Proper eye care is one of the most essential aspects people tend to ignore during, or when planning their travel. The following tips might help you in keeping your eyes healthy when traveling:
1. Pack accordingly
Pack the following:
-
- Lubricating eye drops: Consider packing allergy-specific eye drops that are specially formulated for allergies.
- Eye wash solution: If you have something in your eye — an eyelash, a fleck of dust — you might be tempted to head to the nearest restroom to wash out your eye with tap water. Stop. That tap water could contain impurities or minerals which may further irritate your eyes or cause an infection. Use a sterile eye wash instead—purchased at your drugstore.
- Sunglasses and a hat – Goggles if you plan to go swimming
- Sleep mask
2. Don’t wear contacts for long-haul trips.
If you’re about to take a long road trip or get on a plane, play it safe by opting for glasses from the start. Make sure to aim air vents away from your eyes, constant temperature fluctuations and lack of humidity could irritate your eyes.
3. Apply a warm compress at the end of each leg of the trip
Once you reach your destination, wet a washcloth with warm water and drape it over your eyes for 5-10 minutes. If your eyes feel like they have something in them, try an eye wash solution to irrigate your eyes.
4. Take steps to manage eye strain.
Eye strain is common, and when you’re a tired traveler, it could get the best of you. The best ways to manage eye strain include limiting screen time and adjusting your lighting, so whether you’re working on your computer or watching in-flight movies, be sure to take frequent breaks. A simple approach is the 20-20-20 rule: Every 20 minutes look away from your screen for 20 seconds and focus on something 20 feet away.
5. Invest in good sunglasses and wear them
Sunglasses help you avoid glare and air borne foreign particles. They also protect from UV rays. According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology, you should buy glasses that are 100% UV-resistant. The term “polarized” means they cut glare, not UV rays. AAO recommends buying sunglasses that are large to provide optimal coverage.
Tips for beating dry eyes when traveling 
- Eat a healthy diet of foods that nourish your eyes like Omega 3s and foods rich in Vitamin A. Always make sure you drink plenty of water throughout the day, as this will ensure you stay hydrated.
- Always make sure you are taking proper care of your contact lenses and putting them in correctly.
- Wear glasses on a windy day to protect your eyes from becoming dry or irritated. You should also make sure your sunglasses are polarized and filter out 100% of harmful UV rays and block harsh glare off of different surfaces.
- Avoid areas where there is lots of smoke from fires or cigarettes, as smoke can irritate and make dry eyes feel sore.
- Make sure you pack lubricating eye drops and medicated eye drops if you require them so that you can treat your eyes immediately when they begin to feel dry. Some users recommend Bausch & Lomb anti-red drops, Lumify.
- Pack oral allergy medication that will combat any allergies to new pollens or allergens.
These tips will help you take good care of your eyes while traveling.



 The past year has taken a toll on the physical and mental health of millions of people. While we were rightly focused on slowing the spread of the pandemic, widespread shutdowns brought about a more sedentary, inactive lifestyle, which has led to increased weight gain and worsened mental health for many. As we look ahead and as more people receive the vaccine, it is time to start reprioritizing physical activity and placing much needed attention on our health.
The past year has taken a toll on the physical and mental health of millions of people. While we were rightly focused on slowing the spread of the pandemic, widespread shutdowns brought about a more sedentary, inactive lifestyle, which has led to increased weight gain and worsened mental health for many. As we look ahead and as more people receive the vaccine, it is time to start reprioritizing physical activity and placing much needed attention on our health.
