 When you think of cancer, most of us do not think about the eye or vision. Though rare, cancer can start inside or outside of the eye. If cancer starts inside the eyeball it’s called intraocular and if it starts outside the eye (eyelid or in the eye socket) then it’s called extraocular tumor. It can occur in both children and adults. Most major eye centers have specialists who are trained in the diagnosis and treatment of eye cancers.
When you think of cancer, most of us do not think about the eye or vision. Though rare, cancer can start inside or outside of the eye. If cancer starts inside the eyeball it’s called intraocular and if it starts outside the eye (eyelid or in the eye socket) then it’s called extraocular tumor. It can occur in both children and adults. Most major eye centers have specialists who are trained in the diagnosis and treatment of eye cancers.
Here are a few types of cancer in eye:
- Eye Cancer in Children: The most common cancer seen in the eye of children is retinoblastoma. This occurs in children at very early age so these are the youngest cancer patients. This cancer starts inside the eye and affects the retinal cells. This is a cancer that presents very quietly, the child has no pain, no complaints and plays happily without any problem until one day parents notice that the pupil of the eye has some abnormal ‘White Glow’ (leukocoria) rather than the usual ‘red-eye’ reflection seen in a photo—that can be the first sign of retinoblastoma. So, it requires prompt evaluation by an ophthalmologist. Retinoblastoma is a curable cancer but if it is not treated on time, it can grow quickly and fill the eyeball. It can lead to loss of vision and life-threatening problems.
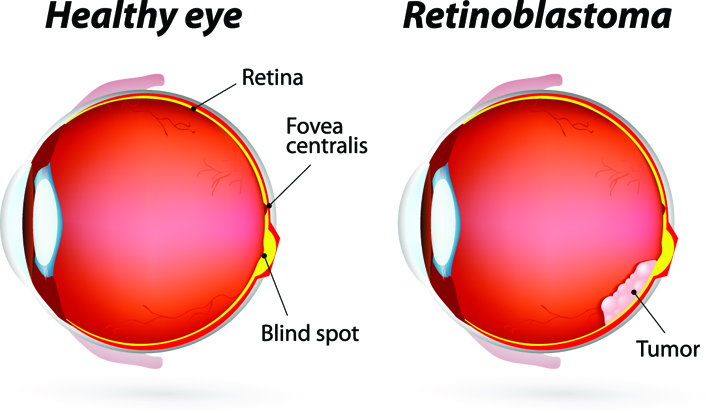 At the later stage of this cancer, the only one way to survive is to remove the eyeball (enucleation). Like many of other types of cancer, retinoblastoma has a genetic component so genetic testing needs to be done. The tumor begins with the RB1 gene mutation that stimulates retinal cells to develop into a tumor called a retinoblastoma. The RB1 mutation can be inherited from the parents, but in some cases it is sporadic and not inherited. There are various treatments such as surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy etc. to cure retinoblastoma cancer. Rarely it can spread beyond the eye.
At the later stage of this cancer, the only one way to survive is to remove the eyeball (enucleation). Like many of other types of cancer, retinoblastoma has a genetic component so genetic testing needs to be done. The tumor begins with the RB1 gene mutation that stimulates retinal cells to develop into a tumor called a retinoblastoma. The RB1 mutation can be inherited from the parents, but in some cases it is sporadic and not inherited. There are various treatments such as surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy etc. to cure retinoblastoma cancer. Rarely it can spread beyond the eye.
- Eye Cancer in Adults: The development of a tumor in the back of the eye in adults can be from a metastatic cancer from elsewhere in the body or can arise in the eye itself. The most common primary eye cancer is called uveal melanoma and is a cluster of rapidly growing cells underneath the retina, which can lead to vision loss. The tumor can also appear as a dark black spot on the iris. Ideally the uveal melanoma can be treated when the tumor is still only in the eye.However, unfortunately, in approximately 50% of patients the uveal melanoma spreads (metastasis) to other part of the body, making it the most dangerous eye cancer in adults. Depending upon its location the uveal melanoma may not cause early symptoms but the patient may experience blurred vision or large numbers of floaters. The uveal melanoma can be diagnosed only when an ophthalmologist or eye care specialist examines your eye.
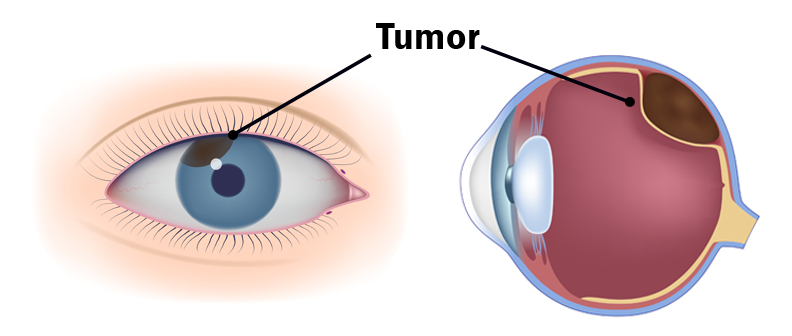 What is the main cause of uveal melanoma? How it starts, grow and spread? These questions are still unanswered. The risk of this cancer increases in persons having fair skin (white), light eye color and inability to tan. There are certain changes in the genes linked to uveal melanoma. Currently the most common are GNAQ and BAP-1 gene mutations that are associated with greater risk of metastasis, where it spreads to other parts of the body. The standard treatment of this tumor is fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB), brachytherapy (radioactive material inside a small capsule placed next to the tumor), radiation therapy and possibly enucleation.
What is the main cause of uveal melanoma? How it starts, grow and spread? These questions are still unanswered. The risk of this cancer increases in persons having fair skin (white), light eye color and inability to tan. There are certain changes in the genes linked to uveal melanoma. Currently the most common are GNAQ and BAP-1 gene mutations that are associated with greater risk of metastasis, where it spreads to other parts of the body. The standard treatment of this tumor is fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB), brachytherapy (radioactive material inside a small capsule placed next to the tumor), radiation therapy and possibly enucleation.
- Metastasis to Eye: Finally, the other types of cancers found in the eyes are because of the spreading of a primary cancer (from a distant site such as the breast, lung or liver) to the eye. Sometimes an eye exam can identify a metastatic tumor before the primary tumor is recognized elsewhere in the body. Examples of cancers that spread to the eye are breast cancer in women and lung cancer in men. Less commonly, the prostate, kidney, gastrointestinal and blood cancers (leukemia and lymphomas) can spread to the eye. Treatment depends on the type of cancer involved.
- Eye Damage from Chemotherapy: Eye problems can also develop through the side effects of chemotherapy or hormone therapies given for tumors outside the eye. When a person has any type of cancer, they often must undergo treatments with chemotherapeutic drugs. A commonly used cancer drug is called cisplatin. When treated with cisplatin, there can be damage to the retinal pigment epithelial cells in the inner part of the retina. Hemorrhages or bleeding can occur within the retina itself and vision can decrease temporarily. If a person is undergoing cancer treatments, it is a good idea to have their eyes checked, especially if they are having any vision problems. The chemotherapy does not actually cause cancers but only side effects.
Therefore, if you are having any decreased vision, it is always makes sense to have a good eye examination to identify any problems at early stage.

