This month of April is dedicated to
This month of April is dedicated to
WOMEN’S EYE HEALTH MONTH
With Women’s History Month, Women’s Eye Health Month and Mother’s Day all happening this spring, we’ve got all of the women in our lives on our minds.
Did you know that blindness affects women more than men? The National Institutes of Health reports that 2/3rds of the people with blindness or visual impairments are women. Often, hormones, and especially life changes such as pregnancy and menopause, cause changes in women’s eyes. Preventing blindness and vision problems requires keeping a healthy lifestyle, avoiding certain habits, and seeing the eye doctor regularly.
Many women aren’t aware that they have a higher risk for developing eye and vision problems. In an effort to create awareness of various eye diseases that women are more prone to have than men, April has been dedicated to educating women about these diseases, along with providing resources and recommendations on the best ways to maintain excellent vision for women.
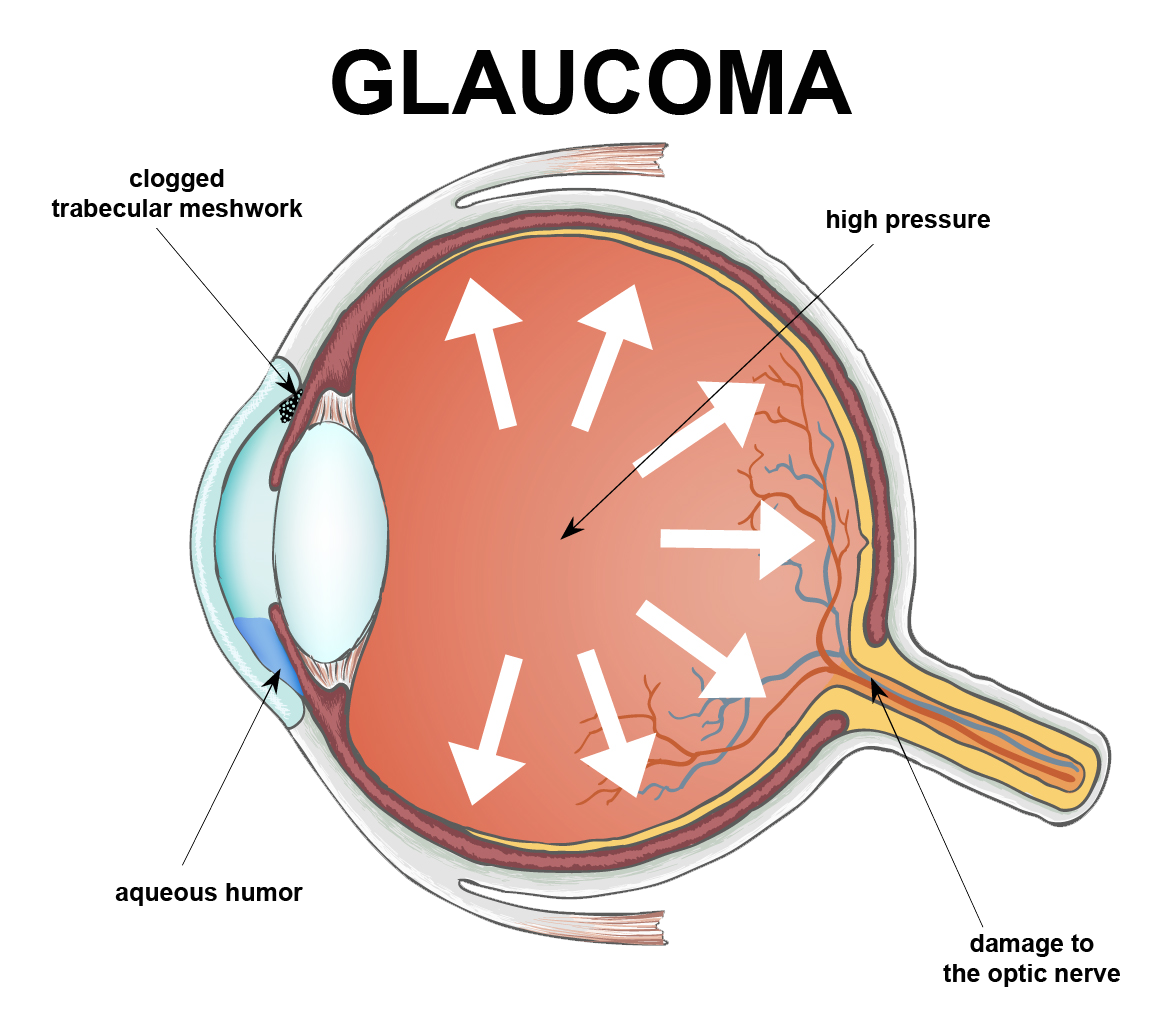
The National Eye Institute also stated that women deal with greater instances of eye disorders, in part, because they tend to live longer than men, are more likely to undergo cancer treatments which affect vision, and experience age-related hormonal changes that can affect the eyes. Women also have higher rates of eye diseases such as cataract, glaucoma, and age-related macular degeneration than men.

