 Costume Contact Lenses such as cat eyes or zombie may make your Halloween costume a bit more frightful although wearing those lenses without a prescription can be more terrifying, as it could result in vision loss or even blindness.
Costume Contact Lenses such as cat eyes or zombie may make your Halloween costume a bit more frightful although wearing those lenses without a prescription can be more terrifying, as it could result in vision loss or even blindness.
You can buy contact lenses, including decorative contact lenses, from your eye doctor or on the Internet. It’s very important that you only buy contact lenses from a company that sells FDA-cleared or approved contact lenses and requires you to provide a prescription. Even if you don’t wear corrective lenses you still need to get fitted properly.
Remember — Buying contact lenses without a prescription is dangerous!
Right now there are a lot of products that you can buy without a prescription but they may not be safe or legal.
You should NEVER buy lenses from:
- street vendors
- salons or beauty supply stores
- boutiques
- flea markets
- novelty stores
- Halloween stores
- convenience stores
- beach shops
- internet sites that do not require a prescription
Know the Risks –
Wearing costume contact lenses can be risky, just like the contact lenses that correct your vision. Wearing any kind of contact lenses, including costume lenses, can cause serious damage to your eyes if the lenses are obtained without a prescription or not used correctly.
These risks include:
- A cut or scratch on the top layer of your eyeball (Corneal Abrasion)
- Allergic reactions like itchy, watery red eyes
- Decreased vision
- Infection
- Blindness
Signs of possible eye infection:
- Redness
- Pain in the eye(s) that doesn’t go away after a short period of time
- Decreased vision
If you have any of these signs, you need to see a licensed eye doctor (optometrist or ophthalmologist) right away! An eye infection could become serious and cause you to become blind if it is not treated.
This Halloween season DEF wants to remind you of the importance of eye safety and to make sure to take the proper steps in ensuring the proper contact lenses.



 Today, people are living longer than ever before so it’s important to be proactive and take responsibility for your health as you age.
Today, people are living longer than ever before so it’s important to be proactive and take responsibility for your health as you age. 
 Maintain a healthy weight. Being overweight increases your risk for diabetes. By exercising regularly, you can help keep your body healthy and prevent vision loss.
Maintain a healthy weight. Being overweight increases your risk for diabetes. By exercising regularly, you can help keep your body healthy and prevent vision loss.  Don’t smoke. Smoking increases your risk for age-related macular degeneration, cataract, and other eye diseases and conditions that can damage the optic nerve.
Don’t smoke. Smoking increases your risk for age-related macular degeneration, cataract, and other eye diseases and conditions that can damage the optic nerve. Wear protective eyewear when outdoors. Protecting your eyes from the sun’s ultraviolet rays when you are outdoors is vital for your eye health. Wearing sunglasses that block 99 to 100 percent of both UV-A and UV-B radiation.
Wear protective eyewear when outdoors. Protecting your eyes from the sun’s ultraviolet rays when you are outdoors is vital for your eye health. Wearing sunglasses that block 99 to 100 percent of both UV-A and UV-B radiation. Know your family history. Talk to your family members about their eye health history. It’s important to know if anyone has been diagnosed with a disease or condition since many are hereditary, such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetes . This will help determine if you are at higher risk for developing an eye disease or condition.
Know your family history. Talk to your family members about their eye health history. It’s important to know if anyone has been diagnosed with a disease or condition since many are hereditary, such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetes . This will help determine if you are at higher risk for developing an eye disease or condition.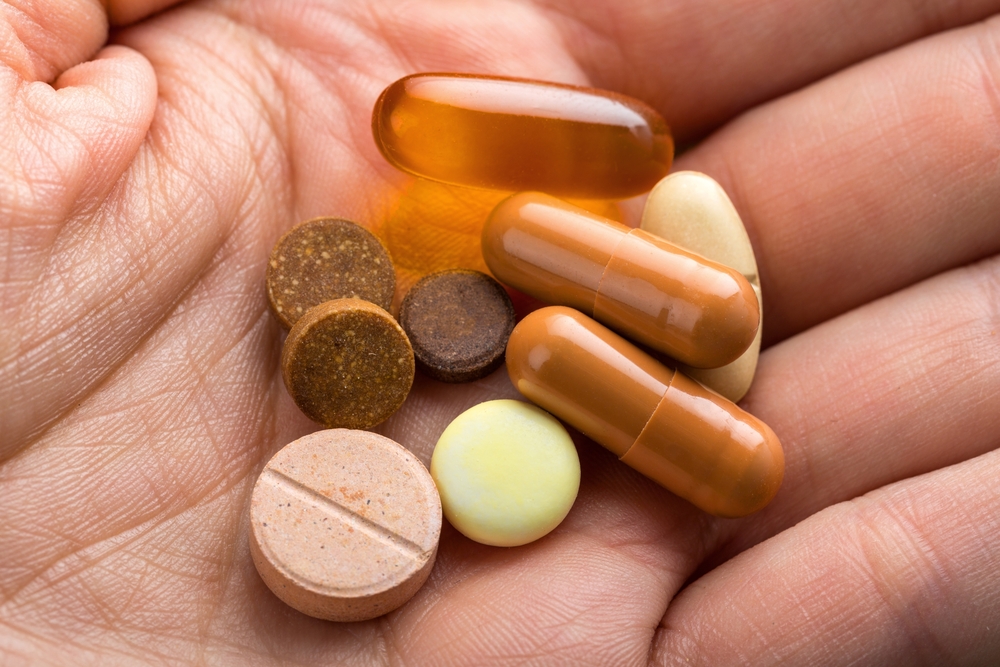 Consider a multivitamin. Vitamins C, E and the mineral zinc have been shown to promote eye health. Vitamins with Lutein and Zeaxanthin have been known to help patients with moderate to severe age-related macular degeneration.
