I love the idea that beauty is in the eyes of the beholder. It reminds us that individuals can make choices about what they perceive to be true beauty.
Let’s consider art… one person’s beautiful can be another person’s junk. If beauty is in the eyes of the beholder, the question is – are we taking the time to appreciate all that surrounds us? From Mother Nature’s unlimited panoplies of possibilities to the innocent smile of a child, beauty is the catalyst that makes being alive the greatest of all human adventures.
I am sure you’ve heard the phrase “stop and smell the roses,” so why not take the time to stop and observe the beauty your eyes can behold.
The Discovery Eye Foundation is working every day to preserve your vision and give all of us the chance to see what’s truly beautiful and treasure it. All you have to do is open your eyes and take a look.
Louis Armstrong said it well:
I see trees of green and red roses too.
I see them bloom for me and you.
And I think to myself,
what a wonderful world.
You’re right Louis… it is a wonderful world if we all just keep appreciating the beauty that’s out there for all of us.
Donate today to help support the Discovery Eye Foundation!
 Tom Sullivan
Tom Sullivan
DEF’s Ambassador of Vision
sullivanvision.com




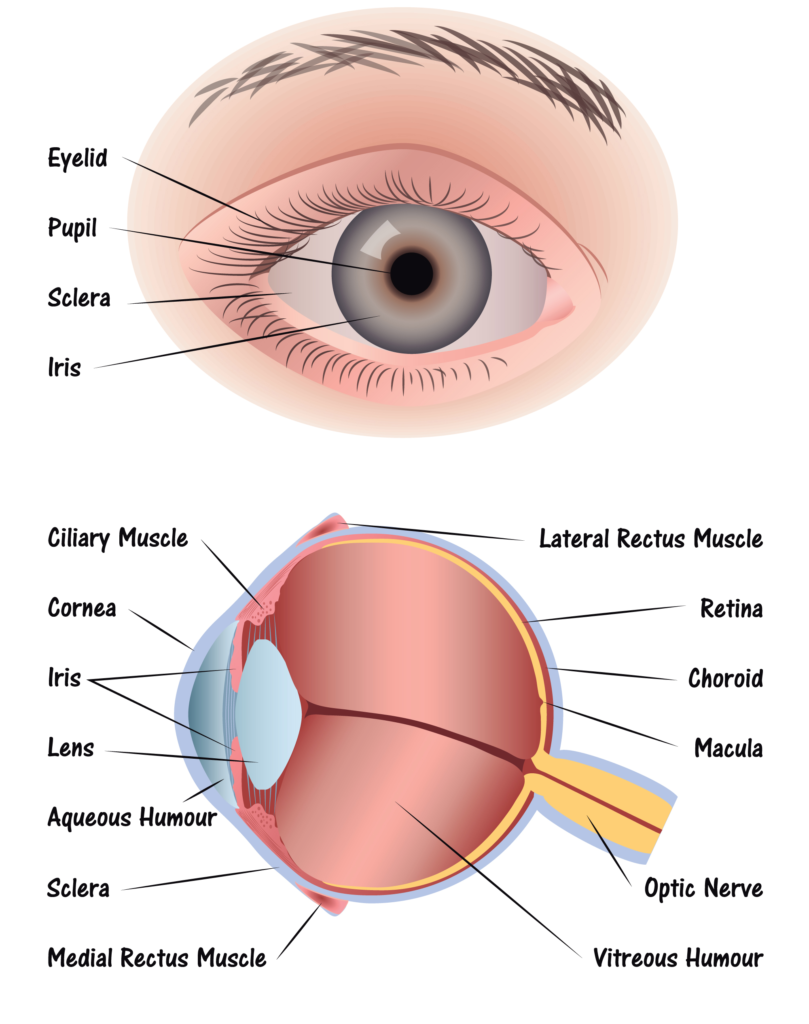 Step 1: Light passes through a thin layer of moisture
