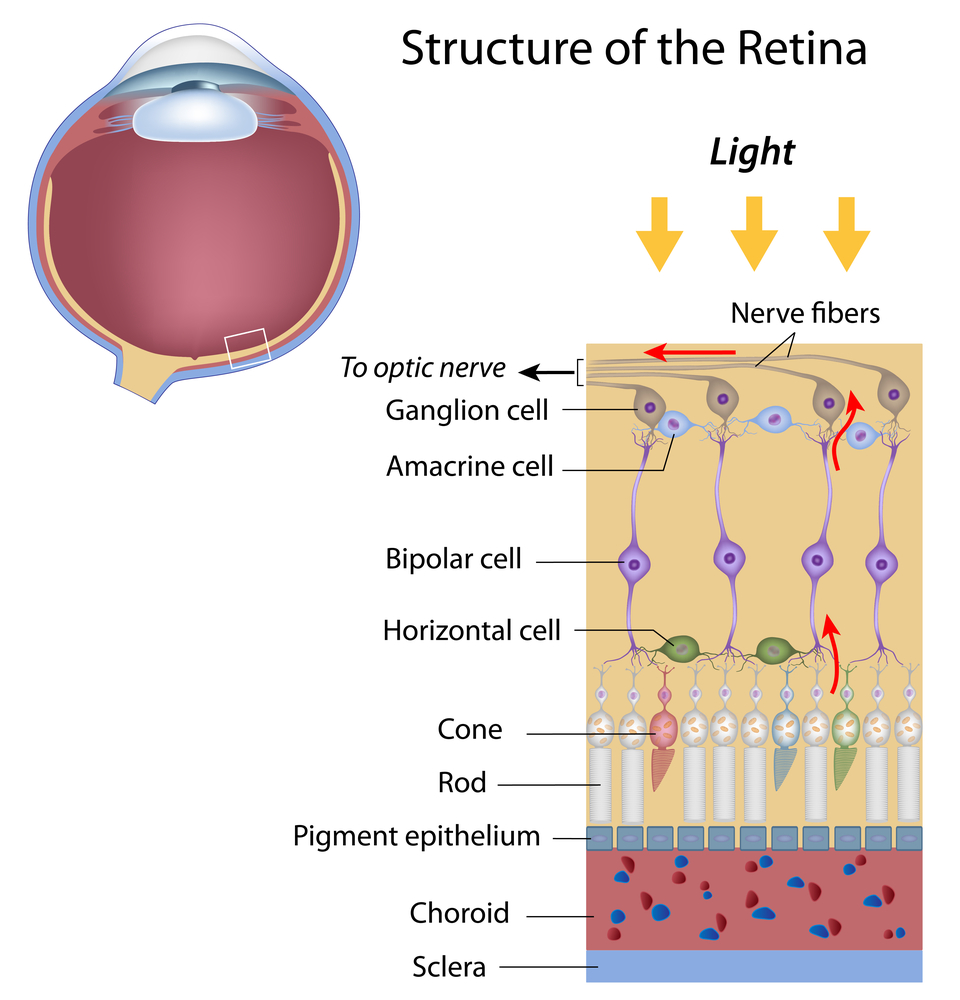
You know to slather on lots of sunblock before going out in the sun, and to keep applying it throughout the day. What about your eyes? Do you always wear a brimmed hat and sunglasses? Even on cloudy days? Can your eyes get sunburned?
The short answer is yes, you can get sunburned eyes, and just like your skin, it could come back and haunt you in the future.

