One of the most common identifying factors of a person is their eye color. Here is what you should know about eye color.
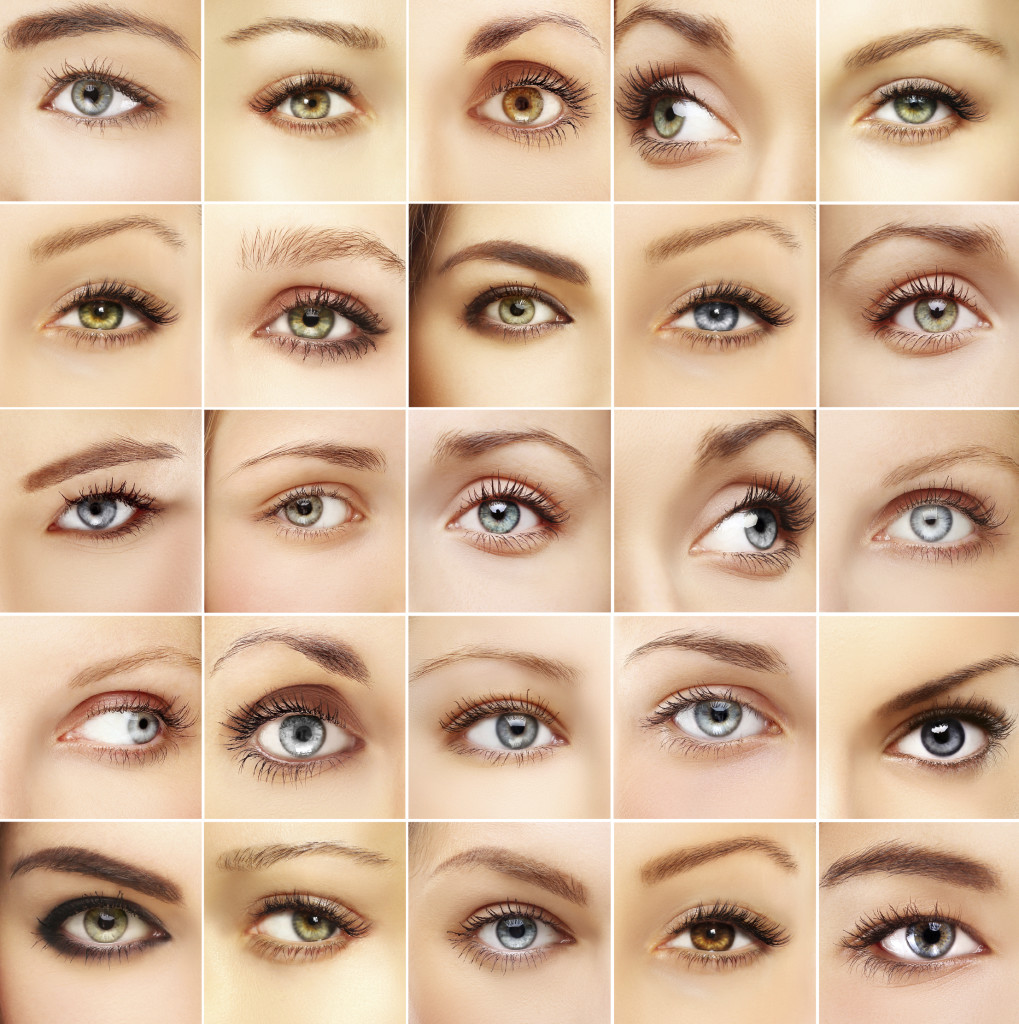

We all know that eye color is genetic, depending on the genes we inherit from our parents. We used to think that brown eyes were “dominant” and blue eyes were “recessive,” but modern science has shown that eye color is not at all that simple. Human eye color originates with three genes, but there may be as many as 50 genes that have influence over eye color. Most people in the world have brown eyes, with the second most common colors being blue and grey. Green is the rarest color.
What gives you your eye color?
