In recognition of Glaucoma Awareness Month, here is a list of the top 20 things you should know in order to help save your vision as you get older.

What is Glaucoma?
1. Glaucoma is not just one eye disease, but includes a group of eye conditions that are a result of damage to the optic nerve thus causing vision loss. While unusually high pressure inside your eye (known as intraocular pressure – IOP) is often the cause, this may not always be the case.
2. It is one of the leading causes of vision loss in the US, and left untreated can result in blindness. It is estimated that 2.2 million people in the US have glaucoma, but only half of them have been diagnosed. While it primarily affects those over 60, it affects all ages with 1 in 10,000 babies born with glaucoma in the US.
3. The two most common types of glaucoma are primary open-angle glaucoma and closed angle glaucoma. Fluid in the eye flows through and area between the iris and the cornea and drains through the trabecular meshwork – this area is the “angle.”
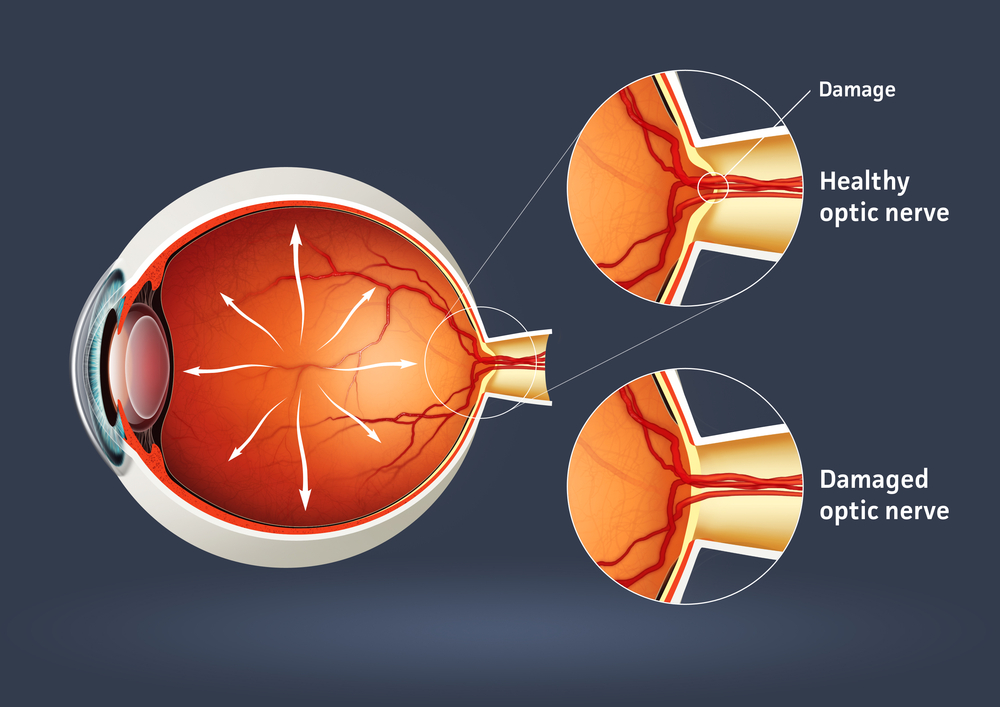
Symptoms
4. Often call the “silent thief of sight,” open angle glaucoma, which affects 90% of those diagnosed, is not indicated by eye pain. There is a gradual loss of peripheral vison, generally in both eyes, and in the advanced stages there is tunnel vision.
5. The symptoms of closed angle glaucoma are easier to recognize and include eye pain, blurred vision, nausea and vomiting, vision issues in low light, halos around light sources and red eyes.
What to Expect From a Glaucoma Exam
6. Tonometry to measure your intraocular pressure. Your eyes will be numbed with eye drops making the procedure painless.
7. Dilated eye exam to look through your pupil to the back of your eye and the optic nerve.
8. Visual field test to check your peripheral vision.
9. Visual acuity to test your ability to see at a distance.
10. Pachymetry to determine the thickness of your cornea. Your eyes are numbed so this will be painless.
11. Gonioscopy to check the angle in the eye where the iris meets the cornea to help determine between open angle and closed angle glaucoma.
Treatment Options
12. Eyedrops are a common treatment options and may include more than one type. The importance here is to let your doctor know your complete medical history and comply completely with your doctor’s instructions to get the desired result. All include side effects and your medical history will allow your doctor to select the safest option. Some examples include:
- Prostaglandins – they increase the outflow of the fluid in your eye and reduce internal pressure.
- Beta Blockers – they reduce the production of fluid in the eye.
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors – they reduce the production of fluid in the eye.
- Cholinergic or miotic agents – they help increase the outflow of fluid from the eye.
- Alpha-adrenergic agents – they reduce the production of fluid in the eye and increase the outflow of fluid.
13. Oral medications, such as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, will be used if the eye drops cannot bring your eye pressure down on their own.
14. Surgery is an option if the medications or don’t work or you can’t tolerate them. In some cases you may need to continue using eyedrops. Surgeries include:
- Trabeculoplasy – laser is used to unblock clogged drainage canals.
- Viscocanalostomy – laser used to remove a small piece of the trabecular meshwork.
- Aqueous shunt implant – small tube is inserted into the eye to improve drainage of the fluid.
Risk Factors
15. Age – you are 6 times more likely to get glaucoma if you are over 60.
16. Family history – you are 4-9 times more likely to get open angle glaucoma if someone else in your family has it.
17. Ethnicity – it plays a big factor in being diagnosed with glaucoma:
- African Americans are at a higher risk than Caucasians of developing glaucoma; develop it earlier and experiencing permanent blindness.
- Mexican-Americans have a greater incidence than Caucasians.
- Asians are at increased risk for closed angle glaucoma, with people of Japanese descent being at higher risk for normal tension glaucoma.
18. Steroid use – long-term use increases the risk by as much 40%.
19. Medical conditions – such as diabetes, high blood pressure and hypothyroidism.
20. Other eye conditions – blunt injuries that “bruise” they eye (most commonly sports-related), retinal detachment and eye tumors, eye inflammation and certain eye surgeries are examples that increase the risk.
You can work to prevent, or at least lessen the effects of glaucoma on your vision by getting regular comprehensive eye exams, use any eye drops prescribed by your doctor to treat eye pressure according to their instructions, eat a healthy diets and wear eye protection to prevent eye injury.
1/20/15
 Susan DeRemer, CFRE
Susan DeRemer, CFRE
Vice President of Development
Discovery Eye Foundation

