 The Difference Between an Optometrist and an Ophthalmologist
The Difference Between an Optometrist and an Ophthalmologist
There are a number of players on your eye-health team, among them your optometrist and your ophthalmologist. It’s not always obvious, however, what position each plays and when you should call on which professional.
Optometrists
An optometrist holds a doctor of optometry (OD) degree. An optometrist generally completes a four-year college program in the sciences, plus four years of postgraduate professional training in optometry school.
Optometrists examine eyes for vision and health problems, and correct refractive errors with glasses and contact lenses. Some optometrists also provide low vision care and vision therapy. In the United States, optometrists may prescribe medications to treat certain eye problems and diseases, and their scope of care can differ by state. While not licensed to perform eye surgery, optometrists can play a role in pre- and post-operative care, if you have eye surgery performed by an ophthalmologist.
Ophthalmologists
An ophthalmologist is a medical doctor (MD) or a doctor of osteopathic medicine (DO), who specializes in eye and vision care. Ophthalmologists complete four years of college, four years of medical school, one year of internship and at least three years of residency in ophthalmology. Some ophthalmologists also have one or two years of additional training to become specialists in cornea, retina, glaucoma, oculoplastics, pediatrics or neuro-ophthalmology.
Ophthalmologists perform eye exams, diagnose and treat diseases, prescribe medications and perform eye surgery. They also prescribe corrective lenses.
Which one do I call?
Both optometrists and ophthalmologists perform routine eye exams, and are both trained to detect, diagnose and manage eye diseases. Both can prescribe corrective lenses, and both must fulfill continuing education requirements to maintain their licenses.
If your eyes are healthy, which type of professional to see is a matter of personal preference. If you already have a medical eye problem, such as diabetes, or a family history of AMD or glaucoma, you should consider seeing an ophthalmologist. While most optometrists offer medical treatment for common eye problems and chronic eye diseases, such as pink eye, dry eye or allergies, certain eye disorders require treatment by an ophthalmologist, particularly if you need surgery, laser therapy or other specialized care.
In some cases, your optometrist and ophthalmologist may work as a team. In such a setup, the optometrist is the equivalent of your primary-care doctor, who monitors your ongoing condition and care, and the ophthalmologist is your specialist, who manages your condition medically and/or performs surgery. For routine care, you may want to check with your insurance provider to see which, if either, professional they cover and for what services.


 C
C
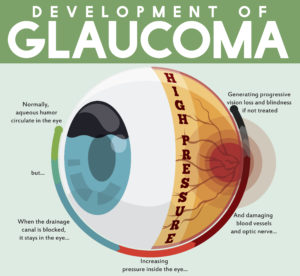 tic nerve, a part of the central nervous system that carries visual information from the eye to the brain.
tic nerve, a part of the central nervous system that carries visual information from the eye to the brain.
 Be sure to start your holiday meal with a salad, it’s an excellent way to ensure that you and your guests get plenty of zeaxanthin and lutein, two nutrients that help protect your central vision. Adding kale, spinach, or romaine lettuce to salads helps your eyes absorb damaging blue light, combats the effects of cigarette smoke and pollution, and also decreases your risk of developing
Be sure to start your holiday meal with a salad, it’s an excellent way to ensure that you and your guests get plenty of zeaxanthin and lutein, two nutrients that help protect your central vision. Adding kale, spinach, or romaine lettuce to salads helps your eyes absorb damaging blue light, combats the effects of cigarette smoke and pollution, and also decreases your risk of developing  Turkey and lean beef, two of the main ingredients in many holiday meals, keep your eyes strong and healthy. Both foods are high in zinc, a nutrient important to the retina and the choroid layer under the retina.
Turkey and lean beef, two of the main ingredients in many holiday meals, keep your eyes strong and healthy. Both foods are high in zinc, a nutrient important to the retina and the choroid layer under the retina.  Zinc is essential for good night vision. Eating foods that are high in the nutrient can also reduce your risk of cataracts and AMD. Other foods that contain zinc include pork, dairy products, chick peas, black-eyed peas, crab, oysters, beans, spinach, mushrooms, cashews, and almonds.