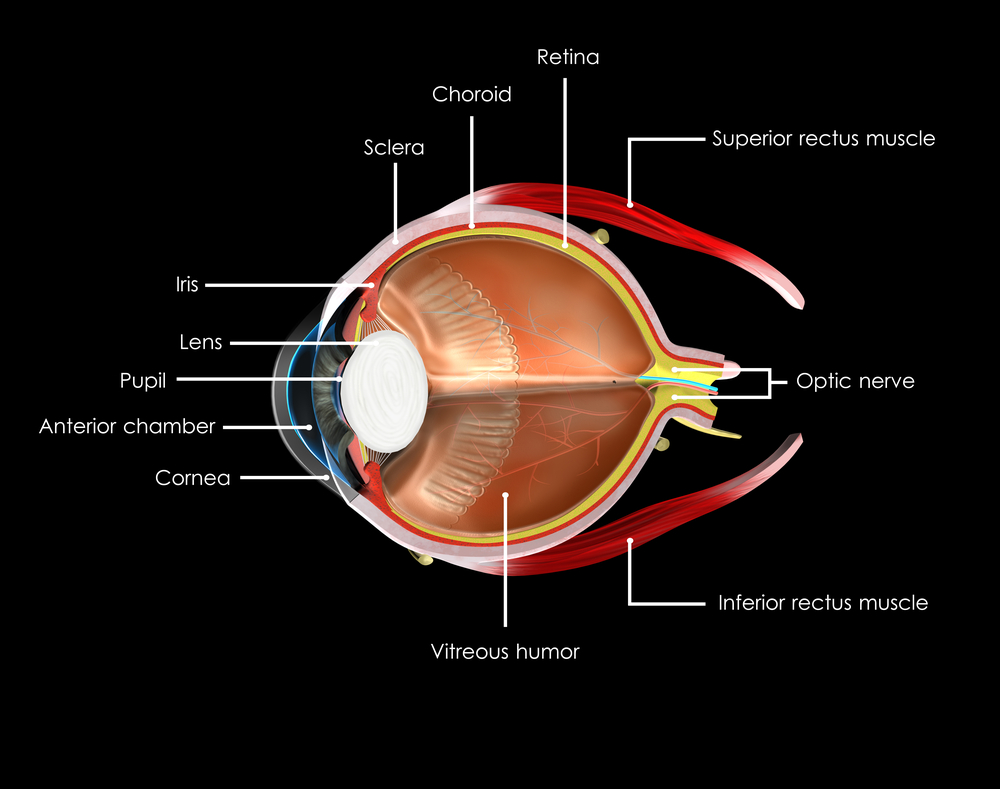
The color of your eyes depends on how much of the pigment melanin you have in your iris. The more pigment you have, the darker your eyes will be. Blue, grey, and green eyes are lighter because there is less melanin in the iris. Most Caucasian babies are born with blue eyes because melanin is not present at birth, but develops with age. However, by the age of three their eye color is determined.
A contributing factor is also your stroma, the front layer of the iris that contains fibers that scatter the light that is reflected outward. This helps to account for why you your eyes might appear to change color or intensify depending on what color you are wearing, amplifying the scattered light reflecting back.
Some children are born with eyes that are not the same color. This can be caused by faulty developmental pigment transport, trauma either in the womb or shortly after birth or a benign genetic disorder. However, because there could be a small chance of it indicating eye disease, such as Horner’s syndrome, it is suggested you have an early eye exam to make sure nothing serious is going on.
Can your eyes change color?
Contrary to popular opinion, your eyes do not change color based on your emotions. The iris is a muscle that expands and contracts to control the size of your pupil. It gets bigger in dim lighting and gets smaller in bright lighting. It also shrinks when you are focusing on close tasks, such as reading a book. Certain emotions can also change the pupil size, such as anger, grief or happiness. This can cause the pigments in the iris compress or spread apart, slightly changing the appearance of your eye color. Also because the pupil is black, your eyes appear darker. There are times when your eye color might darken slightly, such as puberty, pregnancy, and aging for 10%-15% of Caucasians with light-colored eyes.
What else does melanin do?
Besides giving our eyes color, melanin helps to protect them from the sun. Because they have less pigment, light eyes are much more sensitive to harmful UV rays from the sun and electronic devices than brown or black eyes. This makes UV protection even more important for babies and people with light-colored eyes.
Finally, because some people believe that the eyes are the windows to the soul, there are some superstitions about eye color. People with blue eyes are thought to have rich imaginations, people with green eyes have sharp minds, hazel eyes indicate a passionate soul and people with brown eyes are calm, but have underlying passion. What does your eye color say about you?
3/17/16
 Susan DeRemer, CFRE
Susan DeRemer, CFRE
Vice President of Development
Discovery Eye Foundation