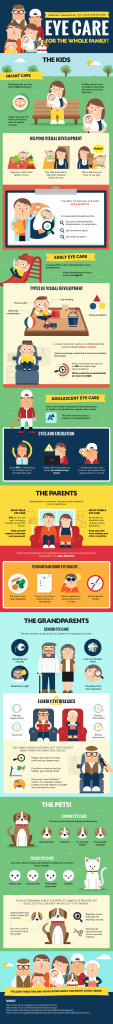
Meet Tom Sullivan – DEF’s Ambassador of Vision
Meet Tom Sullivan – DEF’s Ambassador of Vision
Over the last 40 years, I’ve been committed to working on behalf of blind children and their families. My involvement has spanned the entire gamut of participation – from direct involvement in the classroom and counseling parents to hosting organized 10K races and celebrity golf tournaments that carried my name. In that time, my wife and I raised just over $8 million thanks to the generosity of so many people. Though my commitment to this cause has not changed, I’ve chosen to take on a new challenge that has in every way re-energized my passion.
I’ve recently become the Ambassador of Vision for the Discovery Eye Foundation (DEF), a remarkable organization that funds cutting edge research that I believe someday will eliminate many forms of blindness. The principle reason for my enthusiastic commitment is largely due to the fact that DEF directly funds researchers and avoids institutional restrictions.
As of this blog, DEF is engaged in ongoing efforts to understand 5 main eye diseases – Retinitis Pigmentosa, Macular Degeneration, Keratoconus, Diabetic Retinopathy, and Glaucoma. I can honestly tell you that breakthroughs are not only on the horizon, but in many cases they are imminent. Over the weeks and months I’ll be telling you much more, specifically about our individual research projects.
Any help you may choose to give on behalf of people struggling with vision loss will be deeply appreciated. I look forward to having many of you join my fight for sight. Your help can make a difference! Click here to donate.
 Tom Sullivan
Tom Sullivan
DEF’s Ambassador of Vision
sullivanvision.com








 The Difference Between an
The Difference Between an 
 Be sure to start your holiday meal with a salad, it’s an excellent way to ensure that you and your guests get plenty of zeaxanthin and lutein, two nutrients that help protect your central vision. Adding kale, spinach, or romaine lettuce to salads helps your eyes absorb damaging blue light, combats the effects of cigarette smoke and pollution, and also decreases your risk of developing
Be sure to start your holiday meal with a salad, it’s an excellent way to ensure that you and your guests get plenty of zeaxanthin and lutein, two nutrients that help protect your central vision. Adding kale, spinach, or romaine lettuce to salads helps your eyes absorb damaging blue light, combats the effects of cigarette smoke and pollution, and also decreases your risk of developing  Turkey and lean beef, two of the main ingredients in many holiday meals, keep your eyes strong and healthy. Both foods are high in zinc, a nutrient important to the retina and the choroid layer under the retina.
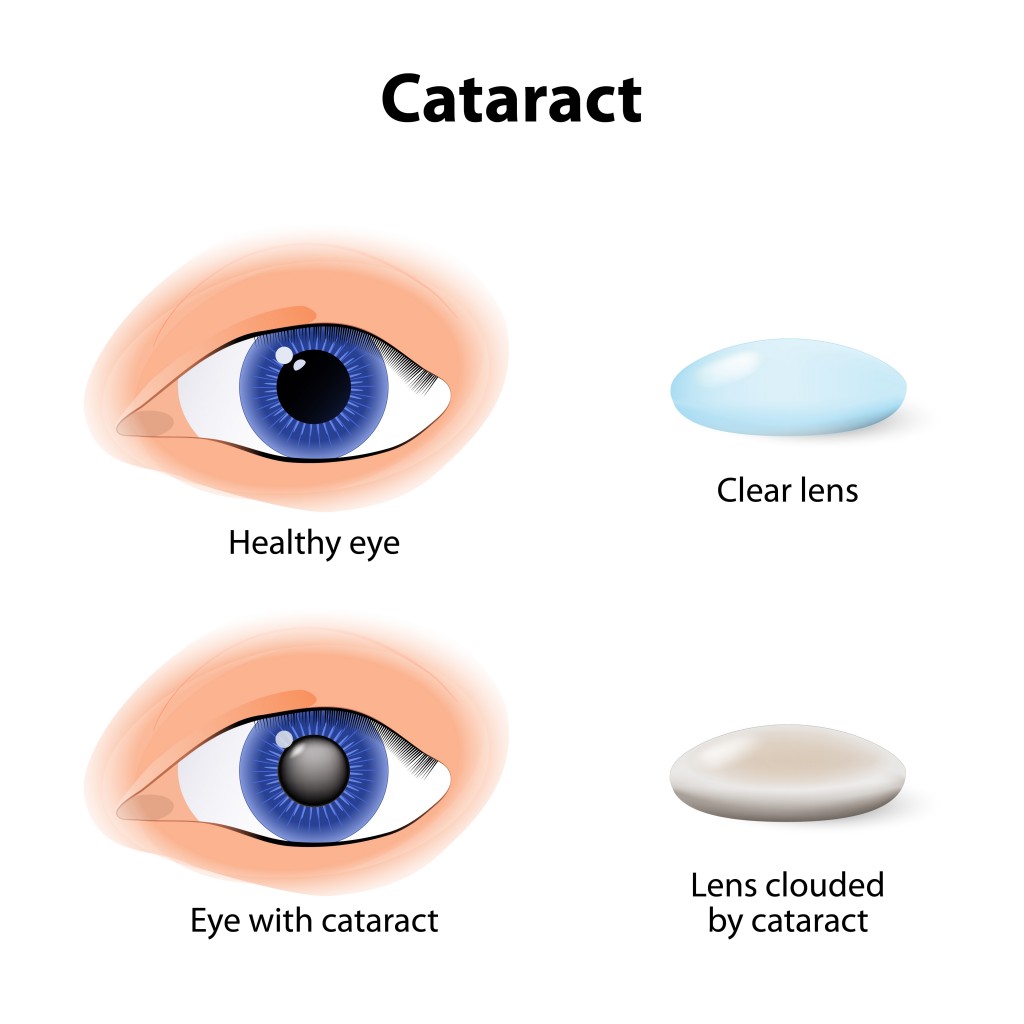
Turkey and lean beef, two of the main ingredients in many holiday meals, keep your eyes strong and healthy. Both foods are high in zinc, a nutrient important to the retina and the choroid layer under the retina.  Zinc is essential for good night vision. Eating foods that are high in the nutrient can also reduce your risk of cataracts and AMD. Other foods that contain zinc include pork, dairy products, chick peas, black-eyed peas, crab, oysters, beans, spinach, mushrooms, cashews, and almonds.