Zinc is essential for good night vision. Eating foods that are high in the nutrient can also reduce your risk of cataracts and AMD. Other foods that contain zinc include pork, dairy products, chick peas, black-eyed peas, crab, oysters, beans, spinach, mushrooms, cashews, and almonds.  It wasn’t an old wives tale, it is true Carrots are good for your eyes! They contain beta carotene, a substance that turns into vitamin A when eaten. Eating carrots can benefit your night vision and could possibly reduce your risk of cataracts, AMD, and dry eyes. Other foods that contain beta carotene include pumpkin, sweet potatoes, and butternut squash. All great ingredients to include into your holiday feast.
It wasn’t an old wives tale, it is true Carrots are good for your eyes! They contain beta carotene, a substance that turns into vitamin A when eaten. Eating carrots can benefit your night vision and could possibly reduce your risk of cataracts, AMD, and dry eyes. Other foods that contain beta carotene include pumpkin, sweet potatoes, and butternut squash. All great ingredients to include into your holiday feast.  Fish contain omega-3 fatty acids, which can reduce your risk of developing AMD, dry eye, and glaucoma. Salmon, mackerel, flounder, tuna, halibut, herring, and sardines would be a great addition to your holiday meals.
Fish contain omega-3 fatty acids, which can reduce your risk of developing AMD, dry eye, and glaucoma. Salmon, mackerel, flounder, tuna, halibut, herring, and sardines would be a great addition to your holiday meals. Whole grains reduce your risk of heart disease, obesity, and type 2 diabetes and can also decrease your risk of AMD. Substituting whole grain flour for white flour in holiday breads and muffins is a simple way to boost your whole grain intake. Other good whole grain sources include wild rice, brown rice, popcorn, oatmeal, bulgur, barley, buckwheat, and couscous.
Whole grains reduce your risk of heart disease, obesity, and type 2 diabetes and can also decrease your risk of AMD. Substituting whole grain flour for white flour in holiday breads and muffins is a simple way to boost your whole grain intake. Other good whole grain sources include wild rice, brown rice, popcorn, oatmeal, bulgur, barley, buckwheat, and couscous.  Fruits high in vitamin C, such as strawberries and oranges, also offer important vision benefits. Vitamin C is an antioxidant, a substance that can prevent cell damage caused by free radicals. Vitamin C-rich foods help keep the collagen in your cornea healthy and reduce the risk of cataracts and AMD. You can also find vitamin C in grapefruit, kiwi, blueberries, peas, broccoli, and tomatoes.
Fruits high in vitamin C, such as strawberries and oranges, also offer important vision benefits. Vitamin C is an antioxidant, a substance that can prevent cell damage caused by free radicals. Vitamin C-rich foods help keep the collagen in your cornea healthy and reduce the risk of cataracts and AMD. You can also find vitamin C in grapefruit, kiwi, blueberries, peas, broccoli, and tomatoes. Summer is almost over and it’s back to school season. As parents, many of us are busy ensuring our kids are ready and prepared for the new year; worrying about school supplies, new clothes, and new haircuts. There is always a long list of things to do before school starts. But something that often gets overlooked is getting your child’s eyes examined annually.
Summer is almost over and it’s back to school season. As parents, many of us are busy ensuring our kids are ready and prepared for the new year; worrying about school supplies, new clothes, and new haircuts. There is always a long list of things to do before school starts. But something that often gets overlooked is getting your child’s eyes examined annually. For example, lutein and zeaxanthin are important antioxidants that help prevent degeneration in the lens and retina. Eating a diet rich in these carotenoids helps reduce the risk of AMD by fighting oxidation in the retinal cells of the eye.
For example, lutein and zeaxanthin are important antioxidants that help prevent degeneration in the lens and retina. Eating a diet rich in these carotenoids helps reduce the risk of AMD by fighting oxidation in the retinal cells of the eye. Eating fatty fish, such as salmon, tuna, mackerel, and sardines, that are rich in omega-3 fatty acids also helps lower the risk of AMD. Omega-3 fatty acids are rich in docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), which is important for eye health and visual function. People with dry eye syndrome (i.e., low tear production) can benefit from a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids because dry eye is linked to low levels of DHA.
Eating fatty fish, such as salmon, tuna, mackerel, and sardines, that are rich in omega-3 fatty acids also helps lower the risk of AMD. Omega-3 fatty acids are rich in docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), which is important for eye health and visual function. People with dry eye syndrome (i.e., low tear production) can benefit from a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids because dry eye is linked to low levels of DHA.




