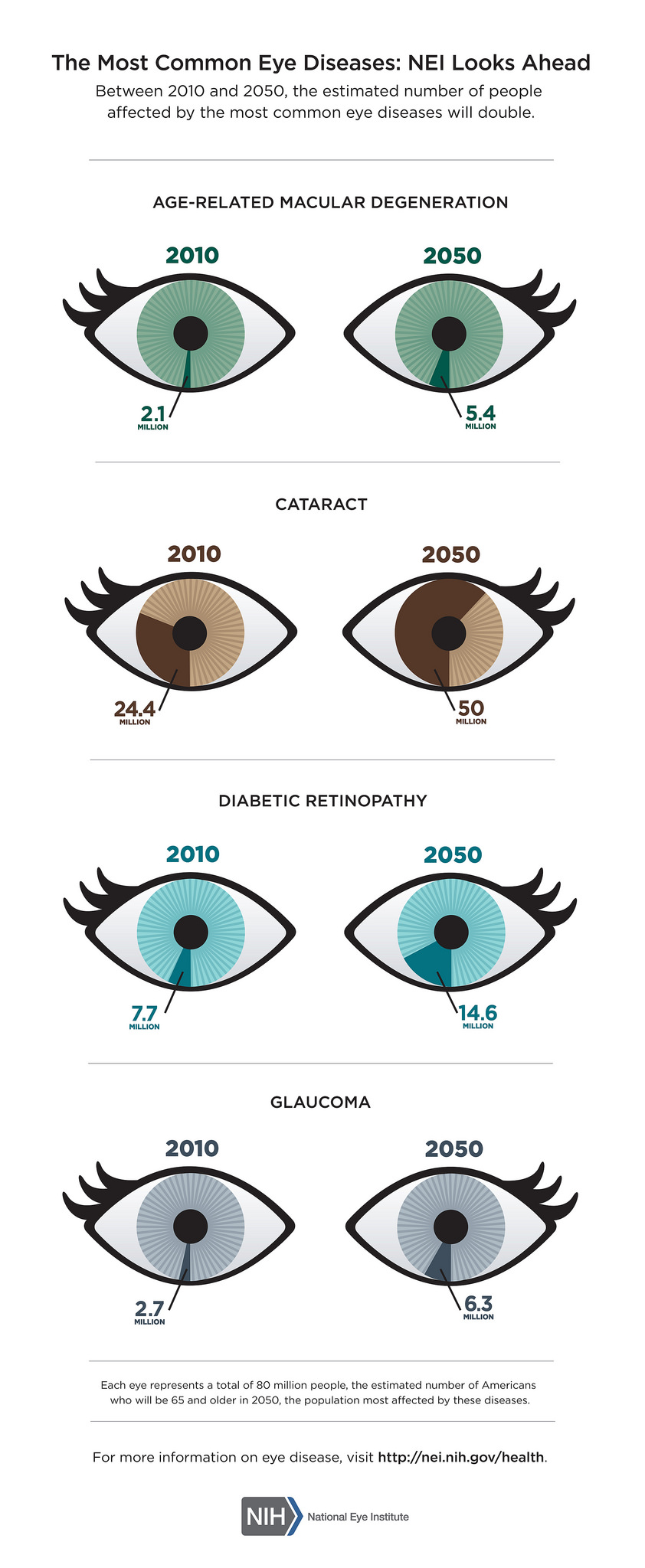
While a person with low vision (due to age-related macular degeneration, cataracts,glaucoma or other eye diseases that are related to aging) can increase font size or graphics by enlarging them with a pinch of the fingers or scroll of the mouse, the result is often blurry and still difficult to see.
If a person is blind and using a screen reader, what they hear may not match what is written or displayed. A picture without underlying descriptive text is worthless. And when a blind person is using a screen reader to read a web site, they will often tab from link to link to scan your article, skipping over your text, to get a sense of what the options are. “Click here” says doesn’t tell the reader anything.
Here are 5 essential elements of accessible web design.
12/15/15
 Susan DeRenmer, CFRE
Susan DeRenmer, CFRE
Vice President of Development
Discovery Eye Foundation