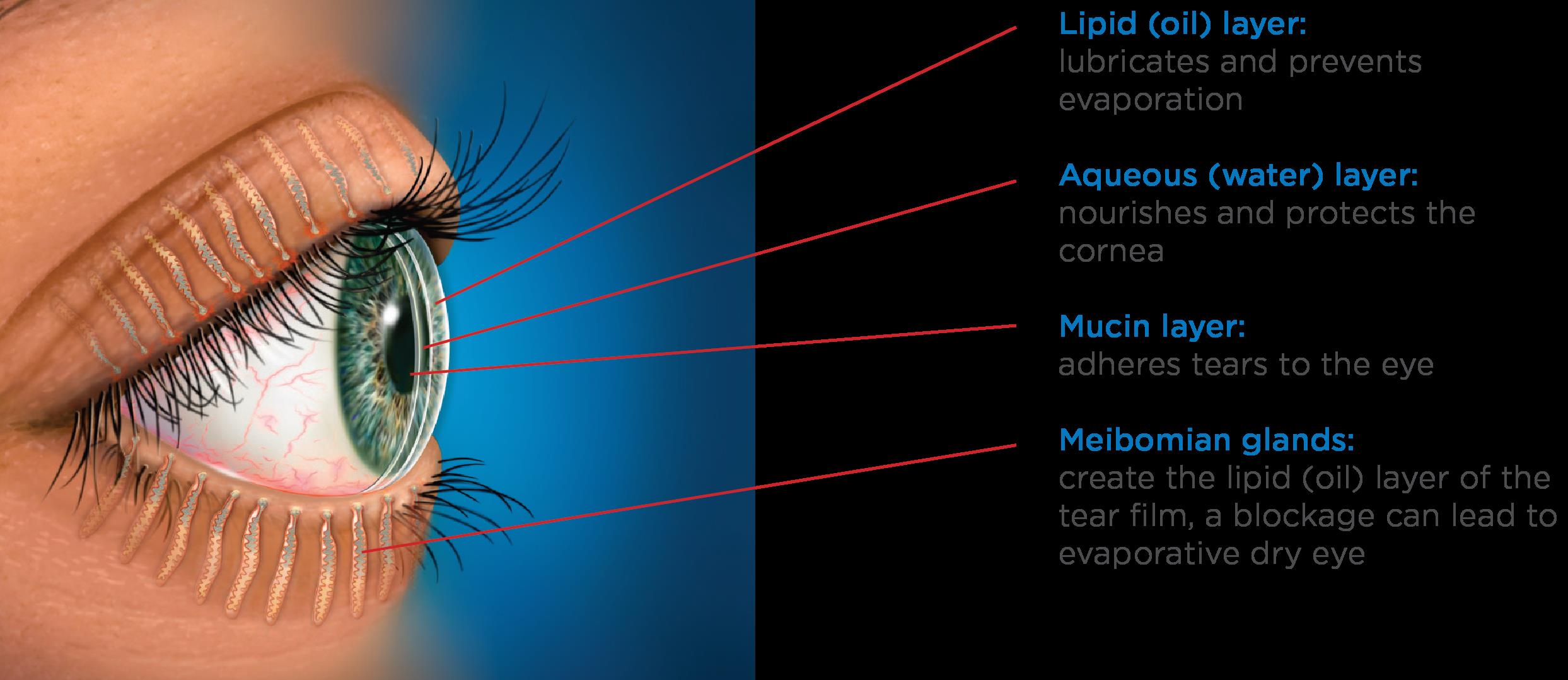
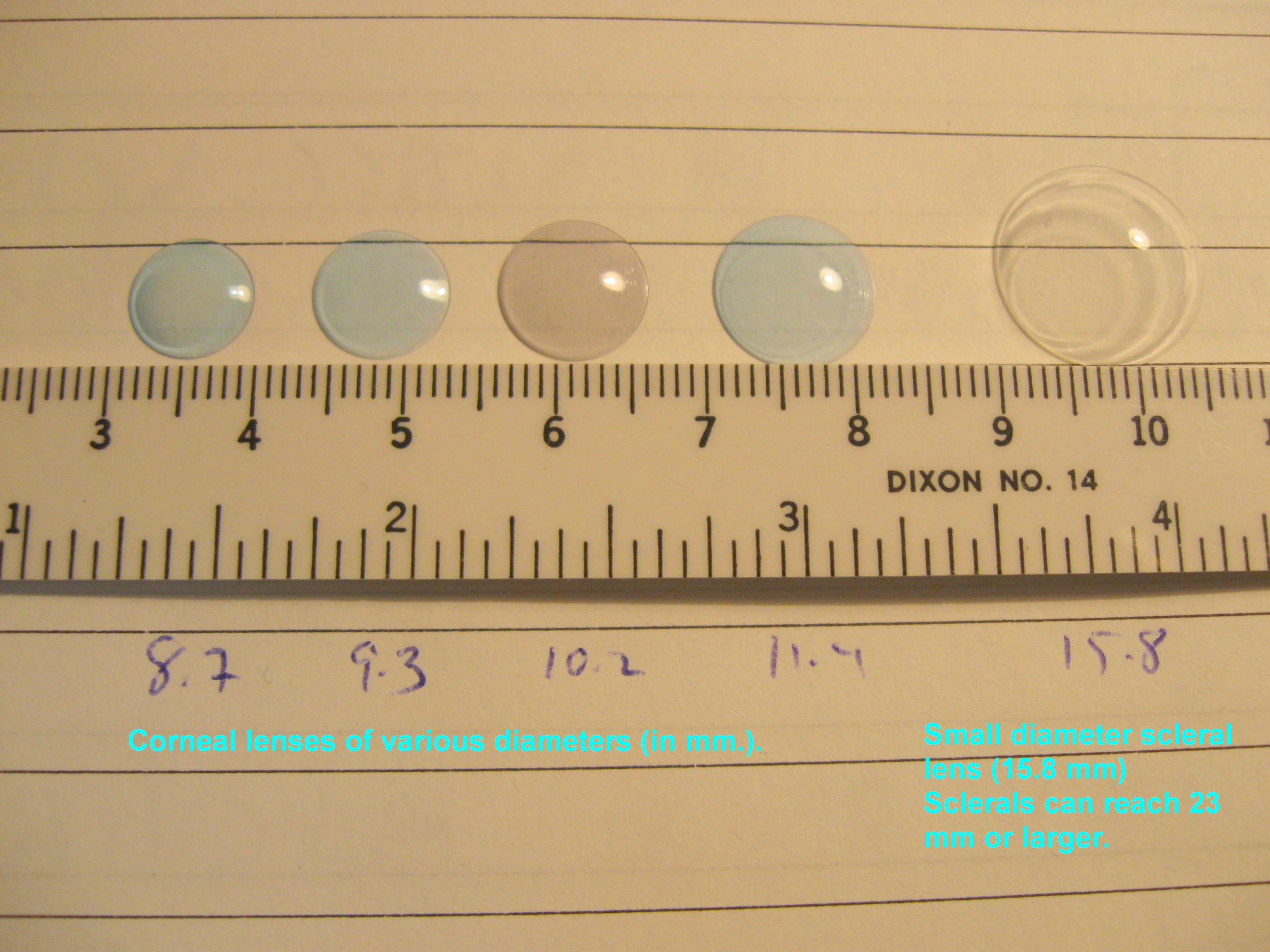
Scleral lens have become very popular and while many enjoy the comfort and vision correction they provide, some find it difficult to apply (insert) and remove these large diameter RGP lenses. If you are one of the many who are having difficulty managing to get your scleral lenses in or out, there are a number of tools available to help.
The Scleral Lens Education Society website provides a wealth of information about the care and handling of these lenses  as well as an excellent video. There are photos demonstrating various ways to hold the lens while applying it …some you may not have tried! If you have trouble with your schleral lenses, see below.
as well as an excellent video. There are photos demonstrating various ways to hold the lens while applying it …some you may not have tried! If you have trouble with your schleral lenses, see below.
Troubleshooting tips and tricks:
- If you are unable to maintain fluid in the bowl of the lens as you bring it towards your eye, make sure that your face is fully parallel to the floor. It may seem like you are nearly standing on your head when you’re in the correct position to apply the lens.
- Lid control is essential; use one hand to hold lids completely out of the way, and don’t release the lids until the lens is actually fully in place and the plunger (or your finger tripod) has been removed.
- If you are unable to successfully apply a solid lens with saline, you could practice applying the lens after filling the bowl of the lens with Celluvisc™ or another non-preserved viscous lubricant. These viscous lubricants will blur your vision compared to saline, however, so you may simply want to use them to practice lens application. Once you’ve mastered this step, switch to saline to give you better vision.
- Try to keep both eyes open as you apply your lenses. This may also help you to position the lenses correctly.
- If you are using a bulbed (DVM) plunger, and can see the opening in the center of the suction cup, look directly at the hole as you bring the lens into position. This will help you to position the lens correctly.
