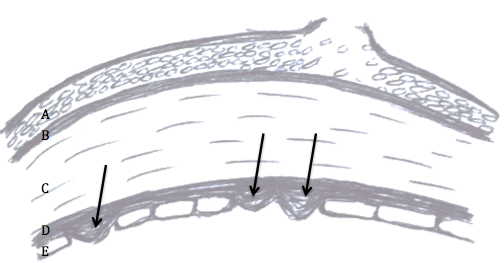
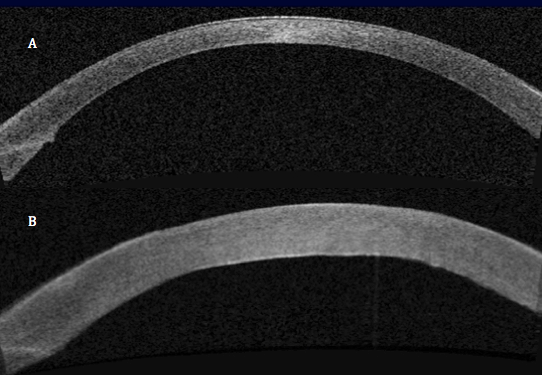
This is the third and final installation of the comprehensive series we have presented on dry eye disease. Dr. Wade first discussed the symptoms you might experience if you have dry eye and the Dr. Garg explained the process of diagnosing they type of dry eye disease you might have. In this article Dr. Farid reviews treatment options based on your diagnosis of dry eye disease.
Treatments for Dry Eye Disease
As our understanding of dry eye disease expands, so do treatment options. We now know that dry eye disease is a multifactorial disease. There is no one cause so there is no one magic cure. Treatments aim to improve tear composition, reduce eye surface inflammation, and target eyelid margin disease. Here, we will review many treatment options, but the treatment combination or “cocktail” that is appropriate for you will depend on your specific type of dry eye disease. This is usually determined after some testing by your eye care provider.
Environmental, Dietary, and Medication Adjustments
Before going into specific dry eye treatments, there are modifiable causes and preventative methods to improve dry eyes. Simple changes in the environment, diet, and medications can be easy ways to improve symptoms.
Environmental Changes
As expected, a dry environment will worsen dry eyes. Humidifiers and moisture goggles have been shown to help alleviate these symptoms. Furthermore, situations that cause decreased blinking, such as prolonged use of computer screens, can worsen dry eyes. Patients should take frequent breaks from computer screens and reading, allowing their eyes to rest and resume normal blinking. When in windy, smoky, or dusty situations, sunglasses can act as a barrier to the eyes, reducing dry eye symptoms. Avoiding wind, fans, or any source of air blowing into the eyes may also help.
Dietary Changes
Drinking adequate water keeps patients hydrated and reduces exacerbations of dry eye symptoms. Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), have been shown in many clinical studies to improve dry eyes. It is believed that these fatty acids help inhibit inflammatory mediators. Essential fatty acids cannot be synthesized and must be ingested through diet. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids include fish, other seafood, and flaxseed oil. Supplements are also available.
Adjusting Medications
Many medications are associated with dry eyes, and patients may benefit from adjusting doses or finding alternative treatments. You can work with your physician to weigh the costs and benefits about modifying your current medications if they are suspected to worsen dry eyes. Some of these medications include: hypertensive drugs, antihistamines, decongestants, antidepressants, acne medications, birth control, and hormone replacement therapy. Eye drops with preservatives, such as glaucoma medications, can also worsen dry eyes.
Lubricating Treatments
For patients with decreased tear production, supplementation of tears or reduction of tear drainage will improve symptoms.
Artificial tears, gels, and ointments
Artificial tears, gels, and ointments are readily available over the counter. Artificial tears are eye drops that are used throughout the day as needed, up to eight times for dry eyes. You must make sure to get “lubricating” drops. There are multiple available brands that are excellent and equivalent in providing artificial moisture. Avoid “redness relief” brands as they are focused on reducing appearance of the vessels in the eyes as opposed to actual dry eye relief. Gels and ointments are thicker and very effective but can blur vision. Non-commercial comparison testing between brands has not been done. Because the ingredients, preservatives, and consistency vary from brand to brand, it is recommended for patients to choose the best option that works well for them based on trial and error.