As we mentioned, hormones are a factor in developing eye problems, but also lifestyle, genetics, pregnancy and more contribute to the problems. Women pass through several biological and hormone changes that men do not. Pregnancy causes changes in the eyes such as dry eyes, puffiness, migraine headaches that affect vision, light sensitivity and more. If a woman is not pregnant, even taking birth control can cause hormonal changes and blood clots in some cases. If a clot happens, that can lead to strokes that affect vision, sometimes permanently.
Later in life, eye problems become more frequent in both men and women. However, women statistically have a higher chance of developing chronic conditions such as lupus, arthritis, multiple sclerosis and more. All of these conditions can affect eye health.
It’s important for women to know the risks for eye-related diseases resulting in vision impairment and take the steps to prevent eventual vision loss. Here are some ways that you can help to protect your eyes and save your eyesight:
- Find out about your family history of eye diseases and conditions.
- Protect your eyes from the sun by wearing 100% UV blocking sunglasses when outdoors.
- Don’t smoke.
- Consume a healthy diet with proper nutrition and special eye health supplements as prescribed by an eye doctor. (Eye Healthy Recipes)
- Adhere to contact lens hygiene and safety.
- Adhere to cosmetic hygiene and safety precautions.
- Protect your eyes against extended exposure to blue light from computers, smartphones and LED lamps.
- If you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant and have diabetes, see an eye doctor for a comprehensive eye exam. In women who have diabetes, diabetic retinopathy can accelerate quickly during pregnancy and can present a risk for the baby as well.
Mothers are often charged with caring for the eye health of the entire family, but too often their own eye health is neglected. It is critical that mothers take care of their eyes and overall health so that they can be in the best condition to care for their families.

Speak to your eye care professional about your personal eye health and vision risks so you can exercise the precautions and measures to protect your eyes. Encourage the other women in your life to do so as well. Once vision is lost, it often cannot be regained and there are many steps you can take to prevent it with proper knowledge and awareness.
