As you age, cataracts become a concern prompting the question – when is the best time for cataract surgery?
There are decades worth of old wives tales floating around regarding cataracts that often lead to unnecessary fear and apprehension for many patients. These myths involve concepts such as “ripeness”, having to wear eye patches afterwards, danger in “waiting too long, etc. Just as the techniques of cataract extraction have changed over the decades, so have the indications to proceed to surgery.

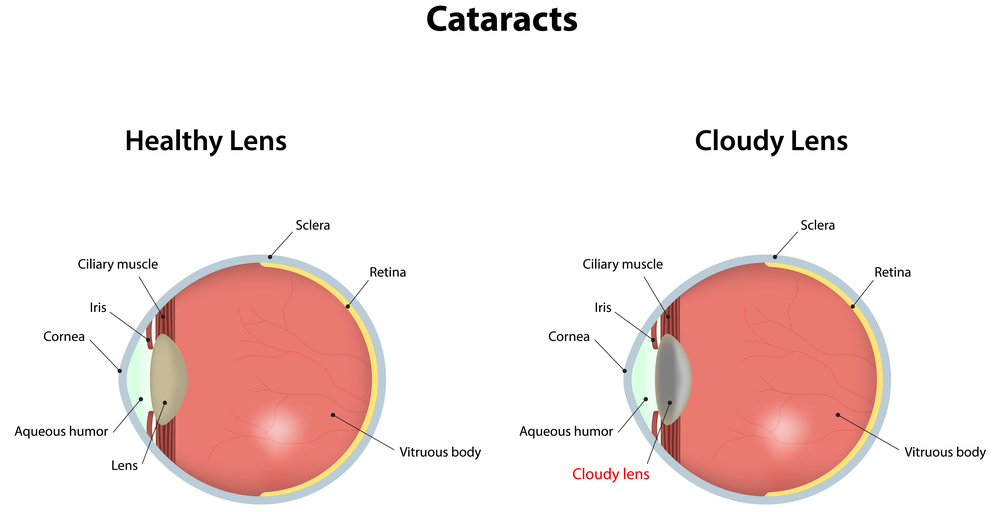
Firstly, cataracts are a normal part of the aging process. Patients should not be alarmed if they are told that they are developing cataracts, even as early as their fifties. As we age, the natural clear lens inside the eye becomes progressively harder, darker, and cloudier. This dark, cloudy lens is what is referred to as a cataract. Cataracts develop at different rates for different people, and even between the two eyes of the same person. It typically takes many years for the lens to become cloudy enough to impact the clarity of vision. There are many different types of cataracts depending of what area of the lens becomes cloudy, but the typical cataract related to normal aging results in a relatively uniform cloudiness with a denser central core, and is referred to as “Nuclear Sclerosis”. Other varieties of cataracts tend to grow more quickly, are relatively uncommon, and often result from certain conditions other than typical aging.
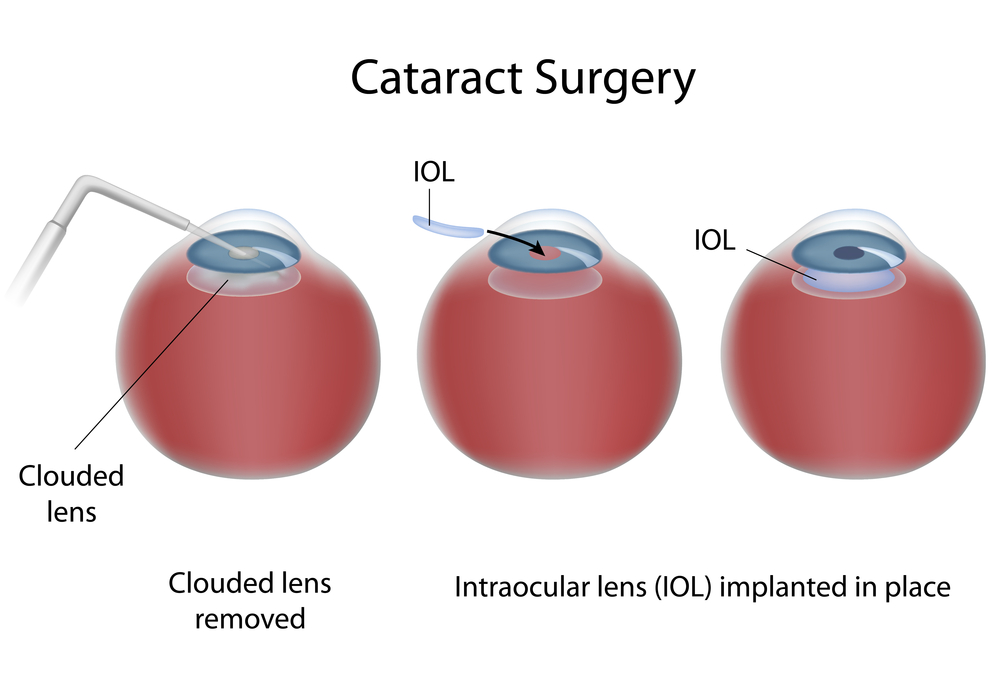
Regardless of what type of cataract the patient has, the treatment is the same: cataract extraction with an implant of an intraocular lens. There have been great advances in lens design over the years, and they now result in excellent, stable, predictable vision for the remainder of the patient’s lifetime and do not typically need to be changed once implanted.
Cataracts result in different symptoms that may be more of less relevant to a specific person’s needs, such as:
- Glare with bright lights
- Difficulty with fine print
- Difficulty following the golf or tennis ball
- Impairment in night driving
- Difficulty with seeing street signs
- Seeing the score or small print on the television
- Fine visual tasks such as threading a needle, etc.
Although cataract surgery is an incredibly successful procedure with only about a 1-2% risk of complications, it still DOES have some risk. Therefore, cataract surgery should only be undertaken when there is something to gain. In other words, the BENEFITS MUST OUTWEIGH THE RISKS. This means that if your symptoms are mild and are not interfering with your activities of daily living, it is not time to accept the risks of surgery. Once your visual impairment progresses