Vision is something we take for granted, but when we start to have trouble seeing it is easy to panic. This blog has covered a variety of eye issues for every age, from children through older adults. Here are a few articles from leading doctors and specialists that you may have missed and might be of interest.

Bill Takeshita, OD, FAAO – Visual Aids and Techniques When Traveling
Michelle Moore, CHHC – The Best Nutrition for Older Adults
Arthur B. Epstein, OD, FAAO – Understanding and Treating Corneal Scratches and Abrasions
The National Eye Health Education Program (NEHEP) – Low Vision Awareness
Maintaining Healthy Vision
Sandra Young, OD – GMO and the Nutritional Content of Food
S. Barry Eiden, OD, FAAO – Selecting Your Best Vision Correction Options
Suber S. Huang, MD, MBA – It’s All About ME – What to Know About Macular Edema
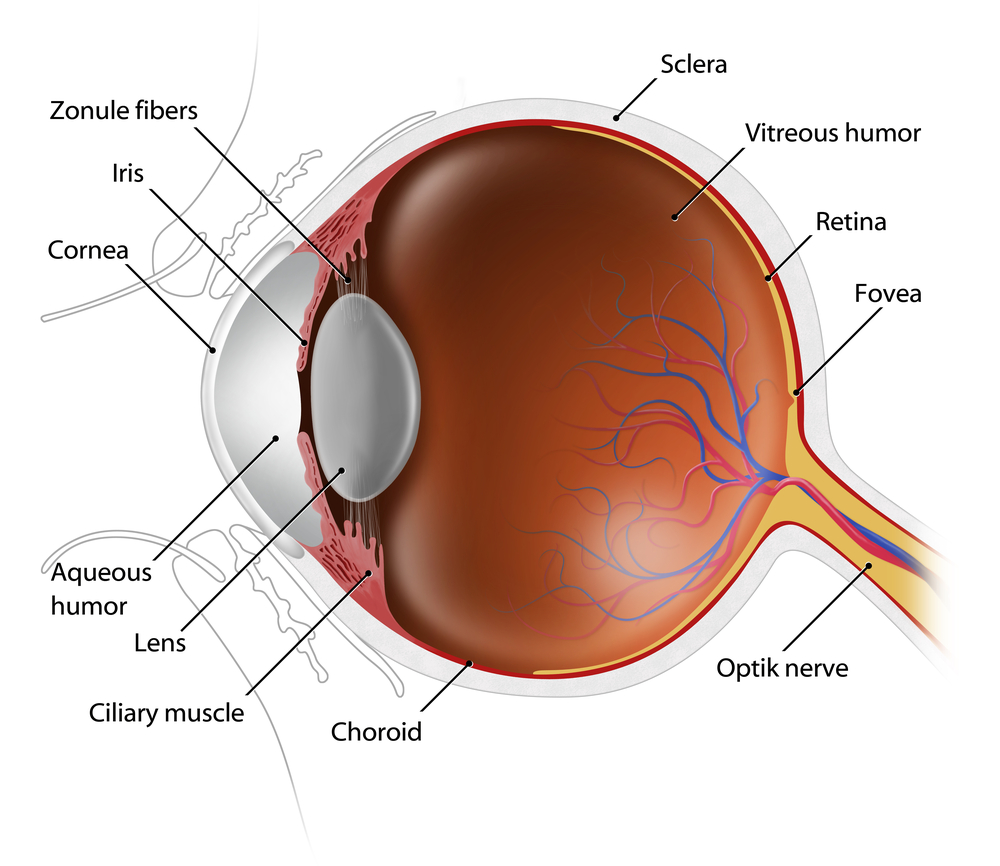
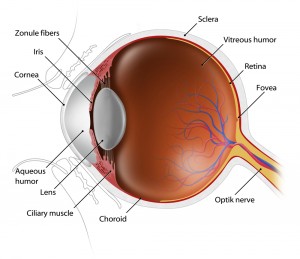
Jun Lin, MD, PhD and James Tsai, MD, MBA – The Optic Nerve And Its Visual Link To The Brain
Ronald N. Gaster, MD FACS – Do You Have a Pterygium?