Zinc is essential for good night vision. Eating foods that are high in the nutrient can also reduce your risk of cataracts and AMD. Other foods that contain zinc include pork, dairy products, chick peas, black-eyed peas, crab, oysters, beans, spinach, mushrooms, cashews, and almonds.  It wasn’t an old wives tale, it is true Carrots are good for your eyes! They contain beta carotene, a substance that turns into vitamin A when eaten. Eating carrots can benefit your night vision and could possibly reduce your risk of cataracts, AMD, and dry eyes. Other foods that contain beta carotene include pumpkin, sweet potatoes, and butternut squash. All great ingredients to include into your holiday feast.
It wasn’t an old wives tale, it is true Carrots are good for your eyes! They contain beta carotene, a substance that turns into vitamin A when eaten. Eating carrots can benefit your night vision and could possibly reduce your risk of cataracts, AMD, and dry eyes. Other foods that contain beta carotene include pumpkin, sweet potatoes, and butternut squash. All great ingredients to include into your holiday feast.  Fish contain omega-3 fatty acids, which can reduce your risk of developing AMD, dry eye, and glaucoma. Salmon, mackerel, flounder, tuna, halibut, herring, and sardines would be a great addition to your holiday meals.
Fish contain omega-3 fatty acids, which can reduce your risk of developing AMD, dry eye, and glaucoma. Salmon, mackerel, flounder, tuna, halibut, herring, and sardines would be a great addition to your holiday meals. Whole grains reduce your risk of heart disease, obesity, and type 2 diabetes and can also decrease your risk of AMD. Substituting whole grain flour for white flour in holiday breads and muffins is a simple way to boost your whole grain intake. Other good whole grain sources include wild rice, brown rice, popcorn, oatmeal, bulgur, barley, buckwheat, and couscous.
Whole grains reduce your risk of heart disease, obesity, and type 2 diabetes and can also decrease your risk of AMD. Substituting whole grain flour for white flour in holiday breads and muffins is a simple way to boost your whole grain intake. Other good whole grain sources include wild rice, brown rice, popcorn, oatmeal, bulgur, barley, buckwheat, and couscous.  Fruits high in vitamin C, such as strawberries and oranges, also offer important vision benefits. Vitamin C is an antioxidant, a substance that can prevent cell damage caused by free radicals. Vitamin C-rich foods help keep the collagen in your cornea healthy and reduce the risk of cataracts and AMD. You can also find vitamin C in grapefruit, kiwi, blueberries, peas, broccoli, and tomatoes.
Fruits high in vitamin C, such as strawberries and oranges, also offer important vision benefits. Vitamin C is an antioxidant, a substance that can prevent cell damage caused by free radicals. Vitamin C-rich foods help keep the collagen in your cornea healthy and reduce the risk of cataracts and AMD. You can also find vitamin C in grapefruit, kiwi, blueberries, peas, broccoli, and tomatoes.