Step 1: Light passes through a thin layer of moisture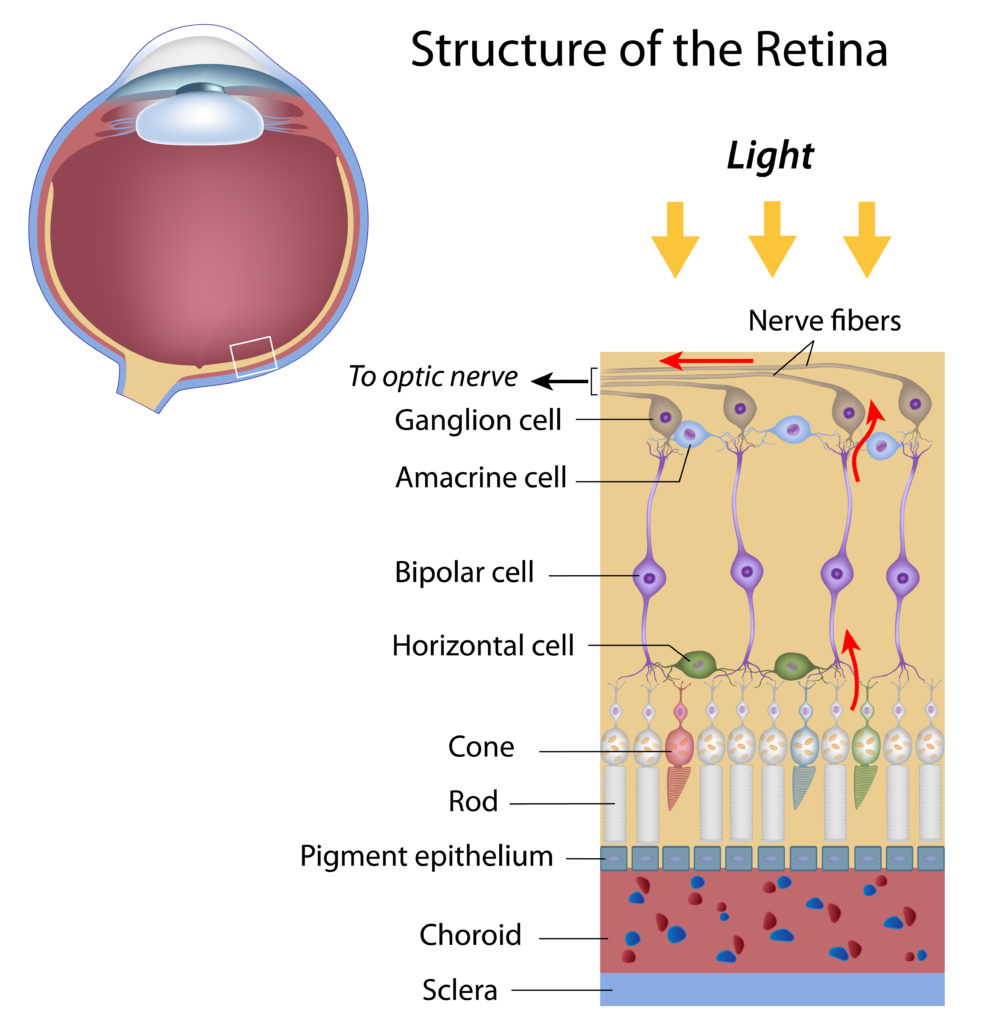
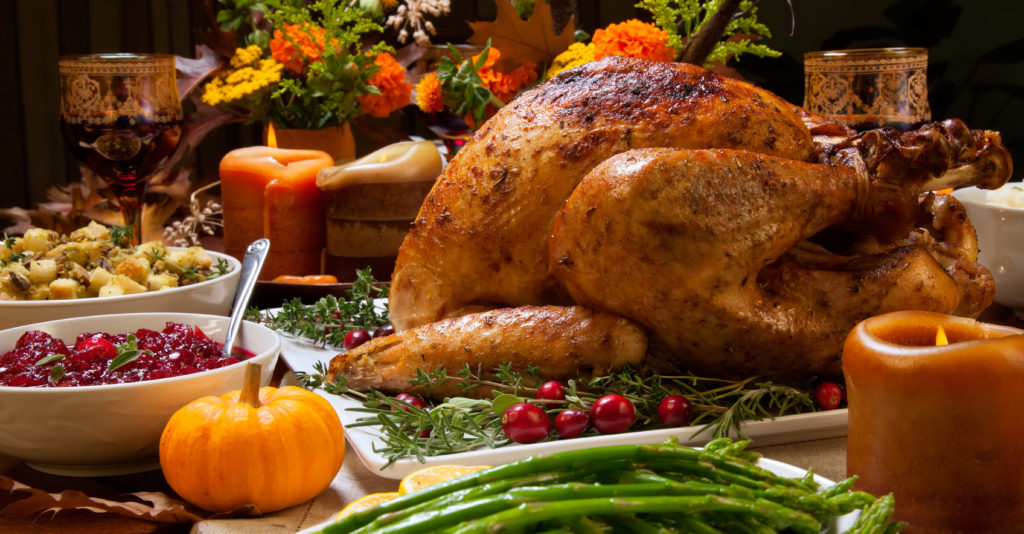
 Thanksgiving is almost here; a meal that nourishes the family bonds and traditions. It’s the one time of the year where you can guarantee your eyes will be bigger than your stomach.
Thanksgiving is almost here; a meal that nourishes the family bonds and traditions. It’s the one time of the year where you can guarantee your eyes will be bigger than your stomach.  Healthy Aging Month is an annual health observance designed to focus national attention on the positive aspects of growing older. Aging is a process that brings many changes. Vision loss and blindness, however, do not have to be one of them. There are several simple steps you can take to help keep your eyes healthy for the rest of your life.
Healthy Aging Month is an annual health observance designed to focus national attention on the positive aspects of growing older. Aging is a process that brings many changes. Vision loss and blindness, however, do not have to be one of them. There are several simple steps you can take to help keep your eyes healthy for the rest of your life. When you think of cancer, most of us do not think about the eye or vision. Though rare, cancer can start inside or outside of the eye. If cancer starts inside the