Sharing meals with family and friends is one of the major highlights of the holiday season. Whether you treat yourself to old recipes or you try new ones, consider adding these eye-healthy foods to your holiday feast!
LEAFY GREEN VEGETABLES
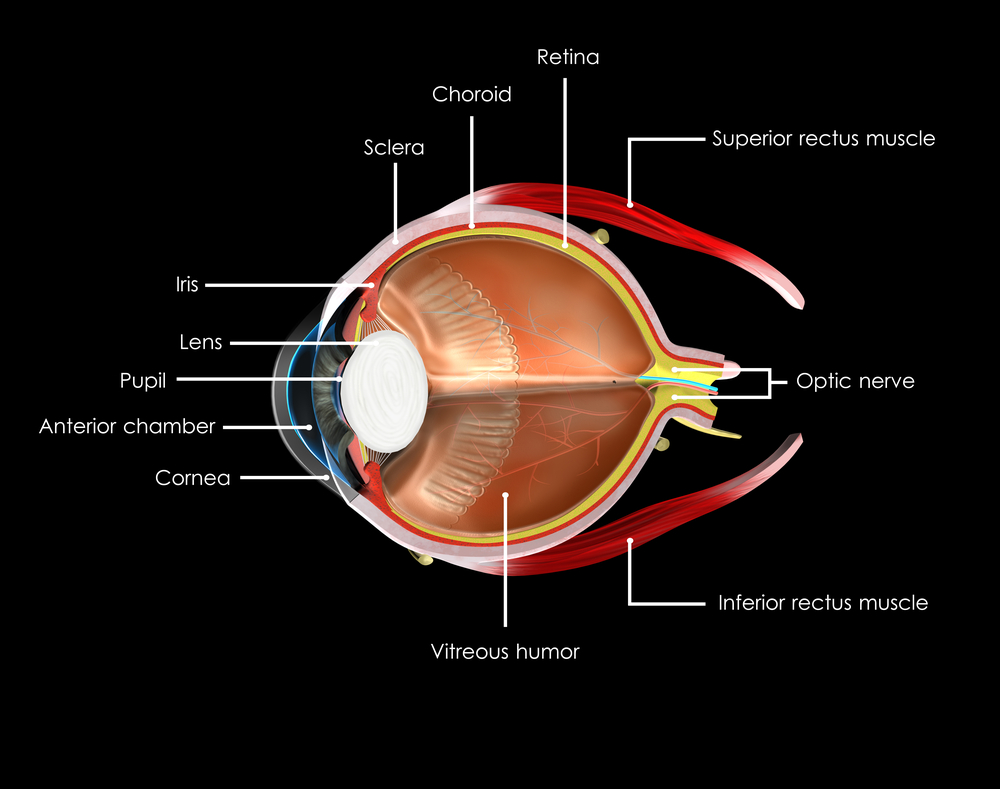
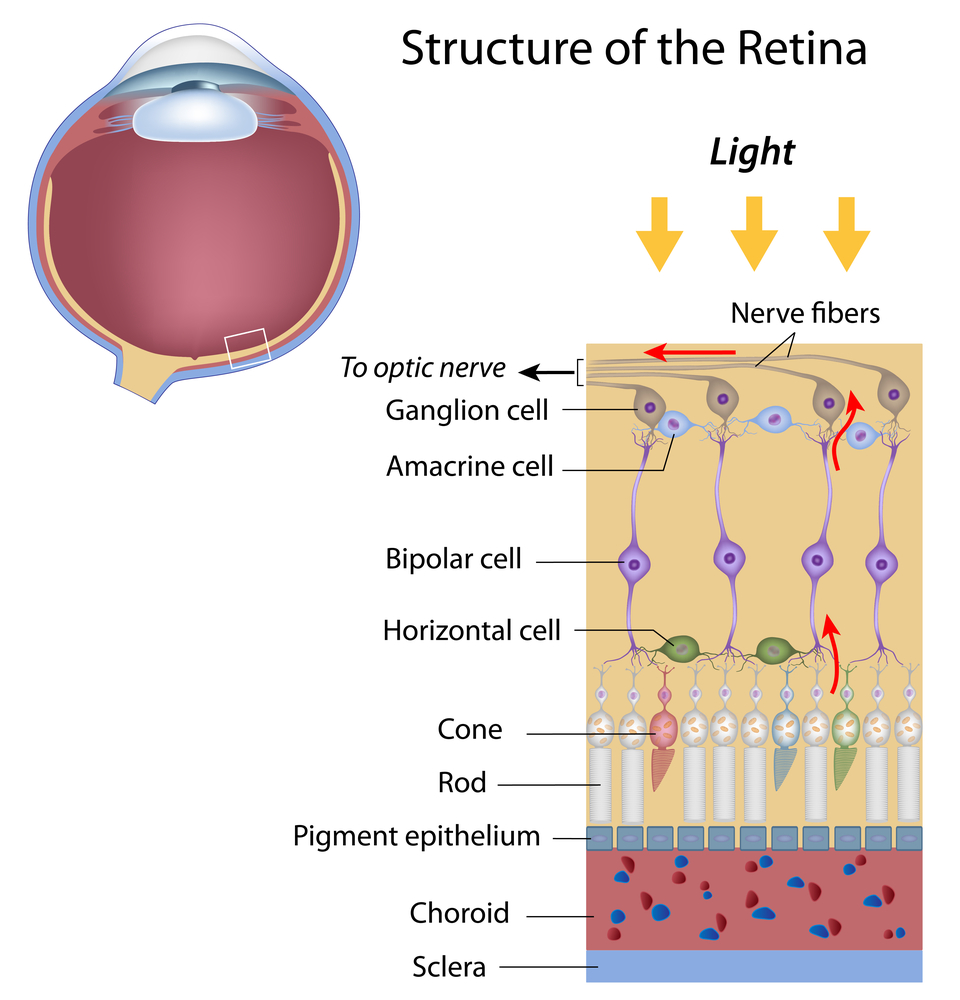
 Be sure to start your holiday meal with a salad, it’s an excellent way to ensure that you and your guests get plenty of zeaxanthin and lutein, two nutrients that help protect your central vision. Adding kale, spinach, or romaine lettuce to salads helps your eyes absorb damaging blue light, combats the effects of cigarette smoke and pollution, and also decreases your risk of developing age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a condition that affects the macula, the part of your retina responsible for central vision. You will also find lutein in grapes, kiwis, broccoli, peas, corn, Swiss chard, and collard greens.
Be sure to start your holiday meal with a salad, it’s an excellent way to ensure that you and your guests get plenty of zeaxanthin and lutein, two nutrients that help protect your central vision. Adding kale, spinach, or romaine lettuce to salads helps your eyes absorb damaging blue light, combats the effects of cigarette smoke and pollution, and also decreases your risk of developing age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a condition that affects the macula, the part of your retina responsible for central vision. You will also find lutein in grapes, kiwis, broccoli, peas, corn, Swiss chard, and collard greens.
TURKEY AND BEEF
 Turkey and lean beef, two of the main ingredients in many holiday meals, keep your eyes strong and healthy. Both foods are high in zinc, a nutrient important to the retina and the choroid layer under the retina.
Turkey and lean beef, two of the main ingredients in many holiday meals, keep your eyes strong and healthy. Both foods are high in zinc, a nutrient important to the retina and the choroid layer under the retina.  Zinc is essential for good night vision. Eating foods that are high in the nutrient can also reduce your risk of cataracts and AMD. Other foods that contain zinc include pork, dairy products, chick peas, black-eyed peas, crab, oysters, beans, spinach, mushrooms, cashews, and almonds.