Many find the DVM plungers helpful. They are readily available at your doctor’s office and online. These are just a few of the places to find them: DMV Corp, Dry Eye Zone, and Amazon.
 Another variation to the standard lens inserters is a ring-style lens applicator by EZI Scleral Lens. It was designed by a post-transplant patient who like so many, had trouble inserting his scleral lens without getting a bubble. Read Tim’s story.
Another variation to the standard lens inserters is a ring-style lens applicator by EZI Scleral Lens. It was designed by a post-transplant patient who like so many, had trouble inserting his scleral lens without getting a bubble. Read Tim’s story.
If you have tried the above techniques and still have trouble applying scleral lenses there are a number of devices available that may help. Dalsey Adaptives has developed the See-Green device that can be used to help successfully apply scleral contact lenses. The See-Green system comes with a stand that holds a lighted plunger (Figure 2). Using this system, you don’t hold the lens, you lower your eye onto it, which leaves both hands free for improved lid control. The light at the center of the plunger is used as a target to help you position the lens centrally on the eye. Click here to see the detailed instruction sheet.
that can be used to help successfully apply scleral contact lenses. The See-Green system comes with a stand that holds a lighted plunger (Figure 2). Using this system, you don’t hold the lens, you lower your eye onto it, which leaves both hands free for improved lid control. The light at the center of the plunger is used as a target to help you position the lens centrally on the eye. Click here to see the detailed instruction sheet.
Scleral lenses offer good vision and comfort but can be challenging to manage. Discuss these options with your eye care professional to get his or her recommendation for your specific situation.
1/28/16
 Cathy Warren, RN
Cathy Warren, RN
Executive Director
National Keratoconus Foundation