Anthony B. Nesburn, MD, FACS – Three Generations of Saving Vision
Chantal Boisvert, OD, MD – Vision and Special Needs Children
Judith Delgado – Driving and Age-Related Macular Degeneration
David L. Kading OD, FAAO and Charissa Young – Itchy Eyes? It Must Be Allergy Season
Lauren Hauptman – Traveling With Low Or No Vision / Must Love Dogs, Traveling with Guide Dogs / Coping With Retinitis Pigmentosa
Kate Steit – Living Well With Low Vision Online Courses
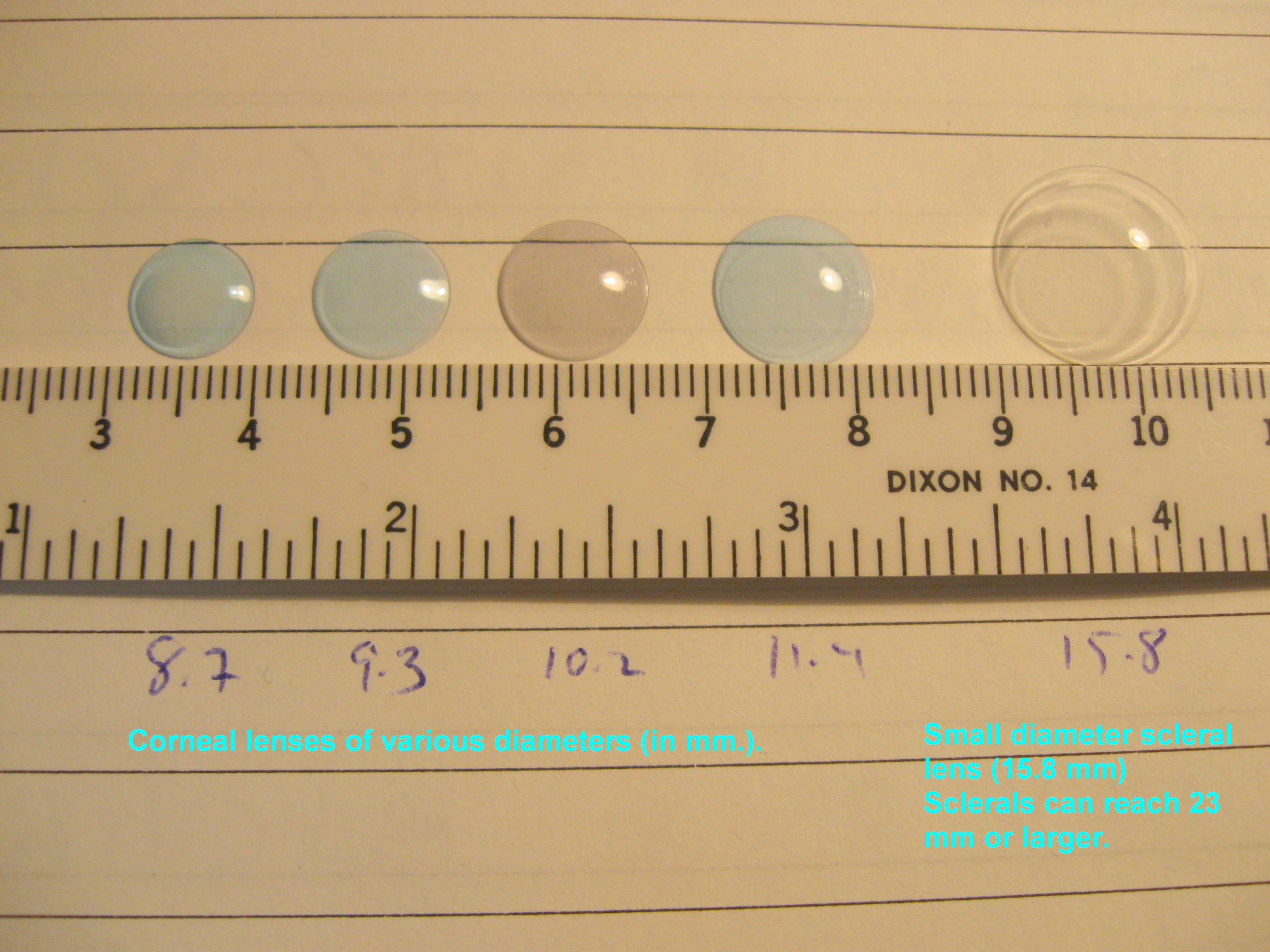
Bezalel Schendowich, OD – What Are Scleral Contact Lenses?
In addition here are few other topics you might find of interest, including some infographics and delicious recipes.
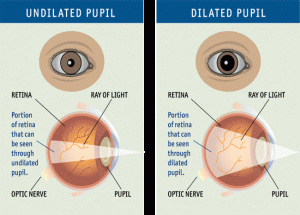
Pupils Respond to More Than Light
10 Tips for Healthy Eyes (infographic)
The Need For Medical Research Funding
Protective Eyewear for Home, Garden & Sports
7 Spring Fruits and Vegetables (with some great recipes)
6 Ways Women Can Stop Vision Loss
6 Signs of Eye Disease (infographic)
How to Help a Blind or Visually Impaired Person with Mobility
Your Comprehensive Eye Exam (infographic)
Famous People with Vision Loss – Part I
Famous People with Vision Loss – Part II
Development of Eyeglasses Timeline (infographic)
What eye topics do you want to learn about? Please let us know in the comments section below.
7/21/15
 Susan DeRemer, CFRE
Susan DeRemer, CFRE
Vice President of Development
Discovery Eye Foundation