Zinc is essential for good night vision. Eating foods that are high in the nutrient can also reduce your risk of cataracts and AMD. Other foods that contain zinc include pork, dairy products, chick peas, black-eyed peas, crab, oysters, beans, spinach, mushrooms, cashews, and almonds.
CARROTS
 It wasn’t an old wives tale, it is true Carrots are good for your eyes! They contain beta carotene, a substance that turns into vitamin A when eaten. Eating carrots can benefit your night vision and could possibly reduce your risk of cataracts, AMD, and dry eyes. Other foods that contain beta carotene include pumpkin, sweet potatoes, and butternut squash. All great ingredients to include into your holiday feast.
It wasn’t an old wives tale, it is true Carrots are good for your eyes! They contain beta carotene, a substance that turns into vitamin A when eaten. Eating carrots can benefit your night vision and could possibly reduce your risk of cataracts, AMD, and dry eyes. Other foods that contain beta carotene include pumpkin, sweet potatoes, and butternut squash. All great ingredients to include into your holiday feast.
FISH
 Fish contain omega-3 fatty acids, which can reduce your risk of developing AMD, dry eye, and glaucoma. Salmon, mackerel, flounder, tuna, halibut, herring, and sardines would be a great addition to your holiday meals.
Fish contain omega-3 fatty acids, which can reduce your risk of developing AMD, dry eye, and glaucoma. Salmon, mackerel, flounder, tuna, halibut, herring, and sardines would be a great addition to your holiday meals.
WHOLE GRAINS
 Whole grains reduce your risk of heart disease, obesity, and type 2 diabetes and can also decrease your risk of AMD. Substituting whole grain flour for white flour in holiday breads and muffins is a simple way to boost your whole grain intake. Other good whole grain sources include wild rice, brown rice, popcorn, oatmeal, bulgur, barley, buckwheat, and couscous.
