I can only imagine my wife’s beautiful face. Oh sure, I’ve touched it and kissed it many times. I’ve felt the lines with the tips of my fingers, tracing our lives together, and I’ve heard her smile. I understand that’s not really seeing it. It’s not seeing her eyes as they sparkle with something funny I said; or, when she looks at me with love reserved only for those who are truly in love.
I can only imagine my wife’s beautiful face. Oh sure, I’ve touched it and kissed it many times. I’ve felt the lines with the tips of my fingers, tracing our lives together, and I’ve heard her smile. I understand that’s not really seeing it. It’s not seeing her eyes as they sparkle with something funny I said; or, when she looks at me with love reserved only for those who are truly in love.
She’s often tried to explain the flash and colors of a sunset and the cotton softness of clouds as they drift across the sky. And, what about a rainbow made up of all the colors that somehow promise all of us that things in the world will get better.
How amazing it would be to see my daughter Blythe skiing her favorite Colorado Mountain trail or my son Tom riding a California wave, both so secure and happy enjoying the sports they love.
There is so much more I wish I could see, but it’s not going to happen because I am blind. I am left with only imagining what it’s like to have the gift of sight.
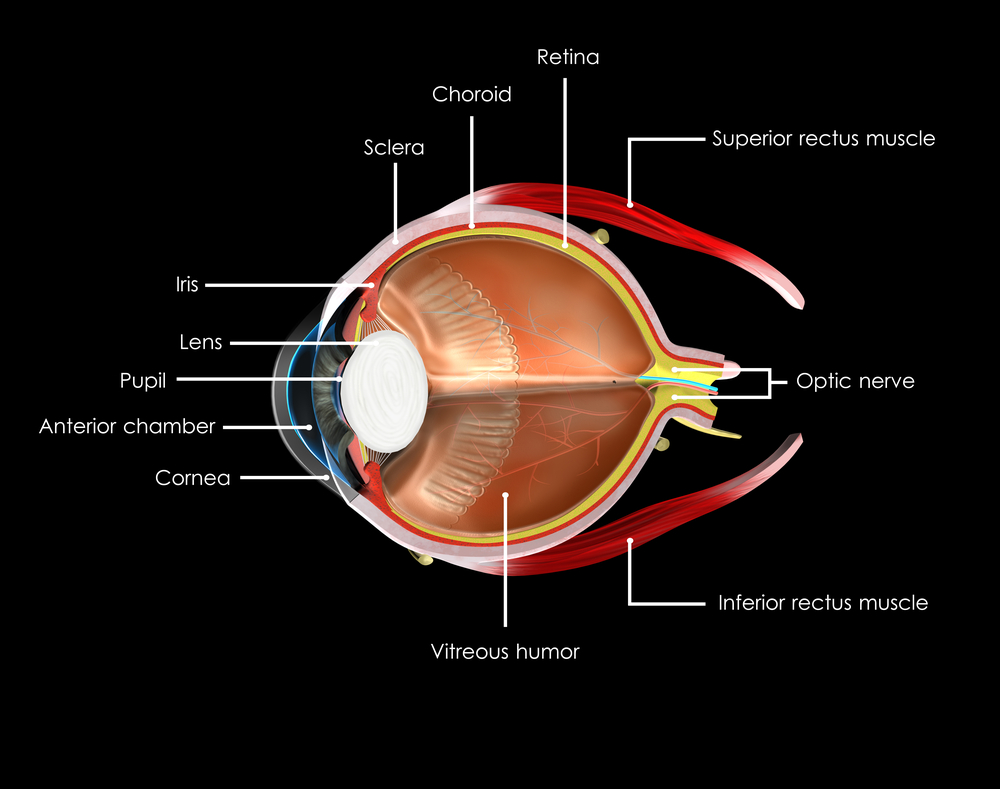
I can only empathize with how a person feels when their vision is threatened by glaucoma or diabetic retinopathy, retinitis pigmentosa, and the most devastating of all, macular degeneration.
At the Discovery Eye Foundation (DEF) our researchers are working every day to overcome the loss of vision and preserve your ability to treasure all the beauty that surrounds you. I’ve heard it said that the eyes are the windows to the soul. I don’t know if that’s true, but I am sure that they are the single most important sense in the group of five, and that saving vision is a cause that must be supported.
DEF is committed to that mission, and with your help, answers to all forms of eye disease will be discovered. It’s up to all of us to support the research that’s bringing us ever closer to those solutions.
If you want to help, please click the button below or download donation form to donate by mail, click here: DEF donation form



 Tom Sullivan
Tom Sullivan Costume Contact Lenses such as cat eyes or zombie may make your Halloween costume a bit more frightful although wearing those lenses without a prescription can be more terrifying, as it could result in vision loss or even blindness.
Costume Contact Lenses such as cat eyes or zombie may make your Halloween costume a bit more frightful although wearing those lenses without a prescription can be more terrifying, as it could result in vision loss or even blindness.

 Tom Sullivan
Tom Sullivan