Preservatives are used in many eye drops to help them to last longer. Unfortunately, they can be irritating to the eyes, especially when used often (more than 4 drops/day) or with other drops containing preservatives (ie. glaucoma medications). Patients who frequently use eye drops are recommended to use preservative-free (PF) drops. Unfortunately, preservative-free drops are more expensive because they come in “single use” containers. You may be able to extend the life of each single use container by spreading out its contents over multiple uses throughout the day.
Lipid-containing lubricants, such as those with castor oil, attempt to mimic the oils found in the tears, reducing evaporative dry eyes, but more research is necessary to study their efficacy.
Punctal Plugs
Your ophthalmologist can place small plugs at a clinic visit into the punctum, a small hole at the upper and inner lids that drain tears from the eyes. One plug can be added initially, and if more tear retention is required, another plug can be added. There are absorbable and non-absorbable types. Absorbable types are made of collagen and last 1 week to 6 months. Once placed, they are not visible or removable. Non-absorbable plugs are usually silicone, and permanent. They are easily placed by your ophthalmologists and remain visible in follow-up exams. Some patients feel the plugs, and there may be mechanical rubbing, especially when the plug is not the proper size. Some patients may also experience excessive tearing with plugs. If problematic, patients can wait for the plugs to dissolve if absorbable or they can be removed with forceps if non-absorbable.
Autologous Serum
Serum is extracted from a patient’s blood and turned into an eye drop. The growth factors, vitamins, and antibodies present in serum are the same as those in natural tears. Evidence is showing significant promise in alleviating symptoms and signs of chronic dry eye disease. A good collaboration between a phlebotomy lab and compounding pharmacy is necessary to make the products. The products must be kept refrigerated or cold between uses. They can be frozen for long-term storage. Each blood draw provides a supply of drops that can last 3-6 months.
Hydroxypropyl Cellulose Ophthalmic Inserts (Lacrisert)
An insert is available for people who find regular artificial tear use to be difficult. A physician can order the inserts through a pharmacy. The patient places the insert in the inferior fornix of the eye, the area between the lower lid and sclera of the eye. It slowly dissolves over 24 hours, giving constant lubrication.
Anti-inflammatory Treatments
Inflammation is now being recognized as a major underlying cause of chronic and worsening dry eye disease. Many patients who have been suffering from chronic dry eyes, particularly those with autoimmune diseases like Sjogren’s Syndrome, will do well on treatments that reduce the amount of inflammation in the tear film and ocular surface. Your physician can order these medications for you if needed.
Cyclosporine A (Restasis)
The FDA approved Restasis for dry eyes in 2002. This is an immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory eye drop medication. Relief is not instant, and may take 6-8 weeks of sustained use for improvement in dry eye symptoms. Less than 20% of patients may experience a burning sensation with the drops, but the safety and tolerability profile is otherwise excellent.
Antibiotics
Doxycycline and minocycline are used for inflammatory ocular surface and eyelid disease. The antibiotics have a dual effect: they act as anti-inflammatories and anti-microbials. As an anti-microbial, these medications can improve meibomian gland function. They can decrease lid bacterial flora, reducing a cause of meibomian lipid breakdown. A low-dose (doxycycline 20 mg BID) regimen for 1-2 months has been shown to be effective. Side effects are usual mild but include stomach upset, yeast infections, and photosensitivity.
Steroids
Steroids act as anti-inflammatories. Because steroids are associated with complications in long-term use, they are mainly used in short pulses either at the initiation of treatment or as rescue during exacerbations. A short 4-6 week course is generally well tolerated as a “rescue treatment,” or an urgent treatment, to relieve intolerable symptoms quickly before resorting to other treatment options.
Meibomian Gland Treatments
Meibomian glands produce oils that are crucial in preventing our tears from evaporating too quickly. Treatments that target the glands can help patients with meibomian gland dysfunction or lid margin disease.
Warm compresses and lid scrubs
Warm compresses provide heat that warms the oils in the glands, unclogging the glands and improving oil flow. Warm washcloths, small rice bags heated in the microwave, or commercial hydrogel pads are all effective, and no studies have been done to compare the different methods. The heat. The compress should be placed over the eyes for 5-10 minute. Gentle circular or rolling massage of the eyelids can help express the oils from the glands.
