Taking control of glaucoma: The importance of adherence to glaucoma treatment
Glaucoma is known as the “silent thief of sight”: people with glaucoma usually have no symptoms. The only intervention that has been proven to reduce the risk of vision loss in glaucoma is lowering the eye pressure. The most common way to lower eye pressure is with eye drop medications. Glaucoma treatments do not improve vision, but they do to help prevent vision loss from happening.

What does it mean to be “compliant”?
Adherence (the newer term that is replacing “compliance”) with glaucoma treatment usually means taking your eye drops everyday and at the right times and coming to your glaucoma check ups. Your doctor needs to check your eye pressure regularly, as well as look at your optic nerves and measure your visual fields, to monitor your disease.
Why is it difficult to take eye drops everyday?
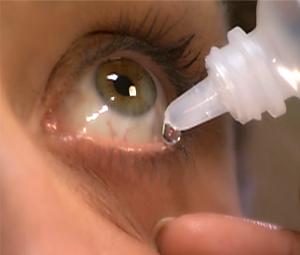
Some people with glaucoma only need 1 or 2 eye drops everyday to control their glaucoma, but some may need as many as 4 glaucoma medications, taken multiple times throughout the day. Imagine using 2 eye drops in the morning, 1 eye drop at noon, 1 at dinnertime, and 2 more in the evening, and doing this everyday for years and years, to help protect your sight. It is easy to see how people could miss some drops. Reasons can include forgetting them (or falling asleep before that bedtime drop), the cost of the medications, the side effects from the eye drops, and many others.
Why is adherence important for glaucoma patients?
In one word: blindness. The eye drops lower the eye pressure, which helps protect the eye from loosing vision from glaucoma. If a patient does not put in their eye drops, then the eye pressure will not be as low as it needs to be during that time and eye can be damaged. The damage from glaucoma is not reversible, so prevention is the goal.
What can you do?
If you have glaucoma and you take eye drops, use them everyday and as close to the right time as possible. Also, see your doctor for your glaucoma check-ups. Ask about your eye pressure readings, your optic nerve appearance, and your visual fields, so that you know what’s going on with your disease. If you are having any trouble getting your drops in (for example, increased cost due to change in insurance, always forgetting the morning drop, red eyes drawing attention at work), then tell your doctor about it, so you can make changes in your treatment plan.
Friends and family members can help, too. If someone you care about has glaucoma, think about asking them if they need any help with their drops. Some ways you might help: look at videos to see eye drop techniques, put in the drops for them, provide gentle reminders, or go with them to doctor’s visits to be a “second set of ears” on instructions and recommendations.
Taking eye drops for glaucoma is not easy, but it does work. Most people who are treated for glaucoma do not go blind. Take control of your disease, by taking your eye drops and going to your glaucoma check-ups.
For more information about glaucoma and treatment, visit www.nei.nih.gov/health/glaucoma.
1/29/15
 Jullia A. Rosdahl, MD, PhD
Jullia A. Rosdahl, MD, PhD
National Eye Health Education Program Glaucoma Subcommittee
Duke Eye Center, Duke University