Consider a multivitamin. Vitamins C, E and the mineral zinc have been shown to promote eye health. Vitamins with Lutein and Zeaxanthin have been known to help patients with moderate to severe age-related macular degeneration. Give your eyes a rest. If you spend a lot of time at the computer or focusing at any one distance, you sometimes forget to blink, resulting in dryness and eye fatigue. Every 20 minutes, look away about 20 feet in front of you for 20 seconds. This can help reduce eyestrain. Consider using a lubricant eye drop during long periods of intense eye use and rest your eyes for 5 minutes.
Give your eyes a rest. If you spend a lot of time at the computer or focusing at any one distance, you sometimes forget to blink, resulting in dryness and eye fatigue. Every 20 minutes, look away about 20 feet in front of you for 20 seconds. This can help reduce eyestrain. Consider using a lubricant eye drop during long periods of intense eye use and rest your eyes for 5 minutes.

 Summer time is officially here and everyone enjoys a dip in a nice, cool pool during the summer months. While swimming is a great form of exercise and a relaxing way to cool down, the water can be hard on your eyes.
Summer time is officially here and everyone enjoys a dip in a nice, cool pool during the summer months. While swimming is a great form of exercise and a relaxing way to cool down, the water can be hard on your eyes. Wear Goggles – Wear a pair of swim goggles every time you swim. Goggles keep pool chemicals out of your eyes.
Wear Goggles – Wear a pair of swim goggles every time you swim. Goggles keep pool chemicals out of your eyes.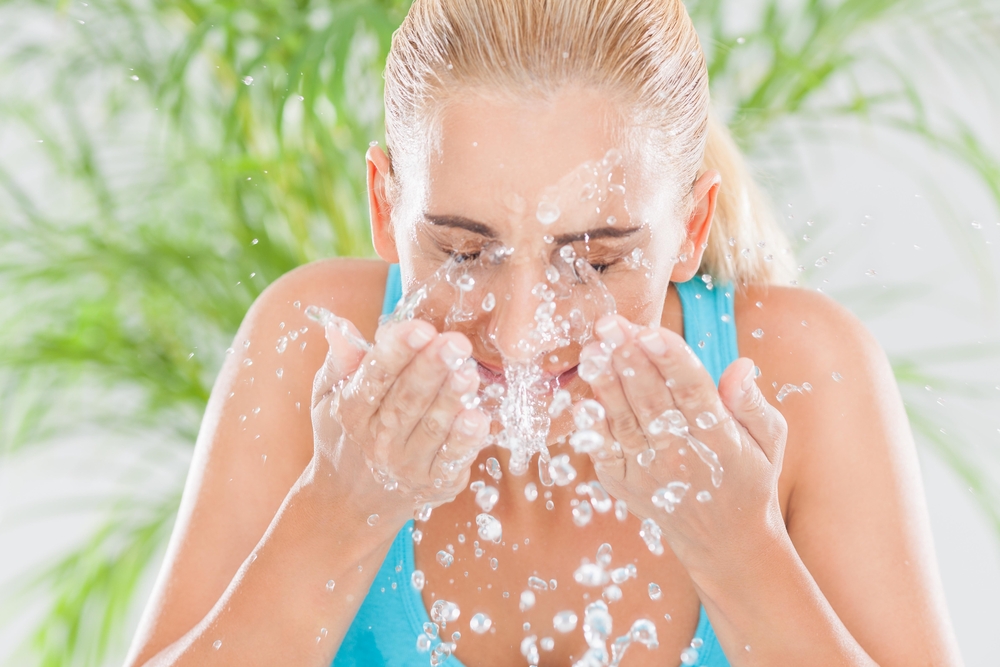 Wash Your Eyes – Immediately after swimming, splash your closed eyes with fresh tap water. This washes chlorine and other chemicals off your eyelids and eyelashes.
