 Low vision is the term used to describe significant visual impairment that can’t be corrected fully with glasses, contact lenses, medication or eye surgery. Low vision causes a person to be unable to accomplish some daily tasks due to sight impairments. Low vision occurs when an individual struggles with any of the following common activities:
Low vision is the term used to describe significant visual impairment that can’t be corrected fully with glasses, contact lenses, medication or eye surgery. Low vision causes a person to be unable to accomplish some daily tasks due to sight impairments. Low vision occurs when an individual struggles with any of the following common activities:
- Reading
- Everyday tasks like personal grooming
- Viewing photos
- Recognizing faces
Millions of Americans experience a normal loss of vision as they get older and the number of individuals who develop vision problems due to health conditions is projected to continue to rise.
There are many things that can cause low vision, including:
- Macular degeneration
- Cataracts
- Diabetes
- Glaucoma
- Injury to the eye
- Birth defects
A few simple approaches can be:
- Getting an eye exam
- Update your reading glasses
- Use bright light for reading
If these do not work for you, ask your eye care professional for help or ask for a referral to a low vision specialist.
Low Vision Technology
Individuals with eye disease related to age, or vision compromised due to injury, may benefit from the usage of low vision devices.
There are two primary categories for low vision devices: Magnifiers for viewing things and objects that are close to you (magnifying lenses or machines), and magnifiers used for viewing objects and images at a distance (telescopic lenses). Many lighted magnifiers for close objects improve readability by increasing illumination. With the advances in technology, many low vision devices are available to provide multiple function (near and distance) magnification and visual aid.
Technology is advancing to meet the growing needs of people with low vision impairment. There are a number of products that can help individuals with low vision. While considering the correct vision enhancer, keep in mind a few objectives:
- What is the visual ability of the individual? Low vision aids are created with different options for specific low vision needs.
- What tasks will the visual enhancer be used for? Find out what each product is best used for to decide if it will meet the needs of the individual.
- Is the device easy to use? The right device should be easy for you to use.
- How much does it cost? The cost of low vision aids can vary depending on a number of factors.
Popular products include:
 Portable magnifiers and lighted magnifiers- offer magnified reading on the go. Perfect for menus, shopping lists, label reading, and more, portable magnifiers can fit in your pocket, purse, or be worn on the belt for quick, easy use.
Portable magnifiers and lighted magnifiers- offer magnified reading on the go. Perfect for menus, shopping lists, label reading, and more, portable magnifiers can fit in your pocket, purse, or be worn on the belt for quick, easy use.
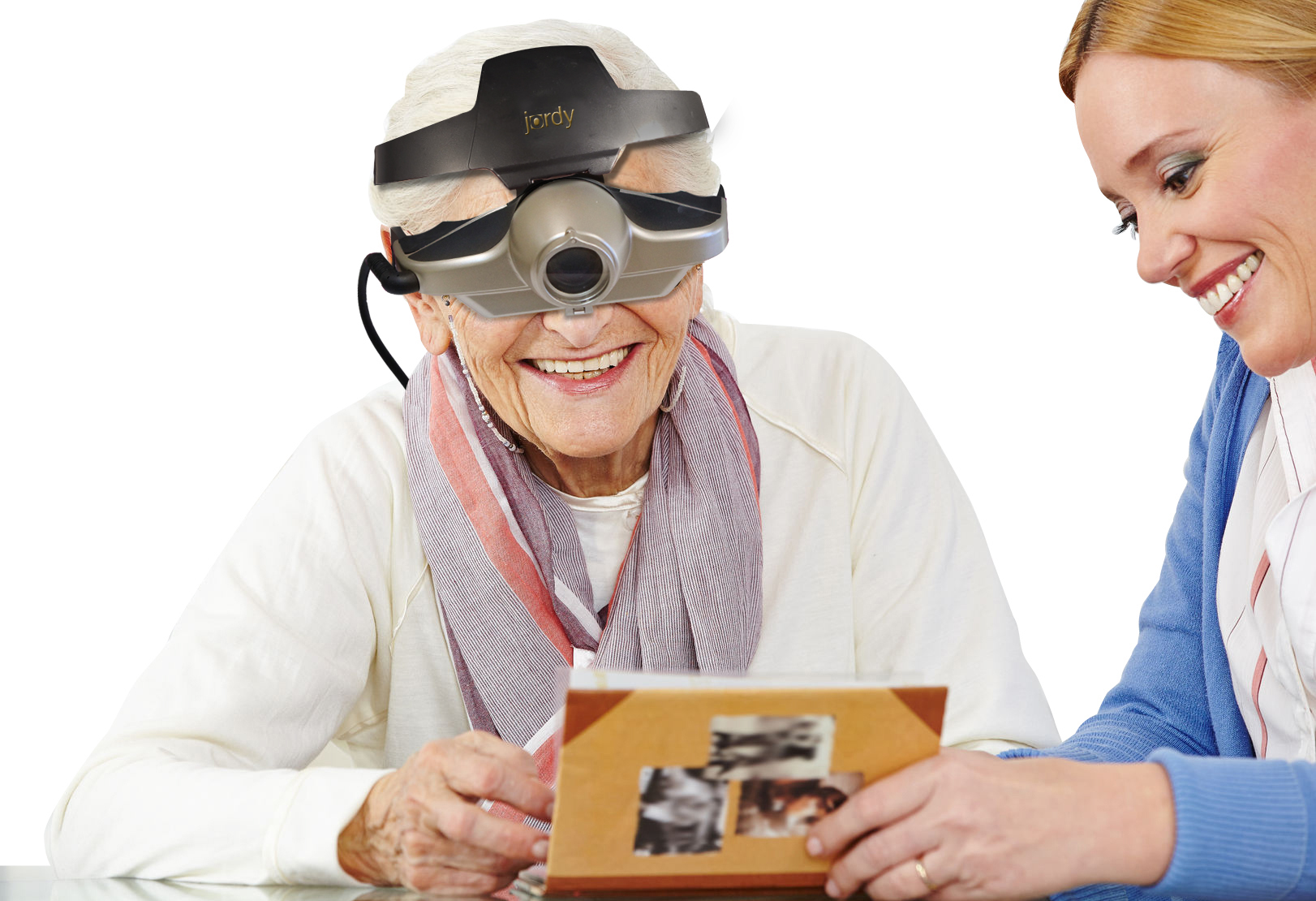 Wearable magnifiers – wearable technology is the future for those with low vision who live an active lifestyle. Wearable options make it possible to see and take part in everyday tasks, such as reading and recognizing faces.