eyeball it’s called intraocular and if it starts outside the eye (eyelid or in the eye socket) then it’s called extraocular tumor. It can occur in both children and adults. Most major eye centers have specialists who are trained in the diagnosis and treatment of eye cancers.
When you think of cancer, most of us do not think about the eye or vision. Though rare, cancer can start inside or outside of the eye. If cancer starts inside the eyeball it’s called intraocular and if it starts outside the eye (eyelid or in the eye socket) then it’s called extraocular tumor. It can occur in both children and adults. Most major eye centers have specialists who are trained in the diagnosis and treatment of eye cancers.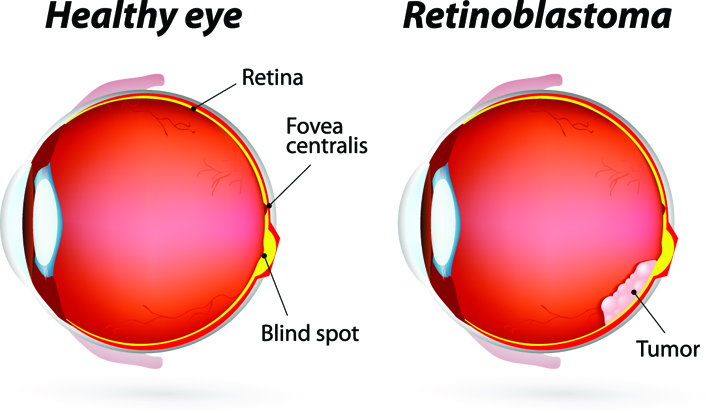 At the later stage of this cancer, the only one way to survive is to remove the eyeball (enucleation). Like many of other types of cancer, retinoblastoma has a genetic component so genetic testing needs to be done. The tumor begins with the RB1 gene mutation that stimulates retinal cells to develop into a tumor called a retinoblastoma. The RB1 mutation can be inherited from the parents, but in some cases it is sporadic and not inherited. There are various treatments such as surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy etc. to cure retinoblastoma cancer. Rarely it can spread beyond the eye.