to the point that YOU feel your activities of daily living and enjoyment are impaired, this is the time to proceed to surgery. This threshold is very different between people. Some people feel impaired with vision of 20/25, and others still function within their scope of usual activities until they are 20/100! The best first-step in determining if it is time for your surgery is to get an up-to date refraction. This means a detailed check for new glasses. Often, cataract development will change a person’s glasses prescription, and updating this can improve the visual symptoms for months to years. When a new glasses prescription no longer improves the sight adequately, this is when surgery is indicated.
For the most part, putting off cataract surgery does not impact the final outcome. It will not harm you or your eye to leave the cataract alone until you are ready. There are of course certain exceptions to this rule, such as in Fuchs’ dystrophy, pseudoexfolation, untreated narrow-angle glaucoma, and some others. However, these are relatively rare conditions that your doctor will speak to you about if you have any of these diagnoses.
In summary, the time to proceed to cataract surgery is something that you as the patient determine. YOU assess your lifestyle needs and your vision performance within your scope of activities. When you feel you are impaired in these activities, the benefits will outweigh the risks, and it’s time to take them out. You should not feel any pressure to urgency in this process.
Once you have determined you are ready to have cataract surgery, your surgeon will discuss with you your options for intraocular lens implantation including astigmatism neutralizing lenses, standard distance or near-vision lenses, multiple focal distance lenses, accommodating lenses, and others. The current standard approach for cataract surgery is called “phacoemulsification” and uses ultrasound technology to remove the cataract. There are also laser devices that assist in making the incisions and breaking up the lens, which many surgeons now employ in addition to the phacoemulsification. In general cataract surgery only takes a few minutes, is performed with topical anesthesia, is pain-free, and has a very short recovery time. No pirate-patches are used these days! Most patients are very happy with the results, but this requires adequate discussion with the surgeon prior to the procedure to best assess the needs of the individual patient. A well- informed patient who participates in their care results in the best outcomes!
6/18/15
 Sameh Mosaed, MD
Sameh Mosaed, MD
Director of Glaucoma Services, Gavin Herbert Eye Institute, UC Irvine
Associate Professor, Cataract and Glaucoma Surgery, UC Irvine School of Medicine