The most important way to prevent vision loss is to ensure you schedule regular eye exams. Don’t wait for symptoms to appear as many eye issues are painless and symptomless, and sometimes by the time you notice symptoms, vision loss is untreatable.
Click here for Eye Healthy Recipes.
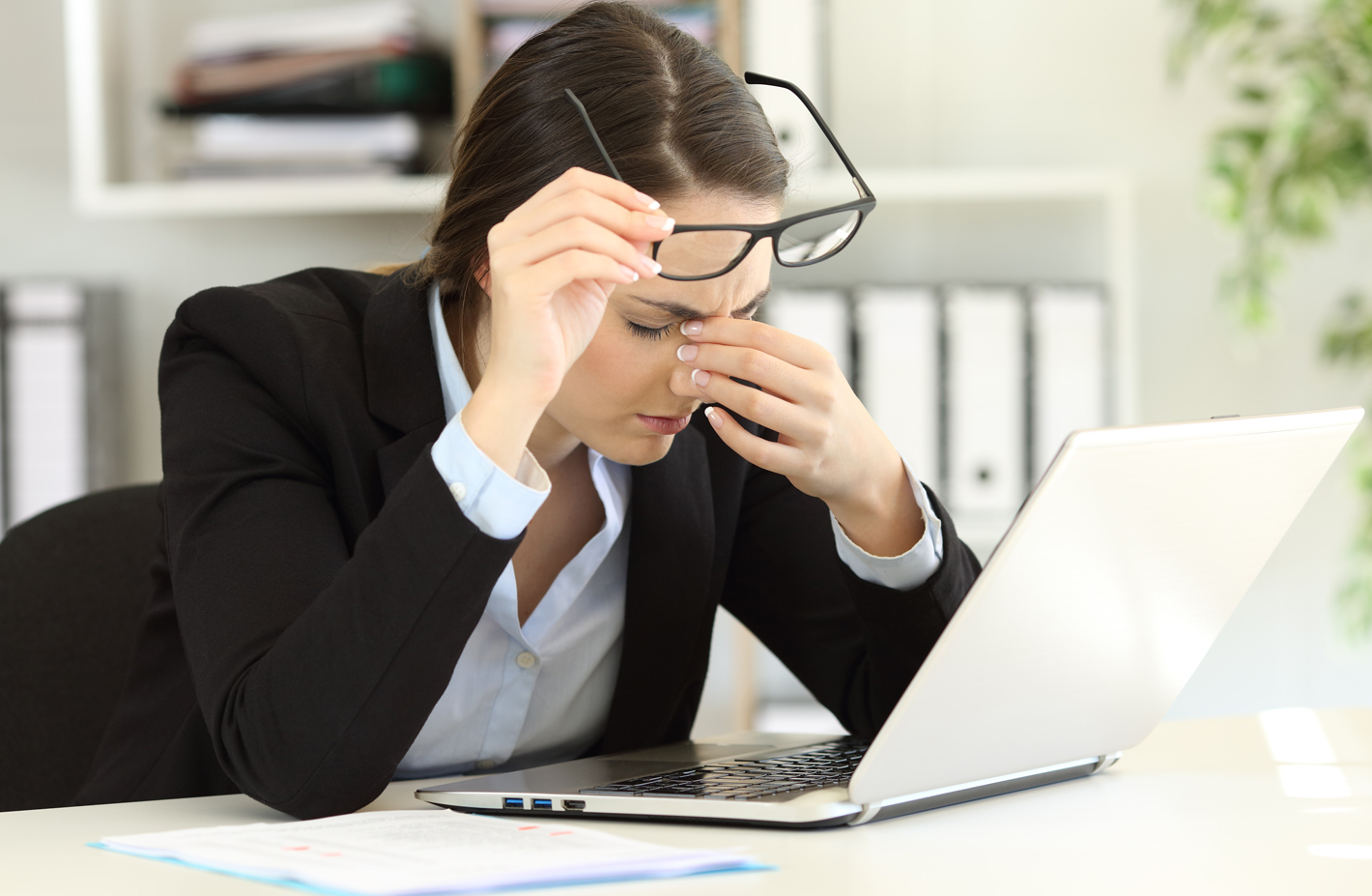




 Rest and blink your eyes – Researchers found that over 30% of people using digital devices rarely take time to rest their eyes. Just over 10% say they never take a break, even when working from home. The eye muscles get overworked and don’t get a chance to relax and recover. Experts suggest the 20-20-20 rule; every 20 minutes, focus your eyes and attention on something 20 feet away for 20 seconds. You can also get up and walk around for a few minutes.
Rest and blink your eyes – Researchers found that over 30% of people using digital devices rarely take time to rest their eyes. Just over 10% say they never take a break, even when working from home. The eye muscles get overworked and don’t get a chance to relax and recover. Experts suggest the 20-20-20 rule; every 20 minutes, focus your eyes and attention on something 20 feet away for 20 seconds. You can also get up and walk around for a few minutes. Reduce exposure to blue light – In the spectrum of light, blue is more high energy and close to ultraviolet light. So, if you use screens throughout the day, ask your eye doctor about the value of computer glasses that block blue light. Reducing exposure to blue light may help lessen vision problems. At home, using digital devices until bedtime can overstimulate your brain and make it more difficult to fall asleep. Eye doctors recommend no screen time at least one to two hours before going to sleep.
Reduce exposure to blue light – In the spectrum of light, blue is more high energy and close to ultraviolet light. So, if you use screens throughout the day, ask your eye doctor about the value of computer glasses that block blue light. Reducing exposure to blue light may help lessen vision problems. At home, using digital devices until bedtime can overstimulate your brain and make it more difficult to fall asleep. Eye doctors recommend no screen time at least one to two hours before going to sleep.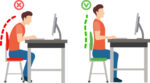 Sit up straight – Proper posture is important. Your back should be straight and your feet on the floor while you work. Elevate your wrists slightly instead of resting them on the keyboard.