Whole grains reduce your risk of heart disease, obesity, and type 2 diabetes and can also decrease your risk of AMD. Substituting whole grain flour for white flour in holiday breads and muffins is a simple way to boost your whole grain intake. Other good whole grain sources include wild rice, brown rice, popcorn, oatmeal, bulgur, barley, buckwheat, and couscous.
FRUIT
 Fruits high in vitamin C, such as strawberries and oranges, also offer important vision benefits. Vitamin C is an antioxidant, a substance that can prevent cell damage caused by free radicals. Vitamin C-rich foods help keep the collagen in your cornea healthy and reduce the risk of cataracts and AMD. You can also find vitamin C in grapefruit, kiwi, blueberries, peas, broccoli, and tomatoes.
Fruits high in vitamin C, such as strawberries and oranges, also offer important vision benefits. Vitamin C is an antioxidant, a substance that can prevent cell damage caused by free radicals. Vitamin C-rich foods help keep the collagen in your cornea healthy and reduce the risk of cataracts and AMD. You can also find vitamin C in grapefruit, kiwi, blueberries, peas, broccoli, and tomatoes.
Sensible food choices, along with regular eye examinations, can help you protect your vision. For eye healthy recipes, visit our EYE COOK section in our website.
Happy Eating and Happy Holidays!


 Many of us just use the basics on our smart phone and never personalize them for our own needs. It is worth taking the time to adjust our phones to take advantage of the special services that may be available and unused. Making a phone call or sending a text message with a smart phone can be challenging, however, with simple modifications, keeping in touch with the world can become a snap. Getting comfortable with your smart phone will make staying in touch with your loved ones very easy.
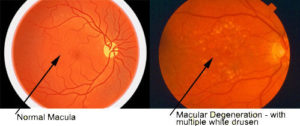
Many of us just use the basics on our smart phone and never personalize them for our own needs. It is worth taking the time to adjust our phones to take advantage of the special services that may be available and unused. Making a phone call or sending a text message with a smart phone can be challenging, however, with simple modifications, keeping in touch with the world can become a snap. Getting comfortable with your smart phone will make staying in touch with your loved ones very easy. In a presentation to the American Society of Retina Specialists, Dr. Ajay E. Kuriyan of the University of Rochester reported that three patients who underwent bilateral intravitreal injection of stem-cells for age-related macular degeneration (AMD) suffered bilateral vision loss. The clinic at which all three procedures were performed did not have a licensed ophthalmologist on-site, and the stem-cell injections were administered by a nurse practitioner, Ocular Surgery News reported. Each patient paid $5,000 for the procedure.
In a presentation to the American Society of Retina Specialists, Dr. Ajay E. Kuriyan of the University of Rochester reported that three patients who underwent bilateral intravitreal injection of stem-cells for age-related macular degeneration (AMD) suffered bilateral vision loss. The clinic at which all three procedures were performed did not have a licensed ophthalmologist on-site, and the stem-cell injections were administered by a nurse practitioner, Ocular Surgery News reported. Each patient paid $5,000 for the procedure.
 The National Eye Institute has recommended that people who are high-risk for developing AMD eat diets rich in green leafy vegetables, whole fruits, any type of nuts and omega 3 fatty acids. Many of these foods have anti-oxidant properties that help to “turn off” genes involved with inflammation, an important factor of retinal diseases. Salmon, mackerel and sardines have the highest levels of omega-3 fatty acids. An analysis that combined the data from 9 different studies showed that fish intake at least twice a week was associated with reduced risk of early and late AMD. Other studies show that Omega-3 fatty acids improve mitochondrial function, decreases production of reactive oxygen species (free radicals that damage cells) and leads to less fat accumulation in the body. The green leafy vegetables contain important protective macular pigments (carotenoids) called lutein and zeaxanthin that reduce the risk of AMD by 43%. High levels of lipid or fat deposits in the body (obesity) can “soak-up” the lutein and zeaxanthin so that they are not available to protect the retina.
The National Eye Institute has recommended that people who are high-risk for developing AMD eat diets rich in green leafy vegetables, whole fruits, any type of nuts and omega 3 fatty acids. Many of these foods have anti-oxidant properties that help to “turn off” genes involved with inflammation, an important factor of retinal diseases. Salmon, mackerel and sardines have the highest levels of omega-3 fatty acids. An analysis that combined the data from 9 different studies showed that fish intake at least twice a week was associated with reduced risk of early and late AMD. Other studies show that Omega-3 fatty acids improve mitochondrial function, decreases production of reactive oxygen species (free radicals that damage cells) and leads to less fat accumulation in the body. The green leafy vegetables contain important protective macular pigments (carotenoids) called lutein and zeaxanthin that reduce the risk of AMD by 43%. High levels of lipid or fat deposits in the body (obesity) can “soak-up” the lutein and zeaxanthin so that they are not available to protect the retina.