Wash Your Eyes – Immediately after swimming, splash your closed eyes with fresh tap water. This washes chlorine and other chemicals off your eyelids and eyelashes.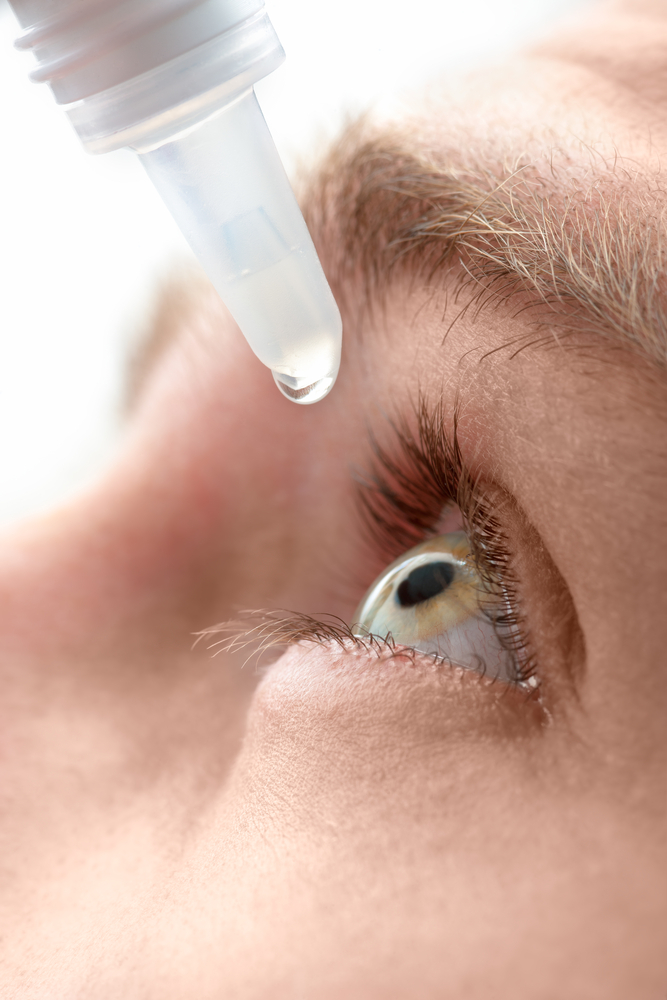 Use Eye Drops – Use over-the-counter lubricating eye drops before and after swimming to keep the tear film balanced and eyes comfortable.
Use Eye Drops – Use over-the-counter lubricating eye drops before and after swimming to keep the tear film balanced and eyes comfortable.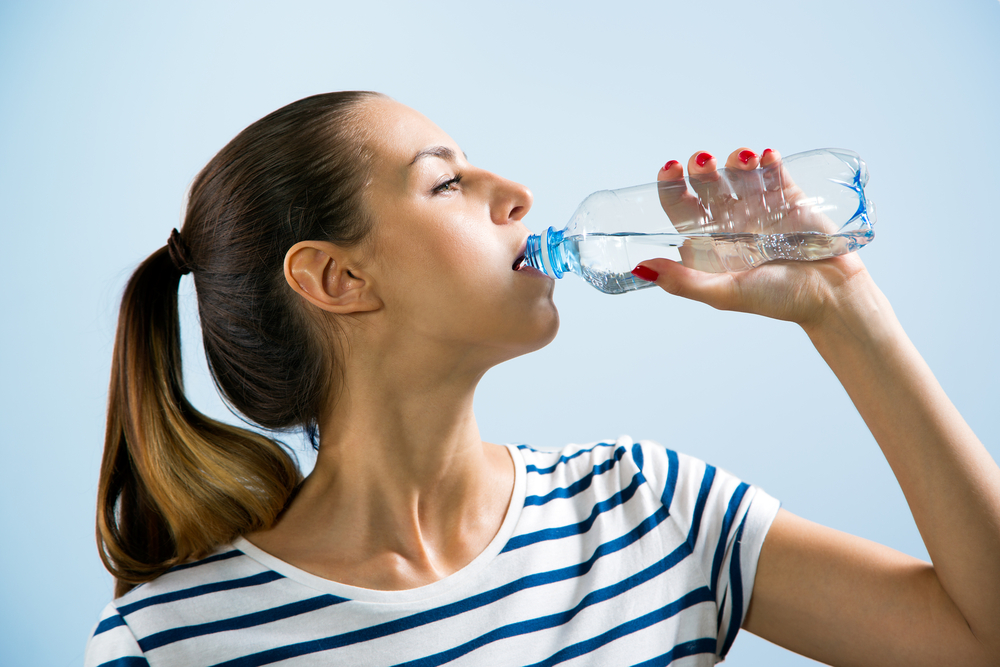 Stay Hydrated – Don’t forget to drink plenty of water. Staying well hydrated is an important part of keeping your eyes moist and comfortable.