Severely sunburned eyes, known as photokeratitis, is a result of prolonged exposure to the sun’s ultraviolet rays and can cause a burning sensation and blurred vision. Realize that these damaging UV rays do not just come directly from the sun, but also from the reflection of these rays from water and sand.
Symptoms of sunburned eyes include:
- Eye pain
- A gritty feeling
- Burning sensation
- Red eyes
- Swollen eyes and/or lids
- Watery eyes
- Blurred vision
- Sensitivity to light
- Glare and halos around lights
- Headaches
These symptoms are temporary and should resolve on their own within 24 to 48 hours. If the symptoms last longer, see your eye doctor immediately.
While waiting for your eyes to recover you might want to:
- Stay indoors and wear sunglasses to help with your increased light sensitivity.
- Keep your eyes moist with preservative-free artificial tears.
- Use OTC pain relievers to help with the pain and follow the recommended dosage.
- DO NOT rub your eyes.
- If you wear contact lenses, remove them immediately and stop wearing them until your eyes have returned to normal.
- You may find that placing a cool, damp cloth over your closed eyes is soothing.
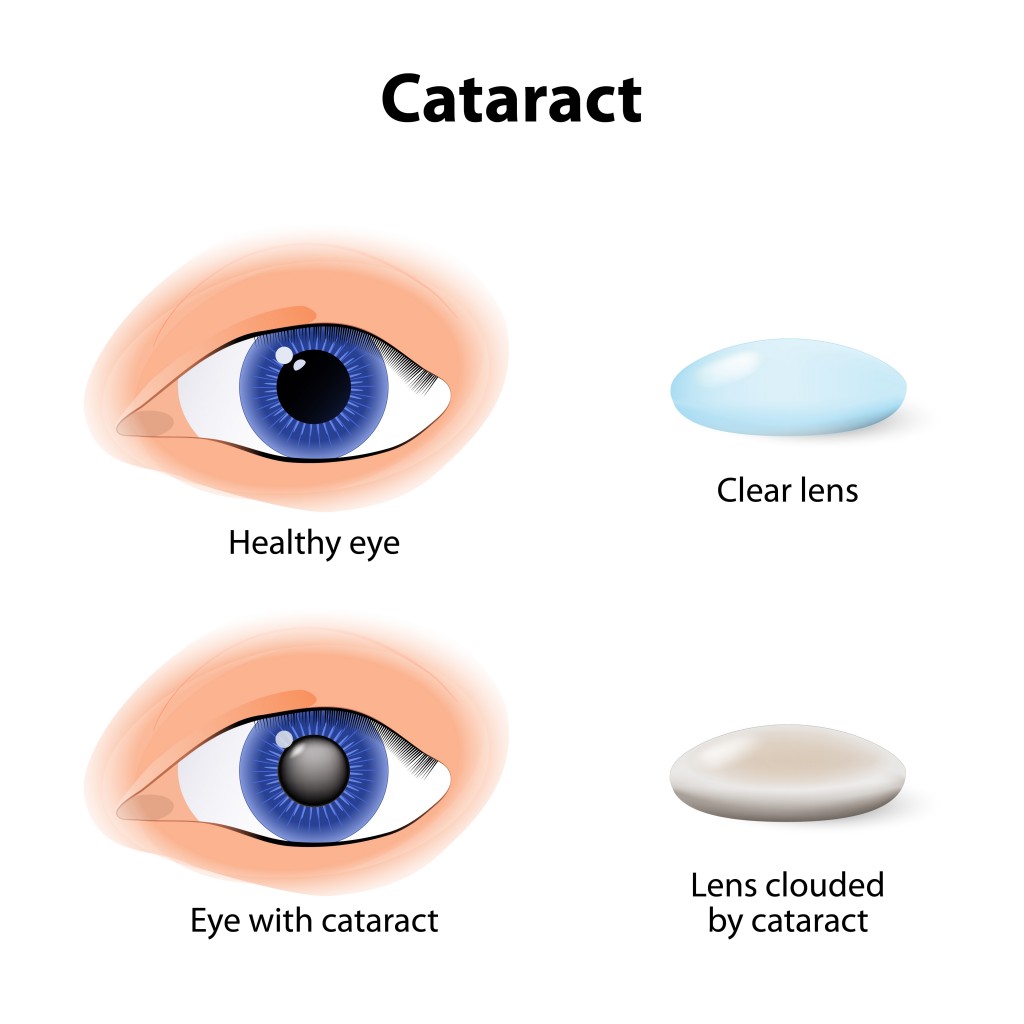
Just like with your skin, the UV rays do have a long-term effect on your eyes. Sunlight can cause a slow deterioration of the cells in your eyes that could lead to eye diseases such as age-related macular degeneration and cataracts. Therefore it is best to limit you exposure to both direct and reflected UV rays.
The best ways to protect your eyes include wearing sunglasses that block 100% of the UV rays and a hat. Not all sunglasses have UV protection, so make sure the ones you select do, and wear them whenever outdoors. Even on a cloudy day as UV rays penetrate clouds. For maximum protection consider wrap-around glasses to protect you from direct and indirect sunlight. If you are participating in sports, goggles or glasses designed for your specific sport might be the best option. And don’t forget to wear a brimmed hat. It will not only protect you from indirect sunlight, it will also protect your face from sunburn.

Discovery Eye Foundation




 The National Eye Institute has recommended that people who are high-risk for developing AMD eat diets rich in green leafy vegetables, whole fruits, any type of nuts and omega 3 fatty acids. Many of these foods have anti-oxidant properties that help to “turn off” genes involved with inflammation, an important factor of retinal diseases. Salmon, mackerel and sardines have the highest levels of omega-3 fatty acids. An analysis that combined the data from 9 different studies showed that fish intake at least twice a week was associated with reduced risk of early and late AMD. Other studies show that Omega-3 fatty acids improve mitochondrial function, decreases production of reactive oxygen species (free radicals that damage cells) and leads to less fat accumulation in the body. The green leafy vegetables contain important protective macular pigments (carotenoids) called lutein and zeaxanthin that reduce the risk of AMD by 43%. High levels of lipid or fat deposits in the body (obesity) can “soak-up” the lutein and zeaxanthin so that they are not available to protect the retina.
The National Eye Institute has recommended that people who are high-risk for developing AMD eat diets rich in green leafy vegetables, whole fruits, any type of nuts and omega 3 fatty acids. Many of these foods have anti-oxidant properties that help to “turn off” genes involved with inflammation, an important factor of retinal diseases. Salmon, mackerel and sardines have the highest levels of omega-3 fatty acids. An analysis that combined the data from 9 different studies showed that fish intake at least twice a week was associated with reduced risk of early and late AMD. Other studies show that Omega-3 fatty acids improve mitochondrial function, decreases production of reactive oxygen species (free radicals that damage cells) and leads to less fat accumulation in the body. The green leafy vegetables contain important protective macular pigments (carotenoids) called lutein and zeaxanthin that reduce the risk of AMD by 43%. High levels of lipid or fat deposits in the body (obesity) can “soak-up” the lutein and zeaxanthin so that they are not available to protect the retina.