The introduction of the excimer laser to eye surgery in the early 1990’s represented a revolutionary innovation in the treatment of refractive errors: nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism. The development of this technology allows the safe and dependable correction of vision in many patients. For the most part, however, keratoconus (KC) patients are not candidates for such procedures for 2 reasons. First, the inherent biomechanical weakness of the keratoconic cornea could worsen if tissue is removed from the already thin cornea. Second, in addition to standard nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism, keratoconic vision is also impeded by higher order aberrations, which can be thought of as static in the eye’s optical system. However, recent advances may make variations of such procedures applicable to selected patients with KC.

LASIK, LASEK, PRK and PTK
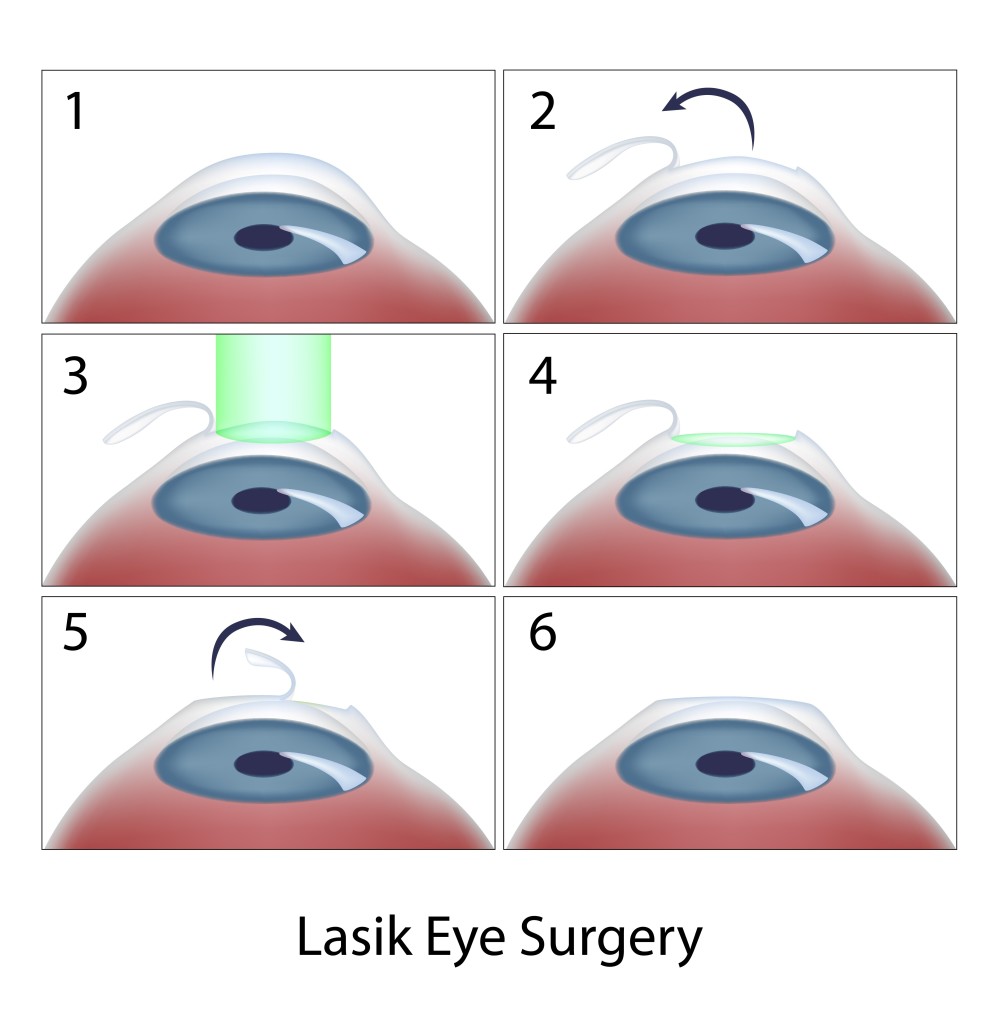
Today, laser in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) is the most popular method of laser eye surgery. LASIK uses an excimer laser to correct nearsightedness, farsightedness, or astigmatism by removing a thin lenslet of tissue from the surface of the cornea (the clear, front “watch crystal” of the eye). This is analogous to removal of a “tissue contact lens”. In LASIK, which is now an “all-laser” technique, a pancake-like thin flap of the cornea is first prepared with a high speed femtosecond laser. The flap acts to preserve the surface epithelial cells (which are like tiles on a floor) to promote quick healing and recovery of vision. Next, the excimer laser is used to remove a small amount of tissue from the corneal surface beneath the flap. The excimer laser used in LASIK produces a beam of invisible ultraviolet light energy, which when applied via an eye tracking mechanism, results in meticulous removal of this “tissue contact lens”. After corneal reshaping, the LASIK procedure is finished when the corneal flap is repositioned. When the flap is replaced, it lies in the bed of excimer laser removed tissue, causing the surface to change shape with the effect of decreasing nearsightedness, farsightedness, or astigmatism.
