Tribulations, Travels and Tennis Balls
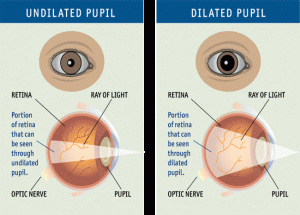
Linda Becker stopped playing tennis at night because she couldn’t see the balls coming at her. “Coincidentally, I saw something about night blindness on TV, so I went to my optometrist,” Becker says. He confirmed she had night blindness and sent her for more testing. An ophthalmologist told her: “I’m sorry, but you have retinis pigmentosa, and you’ll be blind some day.”

“As a young mother, I couldn’t wrap my head around that,” Becker says. So she entered a decade of denial until she started to sideswipe other cars while driving. “I drove into my development one day, and there was a thump over the hood of my car. I thought, ‘Oh my god, what did I do? Did I kill somebody?’ I pulled over, and a police officer who happened to be driving behind me came over to my window. I was devastated. I said, ‘What have I done?’ He told me a jogger who wasn’t paying attention had tripped over the hood of my car. But I knew if I could have seen better, I would have stopped. That was the day I put my car keys down.”
Coping with Retinitis Pigmentosa
Encouraged by her kids to get a guide dog, Becker called Guide Dogs for the Blind (GDB). She learned she needed orientation and mobility (O&M) skills, including knowing how to walk with a white cane, before she could be considered for a dog.
“I called the Braille Institute, and it was daunting, to say the least: Thinking about walking with a white cane, having people know I’m blind and feeling disabled. Going through that whole transition — I didn’t want to even face it,” she recalls. “But I went, and I took classes, until I knew it was time for me to have a guide dog. I’ve always been a dog person, and I’d rather use my dog as a mobility tool than a cane. Plus, I wanted the companionship.”
She successfully completed the GDB requirement of walking one mile to and from her home with the cane. She then completed two weeks of on-site training at GDB’s campus in Oregon, where she was paired with Lyla, a yellow English Lab.
Becker started teaching classes at the Braille Institute and helping others navigate their vision-loss transition. She teaches a 14-week sensory-awareness class. “It helps develop and educate your other senses when you start losing your sight,” she says. “It humbles me. I have no sight now. My transition of going to the Braille Institute, learning to use a white cane, then learning to have a guide dog, taught me a whole lot about myself and feeling very independent. I was able to speak about guide dogs and speak about blindness — and be a teacher.”
She became an outreach ambassador for the Braille Institute, facilitating low-vision support groups throughout Orange County, Calif. She also went to work for GDB as an alumni-outreach representative, putting together workshops and helping people learn about the “guide-dog lifestyle.”
Now 66 years old, Becker finds the most enjoyment in traveling. “Being with a guide dog and in the blindness community took me places,” she says. “I was asked to be a keynote speaker here or an ambassador there. I’d never done that type of thing before, and I’d never traveled much. I just kept hopping on airplanes with my guide dog and going to hotels and trying to figure things out. I ask questions and collect tips, so I can share with others how easy it can be to travel with or without usable sight. It is really exciting, and I’m really driven to go different places.”
Since Lyla’s retirement, Becker travels regularly with her guide dog, Anchorage, a yellow lab. “He gives me courage,” she says. The pair is currently planning a trip to Australia and New Zealand. Becker is no longer daunted by learning new skills, exploring new places or even flying tennis balls — Anchorage is quite happy to deal with those when he is off-duty.
For more on traveling with guide dogs, including Becker’s adventures with Lyla and Anchorage, read “Traveling Tails”.
5/26/15
 Lauren Hauptman
Lauren Hauptman
Lauren Hauptman INK