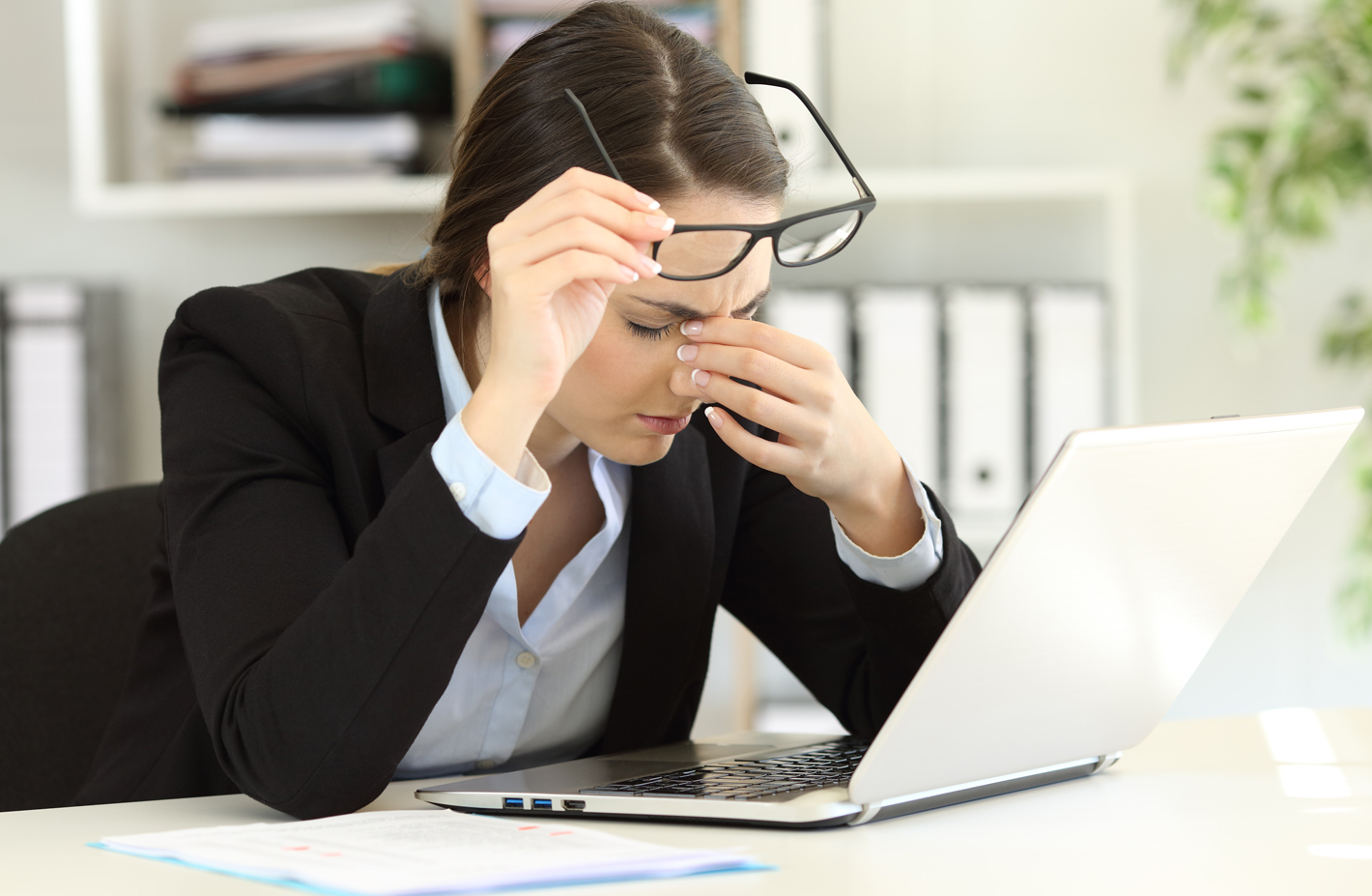






 Rest and blink your eyes – Researchers found that over 30% of people using digital devices rarely take time to rest their eyes. Just over 10% say they never take a break, even when working from home. The eye muscles get overworked and don’t get a chance to relax and recover. Experts suggest the 20-20-20 rule; every 20 minutes, focus your eyes and attention on something 20 feet away for 20 seconds. You can also get up and walk around for a few minutes.
Rest and blink your eyes – Researchers found that over 30% of people using digital devices rarely take time to rest their eyes. Just over 10% say they never take a break, even when working from home. The eye muscles get overworked and don’t get a chance to relax and recover. Experts suggest the 20-20-20 rule; every 20 minutes, focus your eyes and attention on something 20 feet away for 20 seconds. You can also get up and walk around for a few minutes. Reduce exposure to blue light – In the spectrum of light, blue is more high energy and close to ultraviolet light. So, if you use screens throughout the day, ask your eye doctor about the value of computer glasses that block blue light. Reducing exposure to blue light may help lessen vision problems. At home, using digital devices until bedtime can overstimulate your brain and make it more difficult to fall asleep. Eye doctors recommend no screen time at least one to two hours before going to sleep.
Reduce exposure to blue light – In the spectrum of light, blue is more high energy and close to ultraviolet light. So, if you use screens throughout the day, ask your eye doctor about the value of computer glasses that block blue light. Reducing exposure to blue light may help lessen vision problems. At home, using digital devices until bedtime can overstimulate your brain and make it more difficult to fall asleep. Eye doctors recommend no screen time at least one to two hours before going to sleep.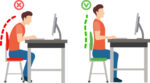 Sit up straight – Proper posture is important. Your back should be straight and your feet on the floor while you work. Elevate your wrists slightly instead of resting them on the keyboard.