Stay Hydrated – Don’t forget to drink plenty of water. Staying well hydrated is an important part of keeping your eyes moist and comfortable.

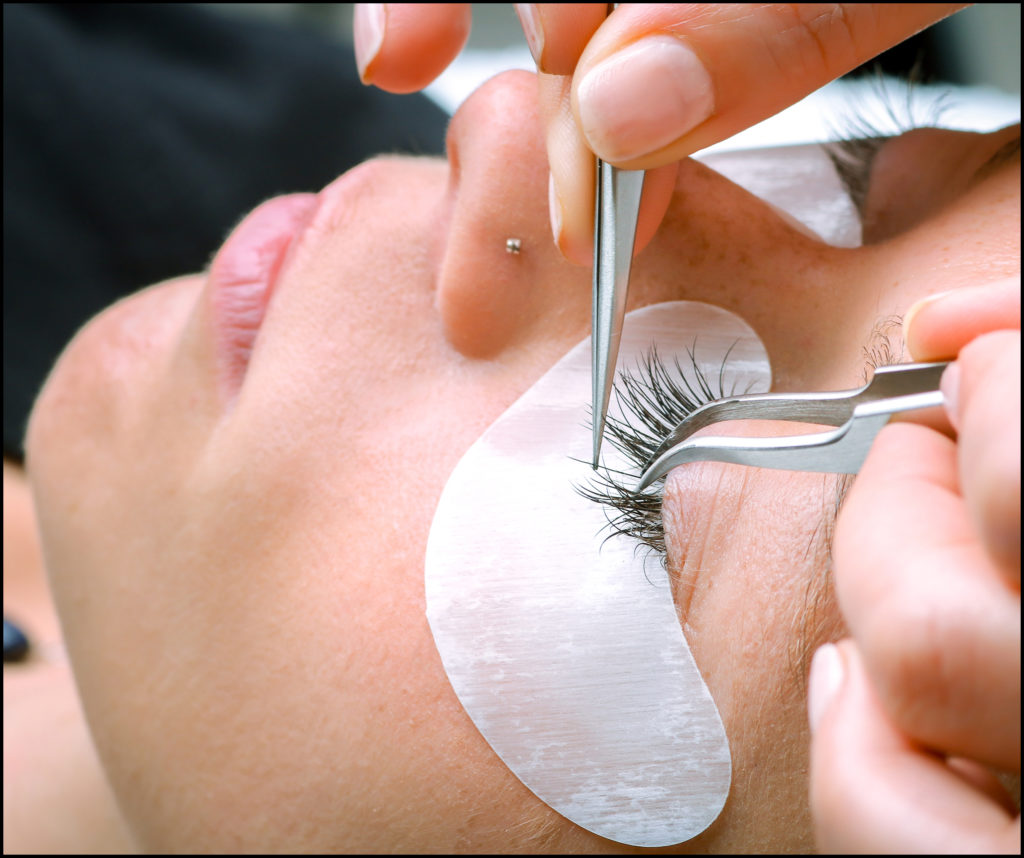 lashes to isolate just one. Then the synthetic lash is placed on the natural lash, holding it for a few seconds while the glue bonds. The tech repeats the process, one lash at a time, attaching 40 to 100 lashes per eye. The tech will use several lengths of lashes, attaching the longest artificial lashes to your longest natural lashes.
lashes to isolate just one. Then the synthetic lash is placed on the natural lash, holding it for a few seconds while the glue bonds. The tech repeats the process, one lash at a time, attaching 40 to 100 lashes per eye. The tech will use several lengths of lashes, attaching the longest artificial lashes to your longest natural lashes.

 The Difference Between an
The Difference Between an 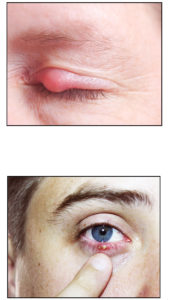 C
C
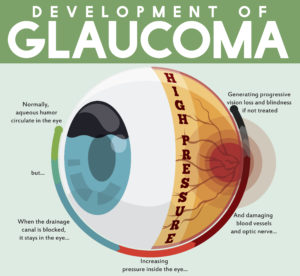 tic nerve, a part of the central nervous system that carries visual information from the eye to the brain.
tic nerve, a part of the central nervous system that carries visual information from the eye to the brain.