At the later stage of this cancer, the only one way to survive is to remove the eyeball (enucleation). Like many of other types of cancer, retinoblastoma has a genetic component so genetic testing needs to be done. The tumor begins with the RB1 gene mutation that stimulates retinal cells to develop into a tumor called a retinoblastoma. The RB1 mutation can be inherited from the parents, but in some cases it is sporadic and not inherited. There are various treatments such as surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy etc. to cure retinoblastoma cancer. Rarely it can spread beyond the eye. 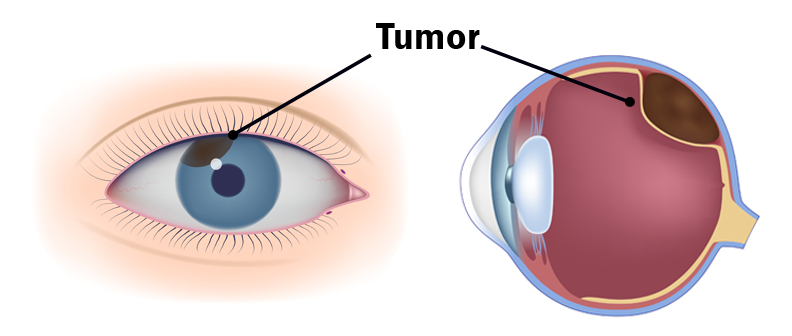

 Portable magnifiers and lighted magnifiers- offer magnified reading on the go. Perfect for menus, shopping lists, label reading, and more, portable magnifiers can fit in your pocket, purse, or be worn on the belt for quick, easy use.
Portable magnifiers and lighted magnifiers- offer magnified reading on the go. Perfect for menus, shopping lists, label reading, and more, portable magnifiers can fit in your pocket, purse, or be worn on the belt for quick, easy use.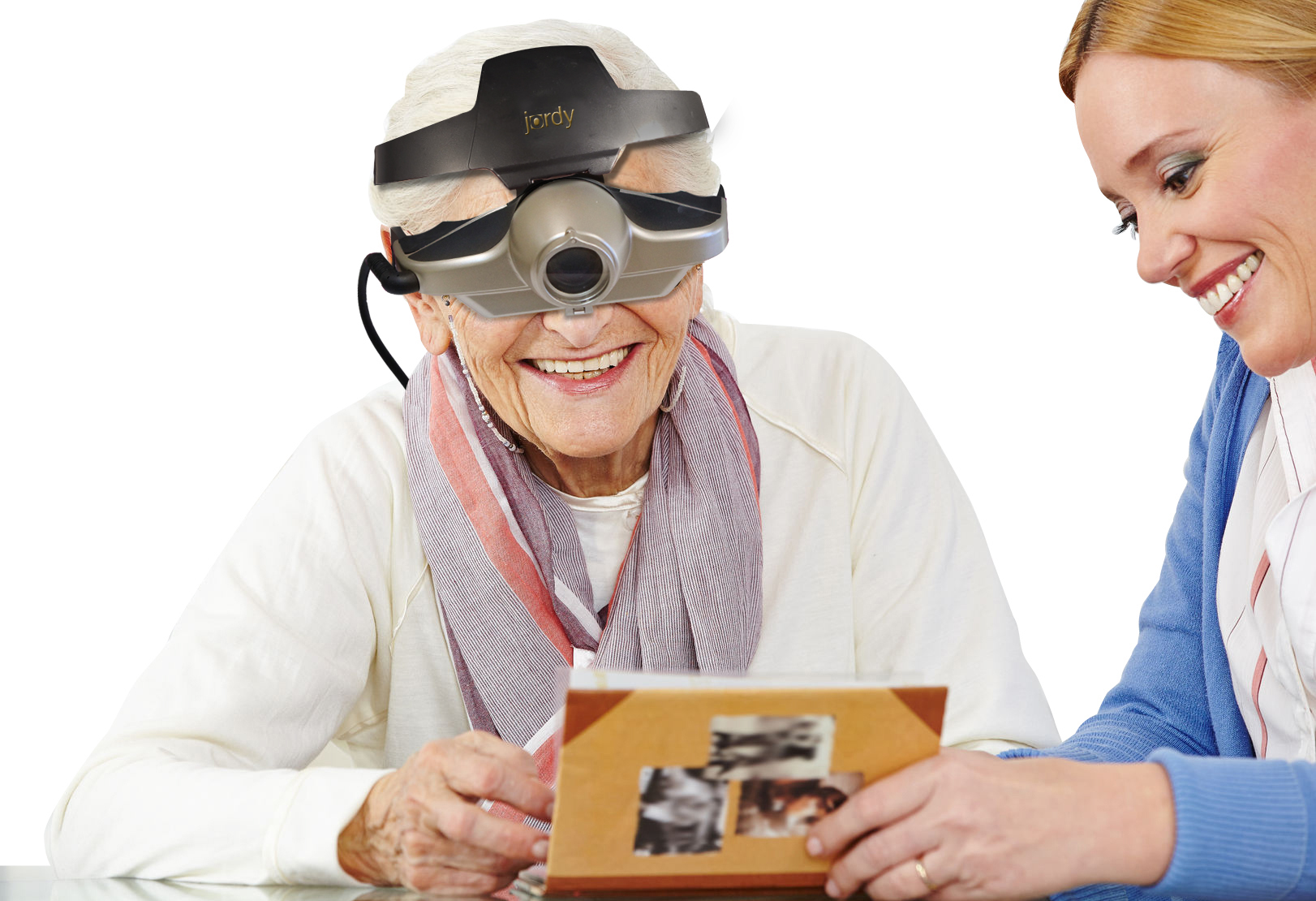 Wearable magnifiers – wearable technology is the future for those with low vision who live an active lifestyle. Wearable options make it possible to see and take part in everyday tasks, such as reading and recognizing faces.
Wearable magnifiers – wearable technology is the future for those with low vision who live an active lifestyle. Wearable options make it possible to see and take part in everyday tasks, such as reading and recognizing faces. Transportable magnification screens– are perfect for close up viewing as well as distance viewing. These great viewers offer great flexibility, from watching TV to using the mirror image feature for self-viewing. There are APPS for smart phones that can be used to magnify reading material.
Transportable magnification screens– are perfect for close up viewing as well as distance viewing. These great viewers offer great flexibility, from watching TV to using the mirror image feature for self-viewing. There are APPS for smart phones that can be used to magnify reading material. Desktop devices for reading books, bills or letters – these have large, bright screens. A reading table offers visual aid for reading books, optional computer connectivity and more. This family of portable magnification units offers up to 75x magnification.
Desktop devices for reading books, bills or letters – these have large, bright screens. A reading table offers visual aid for reading books, optional computer connectivity and more. This family of portable magnification units offers up to 75x magnification.