Sit up straight – Proper posture is important. Your back should be straight and your feet on the floor while you work. Elevate your wrists slightly instead of resting them on the keyboard. Set up monitor properly – Make sure your computer screen is about 25 inches, or an arm’s length, away from your face. The center of the screen should be about 10-15 degrees below eye level. Cut glare by using a matte screen filter. You can find them for all types of computers, phones, and tablets. Increase font size or set the magnification of the documents you are reading to a comfortable size.
Set up monitor properly – Make sure your computer screen is about 25 inches, or an arm’s length, away from your face. The center of the screen should be about 10-15 degrees below eye level. Cut glare by using a matte screen filter. You can find them for all types of computers, phones, and tablets. Increase font size or set the magnification of the documents you are reading to a comfortable size. Consider computer glasses –For the greatest comfort at your computer, you might benefit from having your eye doctor modify your eyeglasses prescription to create customized computer glasses. This is especially true if you normally wear distance contact lenses, which may also become dry and uncomfortable during extended screen time. Computer glasses also are a good choice if you wear bifocals or progressive lenses, because these lenses generally are not optimal for the distance to your computer screen.
Consider computer glasses –For the greatest comfort at your computer, you might benefit from having your eye doctor modify your eyeglasses prescription to create customized computer glasses. This is especially true if you normally wear distance contact lenses, which may also become dry and uncomfortable during extended screen time. Computer glasses also are a good choice if you wear bifocals or progressive lenses, because these lenses generally are not optimal for the distance to your computer screen. Get an Eye Exam – If you have tried all these tips and eye strain is still an issue, it might be time to see an eye care professional to schedule an eye exam. The exam may even detect underlying issues before they becomes worse.
Get an Eye Exam – If you have tried all these tips and eye strain is still an issue, it might be time to see an eye care professional to schedule an eye exam. The exam may even detect underlying issues before they becomes worse.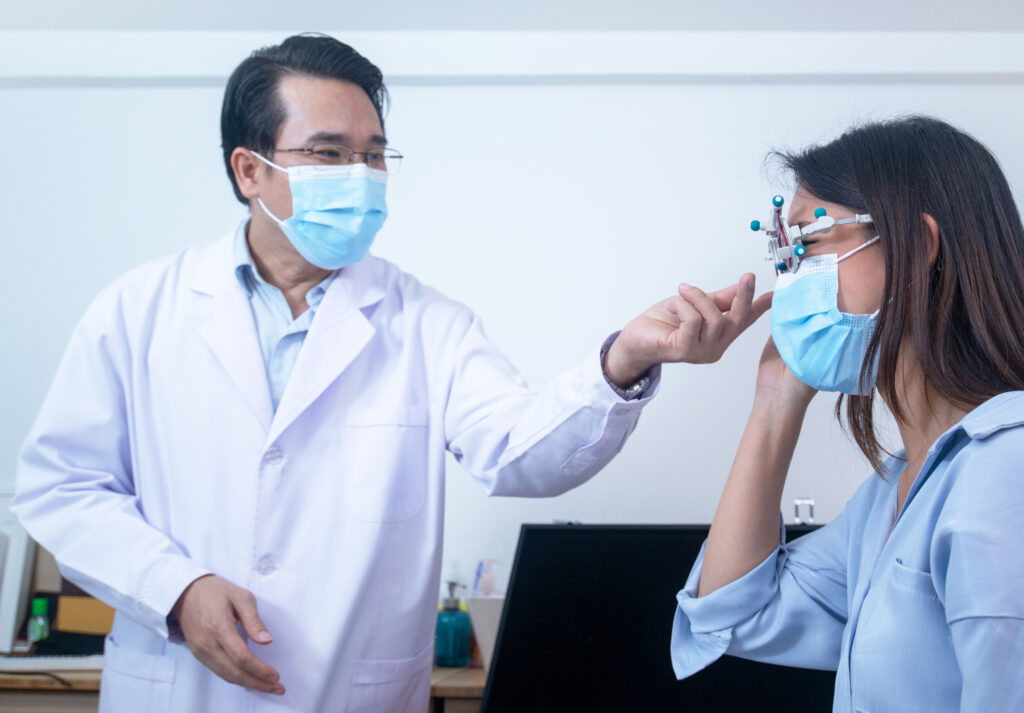 Taking care of your health is critical and you may have concerns related to eye health as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. The offices of Ophthalmologists and Optometrists are resuming the delivery of comprehensive eye and vision care and implementing new protocols to provide care in a safe and healthy environment.
Taking care of your health is critical and you may have concerns related to eye health as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. The offices of Ophthalmologists and Optometrists are resuming the delivery of comprehensive eye and vision care and implementing new protocols to provide care in a safe and healthy environment.

 Tom Sullivan
Tom Sullivan