Sit up straight – Proper posture is important. Your back should be straight and your feet on the floor while you work. Elevate your wrists slightly instead of resting them on the keyboard. Set up monitor properly – Make sure your computer screen is about 25 inches, or an arm’s length, away from your face. The center of the screen should be about 10-15 degrees below eye level. Cut glare by using a matte screen filter. You can find them for all types of computers, phones, and tablets. Increase font size or set the magnification of the documents you are reading to a comfortable size.
Set up monitor properly – Make sure your computer screen is about 25 inches, or an arm’s length, away from your face. The center of the screen should be about 10-15 degrees below eye level. Cut glare by using a matte screen filter. You can find them for all types of computers, phones, and tablets. Increase font size or set the magnification of the documents you are reading to a comfortable size. Consider computer glasses –For the greatest comfort at your computer, you might benefit from having your eye doctor modify your eyeglasses prescription to create customized computer glasses. This is especially true if you normally wear distance contact lenses, which may also become dry and uncomfortable during extended screen time. Computer glasses also are a good choice if you wear bifocals or progressive lenses, because these lenses generally are not optimal for the distance to your computer screen.
Consider computer glasses –For the greatest comfort at your computer, you might benefit from having your eye doctor modify your eyeglasses prescription to create customized computer glasses. This is especially true if you normally wear distance contact lenses, which may also become dry and uncomfortable during extended