Lid scrubs are useful particularly in cases of blepharitis, or mild inflammation of the lids, that cause them to become crusted. There are excellent over the counter commercial lid soap formulations that work well to clean the lid margins. Alternatively, baby shampoo and a washcloth gently applied to the lids can work as well.
Thermal pulsation (Lipiflow)
Lipiflow is an FDA approved in-office treatment for meibomian gland dysfunction and dry eyes. During the 12-minute procedure, a device is placed over the eye and eyelids that provides localized warmth and pressure on the lids (Figure 1).
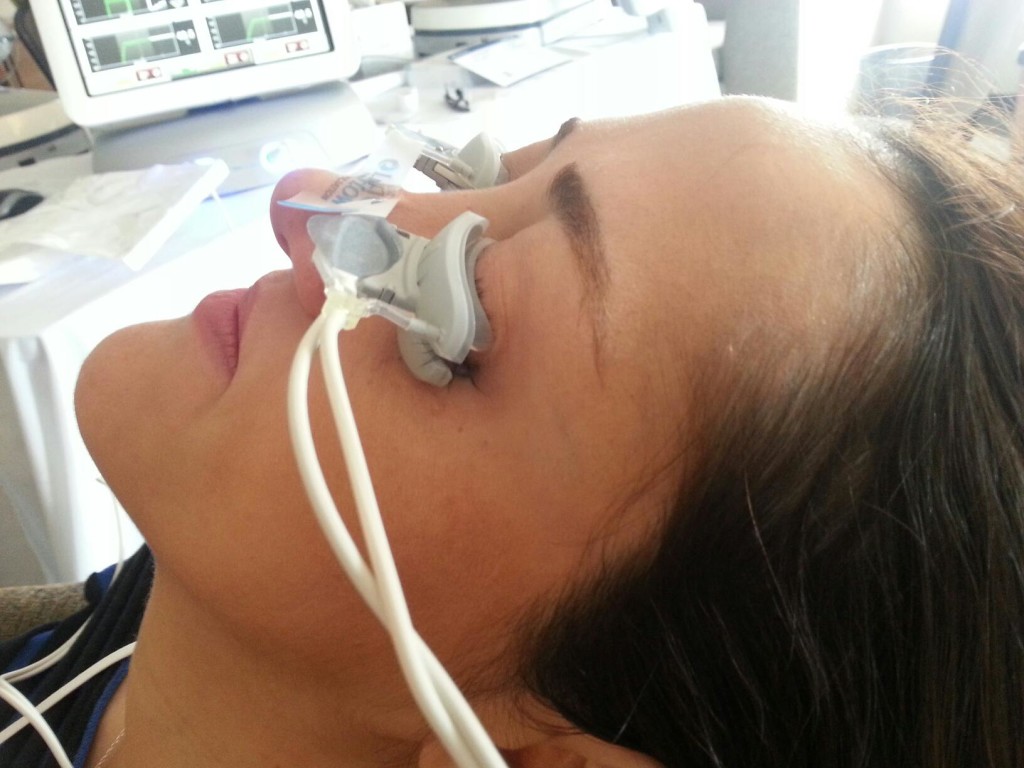
The procedure is 100% safe and very effective at clearing out the trapped oil glands and allowing smooth flow to be re-established. After approximately one month, the consistency of the oils in the tear flow will have improved remarkably with associated improvement in dry eye symptoms. With one procedure, the effects last between 12-24 months.
Intense Pulsed Light (IPL)
Originally approved for acne and rosacea dermatologic disease, IPL uses bursts of light to minimize blood vessel size. It can be used off-label for ocular rosacea and meibomian gland dysfunction, but results have not been reported.
Summary
There are many treatment options for dry eye disease. Generally, conservative over-the-counter treatments should be tried first. Commonly, environmental changes, dietary changes, artificial tears, and warm compresses will improve the majority of dry eye symptoms to tolerable levels. However, when these options are exhausted, there are many additional options for patients. Work closely with a trusted health professional to determine the optimal treatment combination as each patient is different.
8/25/15
 Marjan Farid, MD
Marjan Farid, MD
Director of Cornea, Cataract, and Refractive Surgery
Vice-Chair of Ophthalmic Faculty
Director of the Cornea Fellowship Program
Associate Professor of Ophthalmology
Gavin Herbert Eye Institute, University of California, Irvine
 Priscilla Q. Vu, MS
Priscilla Q. Vu, MS
Medical Student
University of California, Irvine School of Medicine