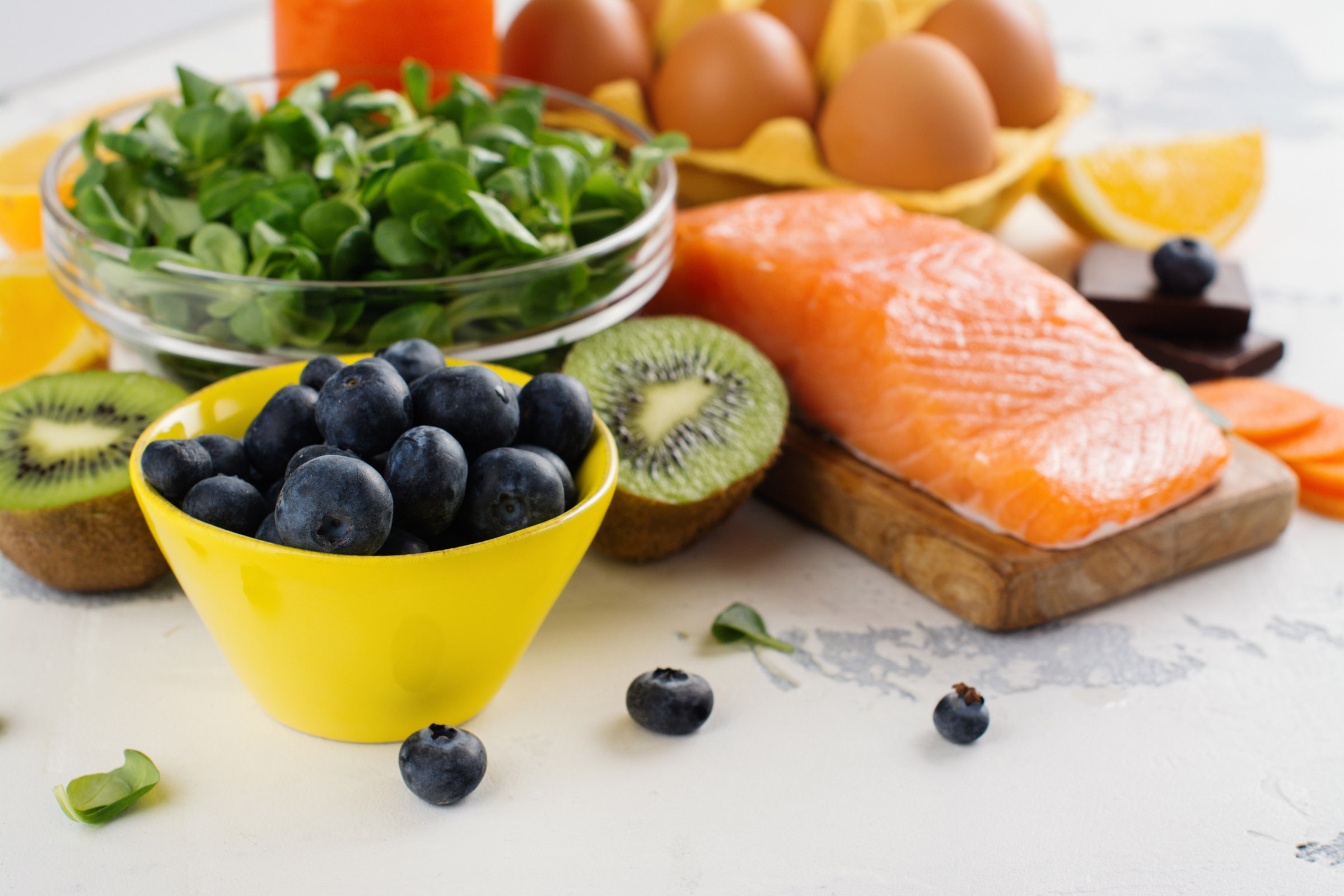
 Good nutrition is important to keep your eyes healthy. Researchers have linked two very important eye nutrients that play a key role in healthy vision. Lutein (LOO-teen) and Zeaxanthin (zee-ah-ZAN-thin), both are potent antioxidants and are best known for protecting your eyes and may reduce your risk for
Good nutrition is important to keep your eyes healthy. Researchers have linked two very important eye nutrients that play a key role in healthy vision. Lutein (LOO-teen) and Zeaxanthin (zee-ah-ZAN-thin), both are potent antioxidants and are best known for