screen time. Computer glasses also are a good choice if you wear bifocals or progressive lenses, because these lenses generally are not optimal for the distance to your computer screen. Get an Eye Exam – If you have tried all these tips and eye strain is still an issue, it might be time to see an eye care professional to schedule an eye exam. The exam may even detect underlying issues before they becomes worse.
Get an Eye Exam – If you have tried all these tips and eye strain is still an issue, it might be time to see an eye care professional to schedule an eye exam. The exam may even detect underlying issues before they becomes worse. Taking care of your health is critical and you may have concerns related to eye health as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. The offices of Ophthalmologists and Optometrists are resuming the delivery of comprehensive eye and vision care and implementing new protocols to provide care in a safe and healthy environment.
Taking care of your health is critical and you may have concerns related to eye health as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. The offices of Ophthalmologists and Optometrists are resuming the delivery of comprehensive eye and vision care and implementing new protocols to provide care in a safe and healthy environment.

 Tom Sullivan
Tom Sullivan


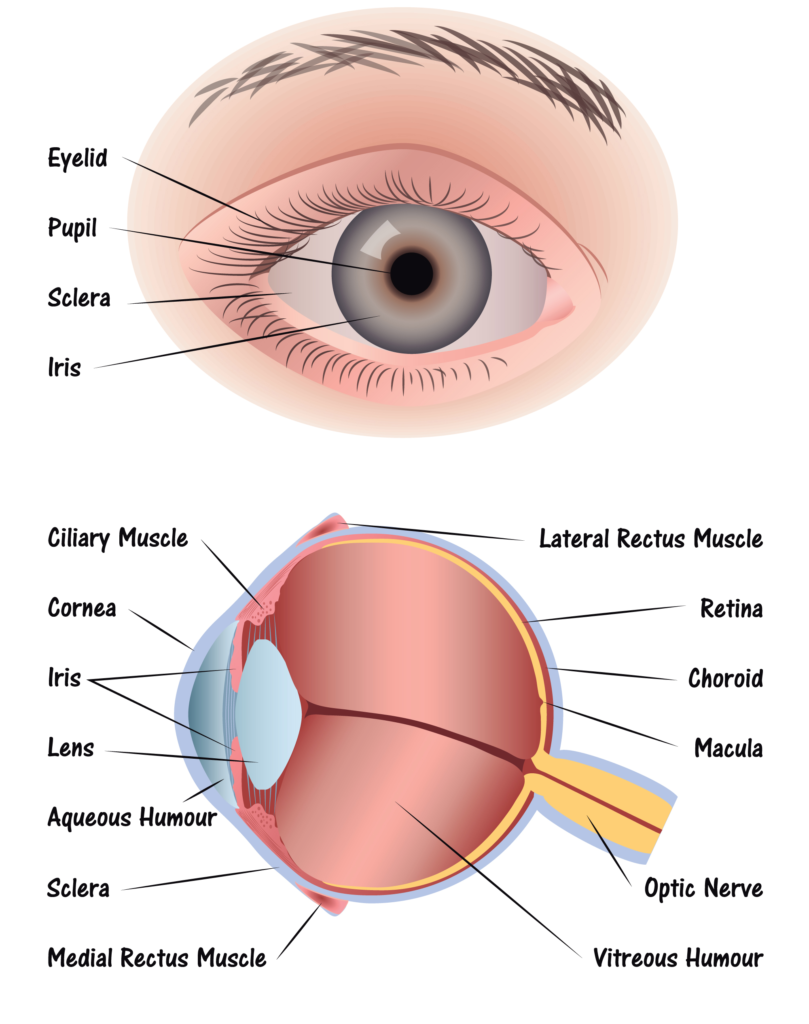 Step 1: Light passes through a thin layer of moisture
Step 1: Light passes through a thin layer of moisture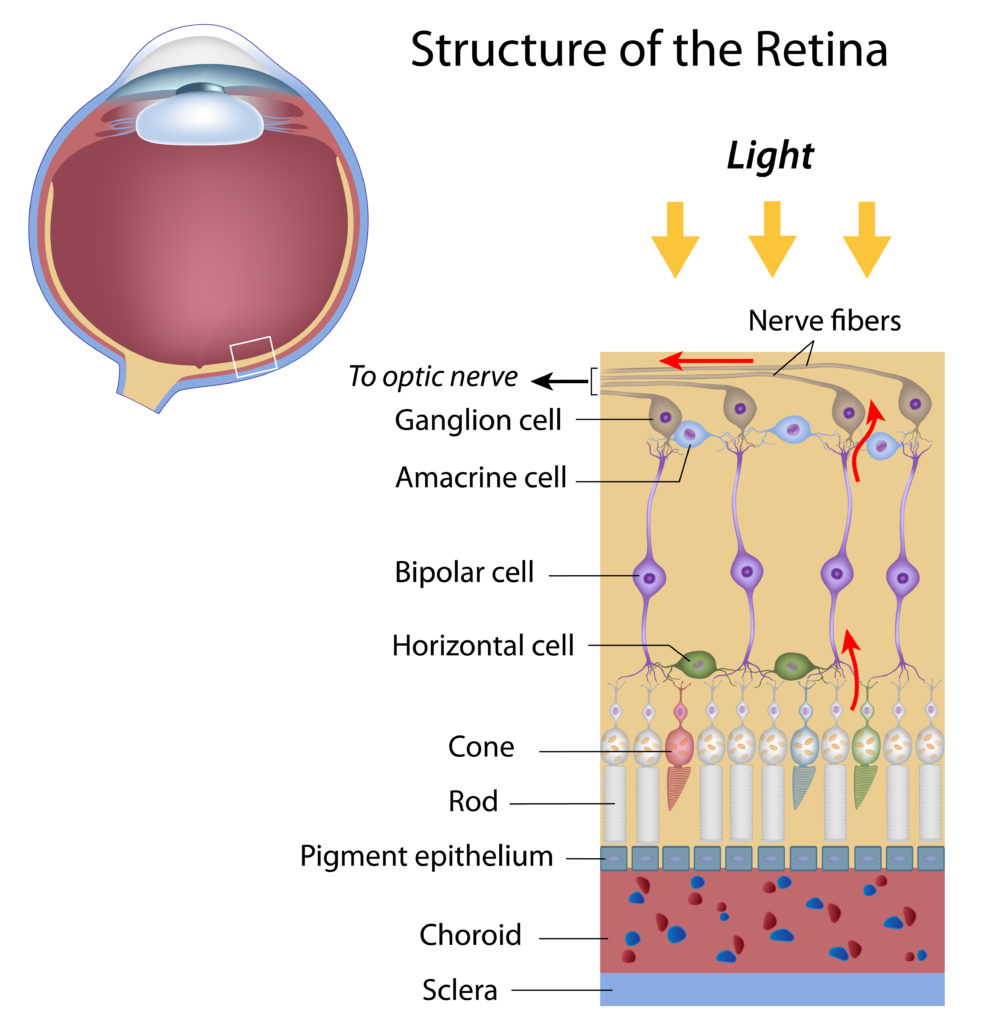
 National Glaucoma Awareness Month reminds all of us to get regular eye exams and show support for those suffering from this condition.
National Glaucoma Awareness Month reminds all of us to get regular eye exams and show support for those suffering from this condition.