Wearable magnifiers – wearable technology is the future for those with low vision who live an active lifestyle. Wearable options make it possible to see and take part in everyday tasks, such as reading and recognizing faces.
 Transportable magnification screens– are perfect for close up viewing as well as distance viewing. These great viewers offer great flexibility, from watching TV to using the mirror image feature for self-viewing. There are APPS for smart phones that can be used to magnify reading material.
Transportable magnification screens– are perfect for close up viewing as well as distance viewing. These great viewers offer great flexibility, from watching TV to using the mirror image feature for self-viewing. There are APPS for smart phones that can be used to magnify reading material.
 Desktop devices for reading books, bills or letters – these have large, bright screens. A reading table offers visual aid for reading books, optional computer connectivity and more. This family of portable magnification units offers up to 75x magnification.
Desktop devices for reading books, bills or letters – these have large, bright screens. A reading table offers visual aid for reading books, optional computer connectivity and more. This family of portable magnification units offers up to 75x magnification.
Consult a Low Vision Specialist–Consider making an appointment with a trained low vision specialist if you have specialized needs. They are available in larger cities or can be found by contacting The Braille Institute or by an internet search. Talk with your low vision specialist to find out which is right for you and where you can find them.
In addition to low vision devices and good lighting, inexpensive non-optical adaptive aids can assist with routine daily activities. These devices include:
- Large-print cookbooks
- Large-numbered playing cards, clocks, telephones and watches
- Electronic “talking” clocks, kitchen timers, thermometers, blood pressure meters and even pill bottles
- Large felt-tip pens and wide-lined paper for writing notes
- Color-coded pill boxes
- Signature guides help in writing your signature in the correct place
Many of these items can be found at your local drugstore, discount store or bookstore. Your low vision specialist can recommend retail sources for non-optical adaptive aids.
Vision loss can definitely be alarming but learning how to adapt, with the aid of low-vision specialists, can result in continued independence. As low vision aids are tools focused on helping with the physical aspect, it is also important to seek the help of a counselor for psychological counseling if needed or join a support group, that may provide the help you need. Finally, maintaining a social network and asking for help will enrich your life, and help maintain your independence and quality of life.
Resources:
www.enhancedvision.com
www.allaboutvision.com
www.nei.nih.gov
www.brailleinstitute.org
www.visionaware.org
www.aao.org
www.amd.org
www.californiaphones.org


 The other day my daughter Blythe asked me which Christmas I consider to be my favorite. I had to think a minute, because as a family, the Sullivan’s have had some great ones. I was about to say the first time you and your brother Tom were old enough to really get into Santa, being absolutely sure that the fat man brought your presents right down the chimney. I was about to say that, and then I remembered.