protecting your eyes and may reduce your risk for 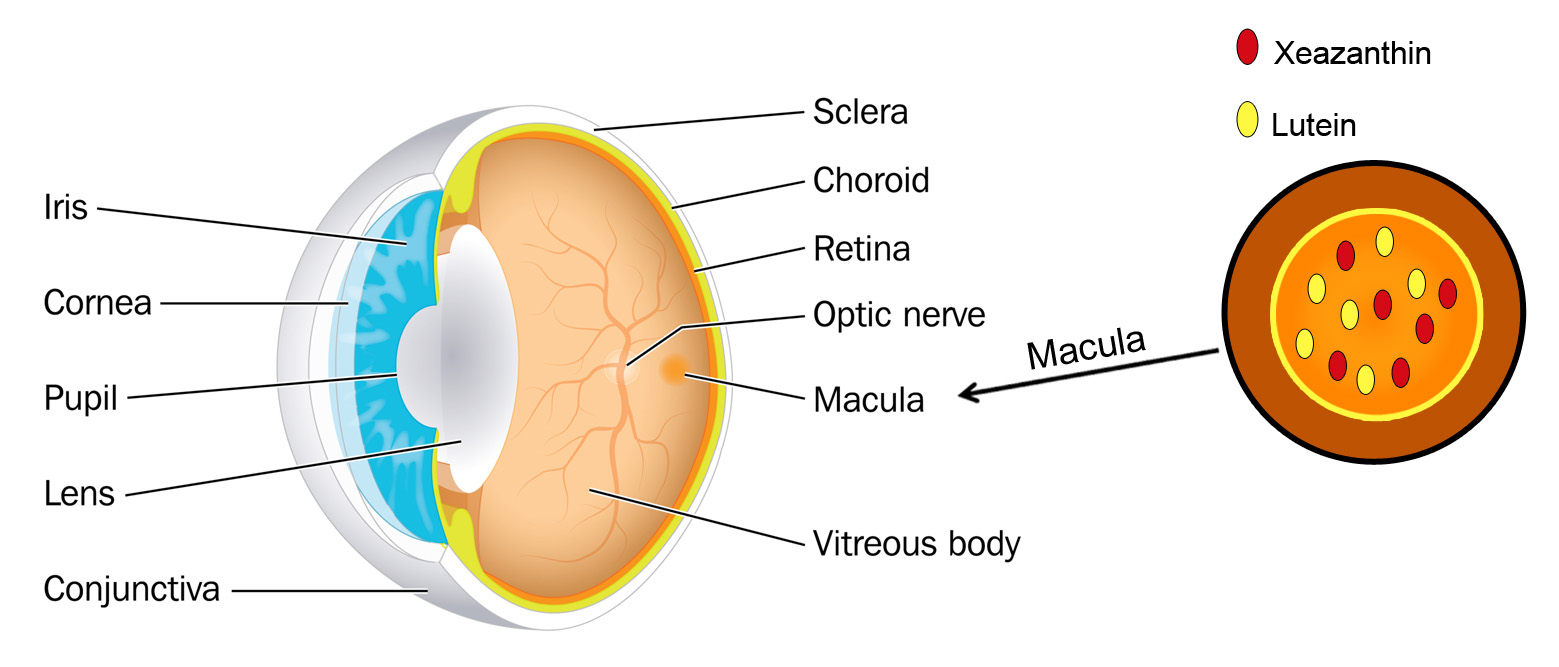
 Diets rich in these two nutrients may help hold off age-related eye diseases. The best natural food sources of lutein and zeaxanthin are green leafy vegetables and other green or yellow vegetables. Among these, cooked kale and cooked spinach top the list.
Diets rich in these two nutrients may help hold off age-related eye diseases. The best natural food sources of lutein and zeaxanthin are green leafy vegetables and other green or yellow vegetables. Among these, cooked kale and cooked spinach top the list.