4/22/14
Contact lenses give a person the ability to see without glasses. If you have keratoconus, they are essential for seeing as regular glasses don’t work with an irregularly shaped cornea. But lately these relatively simple lenses have created a whole new world where they can dispense eye medication, measure blood glucose levels and even help the blind see.

Monitoring Blood Sugar
You have heard about Google Glasses, but Google is looking beyond the smartphones of eye wear to monitoring health. They are currently working on a lens with tiny wireless chips and glucose sensors that are sandwiched between two lenses. They would monitor glucose levels once a second and use tiny LED lights, also inside the lenses, to flash when the levels are too high or low. And how big are these electronics? They are no larger than a speck of glitter, with a wireless antenna that is thinner than a human hair. While they are still in development – Google has run clinical research studies and is in discussions with the FDA – it could make blood sugar monitor far less invasive than pricking your finger several times a day.
Drug Delivery for Glaucoma
Getting glaucoma patients to regularly use their eye drops to regulate the pressure in their eyes has always been a problem. They forget, don’t want to be bothered, or have a hard time getting the drops into their eyes. This could change with two research projects exploring the use of contact lenses to deliver medication over a prolonged period of time.
Researchers at Massachusetts Eye and Ear/Harvard Medical School Department of Ophthalmology, Boston Children’s Hospital, and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology who are working on a lens designed with a clear central area and a drug-polymer film made with the glaucoma drug latanoprost, around the edge to control the drug release. These lenses can be made with no refractive power or the ability to correct the refractive error in nearsighted or farsighted eyes.
Another team from University of California, Los Angeles have combined glaucoma medication timolol maleate with nanodiamonds and embedded them into contact lenses. When the drugs interact with the patient’s tears, the drugs are released into the eye. While the nanodiamonds strengthen the lens, there is no difference in water content so they would be comfortable to wear and allow oxygen levels to reach the eye.
Seeing in the Dark
Researchers out of the University of Michigan have developed an infrared sensor that could eventually be used in the production of night vision contact lenses. Thanks to graphene, a tightly-packed layer of carbon atoms, scientists were able to create a super-thin sensor that can be stacked on a contact lens or integrated with a cell phone.
Stem Cells for Cornea Damage
Researchers in Australia are working on a way to treat corneal damage with stem cell infused contact lenses. Stem cells were taken from the subject’s good eye and then plated them onto contact lenses (if there is a defect in both eyes, stem cells are taken from a different part of the eye). After wearing for about two weeks the subjects reported a significant increase in sight.
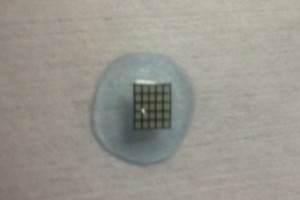
Helping the Blind See
And what good are contact lenses if you are blind? At Bar Ilan University in Israel researchers are creating special lenses that translate images into sensations felt on the eye. It works by taking an image with a smartphone or camera, it is then processed and sent to the contact lens. The custom-made lens is fitted with a series of electrodes that use small electric impulses to relay shapes onto the cornea, similar to braille. After some practice, test subjects were able to identify specific objects.
In expanding the uses of contact lenses, these projects seem to be just the beginning, all reported in the first four months of this year. Researchers and developers are working together to find more and better ways help with vision and medical issues, using contact lenses.
 Susan DeRemer, CFRE
Susan DeRemer, CFRE
Vice President of Development
Discovery Eye Foundation