Laser vision correction can also be performed without a LASIK flap. These procedures, which are also perfomed with the excimer laser, go by a number of names – PRK (photorefractive keratectomy), LASEK (laser epithelial keratomileusis), epi-LASIK, or ASA (Advanced Surface Ablation). Although LASEK and LASIK sound the same, unlike traditional LASIK, LASEK does not require the preparation of a corneal flap. This has two potential advantages. First, risks of making the corneal flap in LASIK are avoided. This may be important in some patients in whom there is an additional risk in making the flap, such as patients with corneal scars or irregularities. Second, since laser treatment is done on the surface, LASEK/PRK preserves more corneal tissue. In particular, patients who have thinner corneas may be more safely treated with a no flap technique rather than LASIK.
At the beginning of the LASEK / PRK eye surgery procedure, the surface cells of the cornea are loosened and removed. The laser treatment then is applied, just as in LASIK, removing the properly shaped “tissue contact lens” for the desired optical correction. At the end of the procedure, a contact lens bandage is applied. Topical drops are used for a few week afterwards to avoid infection and control wound healing.
Vision after LASEK/PRK takes a little while longer to completely improve and stabilize than after LASIK because the epithelium needs to grow and smooth. Substantial improvement usually is noticed the day after the procedure and fluctuates over the next 2 weeks. The contact lens is removed in 5 days in most patients. Driving vision in the days after the procedure can be variable and take up to 2 weeks in some patients.
For both LASIK and LASEK/PRK, there are two basic types of possible side effects. Because patients may respond and heal differently, it is possible that the entire refractive error may not be fully corrected. In this case, vision will be clearer without glasses, but may not be as good as desired. In these situations, patient often can undergo a re-treatment procedure to further improve their vision. In addition, optical side effects include halos around lights and glare, especially at night, and some patients may experience dry eye sensations. Other, more rare, complications include infection or scarring.
Recently, there has been much talk in the keratoconus community about combining corneal collagen crosslinking with topography-guided LASEK/PRK. Topography-guided PRK uses information gained from your corneal map to program the laser to help make your cornea more optically regular. The goal of topography-guided PRK, like Intacs, is to improve corneal contour in the KC patient to improve glasses corrected vision and contact lens tolerance. In general, you will still need contacts and glasses afterwards.
Typically, LASEK/PRK procedures for keratoconus are combined with corneal collagen crosslinking, which has the goal to strengthen the weak keratoconic cornea and decrease progression of corneal mishapening over time. It is important to note that such treatments are not FDA-approved and are not generally available in the U.S. However, a number of international surgeons have been exploring the potential role of combined LASEK/PRK with crosslinking to improve keratoconus outcomes. In our practice, we have also had the opportunity to use Intacs and other procedures to further improve corneal shape in patients who have undergone topography-guided treatments with crosslinking with encouraging results.
In addition to LASIK and LASEK/PRK, the excimer laser may provide a novel therapeutic modality in the treatment of a number of superficial corneal disorders. This treatment is known a phototherapeutic keratectomy or PTK. Whether PTK eye surgery is used alone or as an adjunctive strategy in traditional corneal surgical techniques, a number of disorders affecting the corneal surface may be successfully treated by taking advantage of the excimer laser’s ability to meticulously remove superficial corneal tissue. These include a variety of corneal degenerations and dystrophies, corneal irregularities, and superficial scars, such as surface nodules found at the apex of the keratoconic cone. While some of these conditions, heretofore, could be treated by mechanical superficial keratectomy techniques, PTK may minimize tissue removal and surgical trauma.
So, for patients with keratoconus, it is important to know that, although LASIK type procedures are generally not indicated, research using these advanced technologies continues. A tailored therapeutic approach over time may combine a variety of procedures to optimize the corneal shape and ultimate visual outcome for the patient with keratoconus.
9/15/15
 Peter S. Hersh, MD
Peter S. Hersh, MD
Cornea and Laser Eye Institute – Hersh Vision Group
CLEI Center for Keratoconus