The other day my daughter Blythe asked me which Christmas I consider to be my favorite. I had to think a minute, because as a family, the Sullivan’s have had some great ones. I was about to say the first time you and your brother Tom were old enough to really get into Santa, being absolutely sure that the fat man brought your presents right down the chimney. I was about to say that, and then I remembered.  Colorado, when our children were teenagers and our friend, the marvelous Betty White, joined us for a Christmas Eve sleigh ride none of us will ever forget. The night was perfect. It had snowed earlier that day, and the air had a feeling of Christmas that you could almost taste. Oh, sure, it was cold, but we were bundled up under tons of blankets as two beautiful Clydesdale horses with bells jingling took us through the woods to a magical barn where dinner would be served and carols sung.
Colorado, when our children were teenagers and our friend, the marvelous Betty White, joined us for a Christmas Eve sleigh ride none of us will ever forget. The night was perfect. It had snowed earlier that day, and the air had a feeling of Christmas that you could almost taste. Oh, sure, it was cold, but we were bundled up under tons of blankets as two beautiful Clydesdale horses with bells jingling took us through the woods to a magical barn where dinner would be served and carols sung.  Tom Sullivan
Tom Sullivan I can only imagine my wife’s beautiful face. Oh sure, I’ve touched it and kissed it many times. I’ve felt the lines with the tips of my fingers, tracing our lives together, and I’ve heard her smile. I understand that’s not really seeing it. It’s not seeing her eyes as they sparkle with something funny I said; or, when she looks at me with love reserved only for those who are truly in love.
I can only imagine my wife’s beautiful face. Oh sure, I’ve touched it and kissed it many times. I’ve felt the lines with the tips of my fingers, tracing our lives together, and I’ve heard her smile. I understand that’s not really seeing it. It’s not seeing her eyes as they sparkle with something funny I said; or, when she looks at me with love reserved only for those who are truly in love.
 Today, people are living longer than ever before so it’s important to be proactive and take responsibility for your health as you age.
Today, people are living longer than ever before so it’s important to be proactive and take responsibility for your health as you age. 
 Maintain a healthy weight. Being overweight increases your risk for diabetes. By exercising regularly, you can help keep your body healthy and prevent vision loss.
Maintain a healthy weight. Being overweight increases your risk for diabetes. By exercising regularly, you can help keep your body healthy and prevent vision loss.  Don’t smoke. Smoking increases your risk for age-related macular degeneration, cataract, and other eye diseases and conditions that can damage the optic nerve.
Don’t smoke. Smoking increases your risk for age-related macular degeneration, cataract, and other eye diseases and conditions that can damage the optic nerve. Wear protective eyewear when outdoors. Protecting your eyes from the sun’s ultraviolet rays when you are outdoors is vital for your eye health. Wearing sunglasses that block 99 to 100 percent of both UV-A and UV-B radiation.
Wear protective eyewear when outdoors. Protecting your eyes from the sun’s ultraviolet rays when you are outdoors is vital for your eye health. Wearing sunglasses that block 99 to 100 percent of both UV-A and UV-B radiation. Know your family history. Talk to your family members about their eye health history. It’s important to know if anyone has been diagnosed with a disease or condition since many are hereditary, such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetes . This will help determine if you are at higher risk for developing an eye disease or condition.
Know your family history. Talk to your family members about their eye health history. It’s important to know if anyone has been diagnosed with a disease or condition since many are hereditary, such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetes . This will help determine if you are at higher risk for developing an eye disease or condition. Consider a multivitamin. Vitamins C, E and the mineral zinc have been shown to promote eye health. Vitamins with Lutein and Zeaxanthin have been known to help patients with moderate to severe age-related macular degeneration.
Consider a multivitamin. Vitamins C, E and the mineral zinc have been shown to promote eye health. Vitamins with Lutein and Zeaxanthin have been known to help patients with moderate to severe age-related macular degeneration. Give your eyes a rest. If you spend a lot of time at the computer or focusing at any one distance, you sometimes forget to blink, resulting in dryness and eye fatigue. Every 20 minutes, look away about 20 feet in front of you for 20 seconds. This can help reduce eyestrain. Consider using a lubricant eye drop during long periods of intense eye use and rest your eyes for 5 minutes.
Give your eyes a rest. If you spend a lot of time at the computer or focusing at any one distance, you sometimes forget to blink, resulting in dryness and eye fatigue. Every 20 minutes, look away about 20 feet in front of you for 20 seconds. This can help reduce eyestrain. Consider using a lubricant eye drop during long periods of intense eye use and rest your eyes for 5 minutes.
 Tom Sullivan
Tom Sullivan

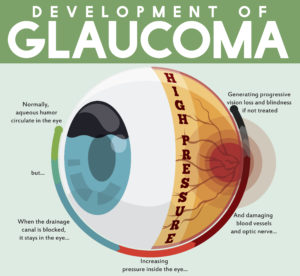 tic nerve, a part of the central nervous system that carries visual information from the eye to the brain.
tic nerve, a part of the central nervous system that carries visual information from the eye to the brain.



