 February is Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) Awareness Month, a time dedicated to educating, supporting, and empowering those affected by this leading cause of permanent vision loss in the US.
February is Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) Awareness Month, a time dedicated to educating, supporting, and empowering those affected by this leading cause of permanent vision loss in the US.
Across the United States, nearly 20 million adults over 40 are living with some form of AMD. As our population ages, that number continues to grow — making awareness, early detection, and research more important than ever.
What Is Age-Related Macular Degeneration?
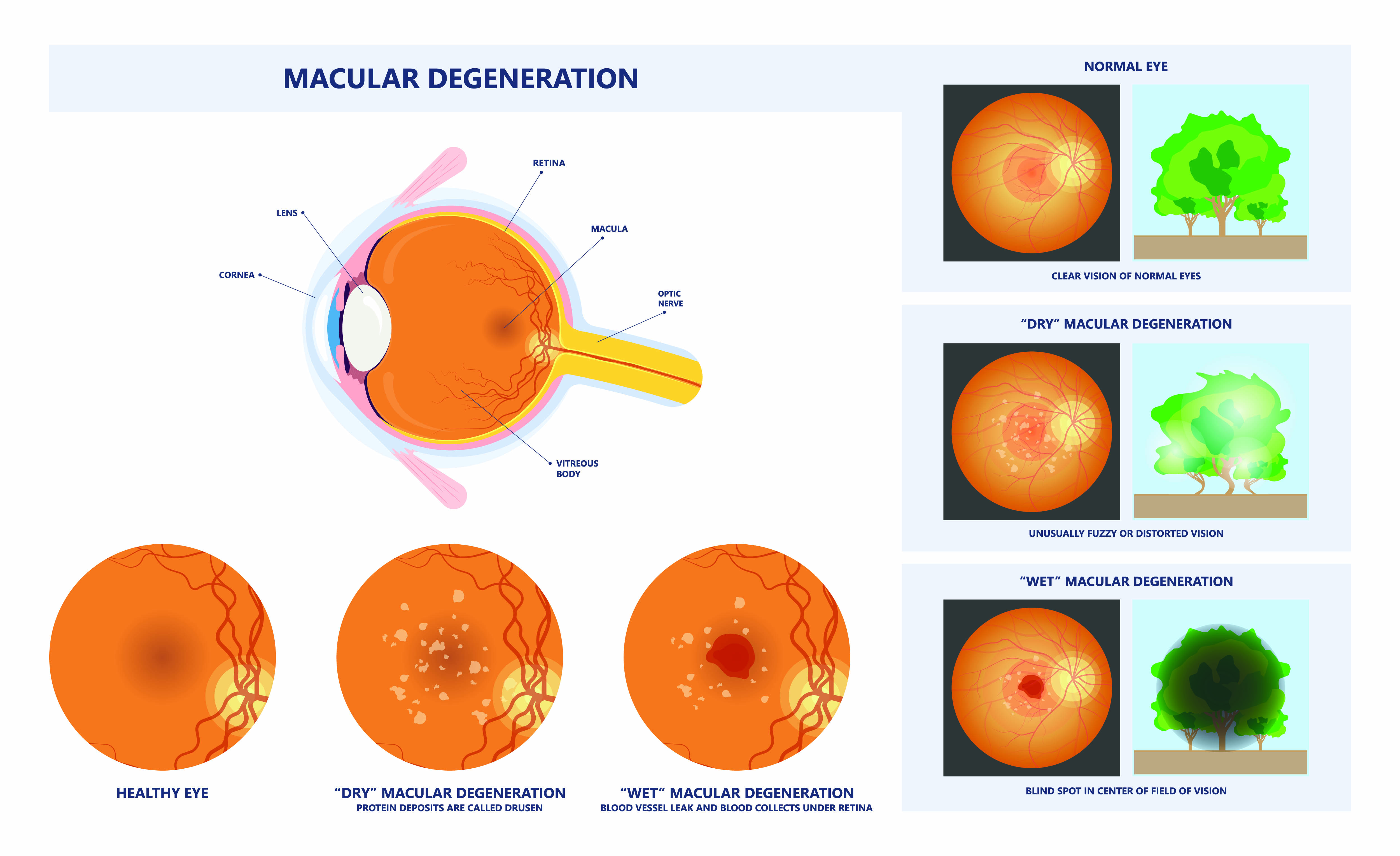
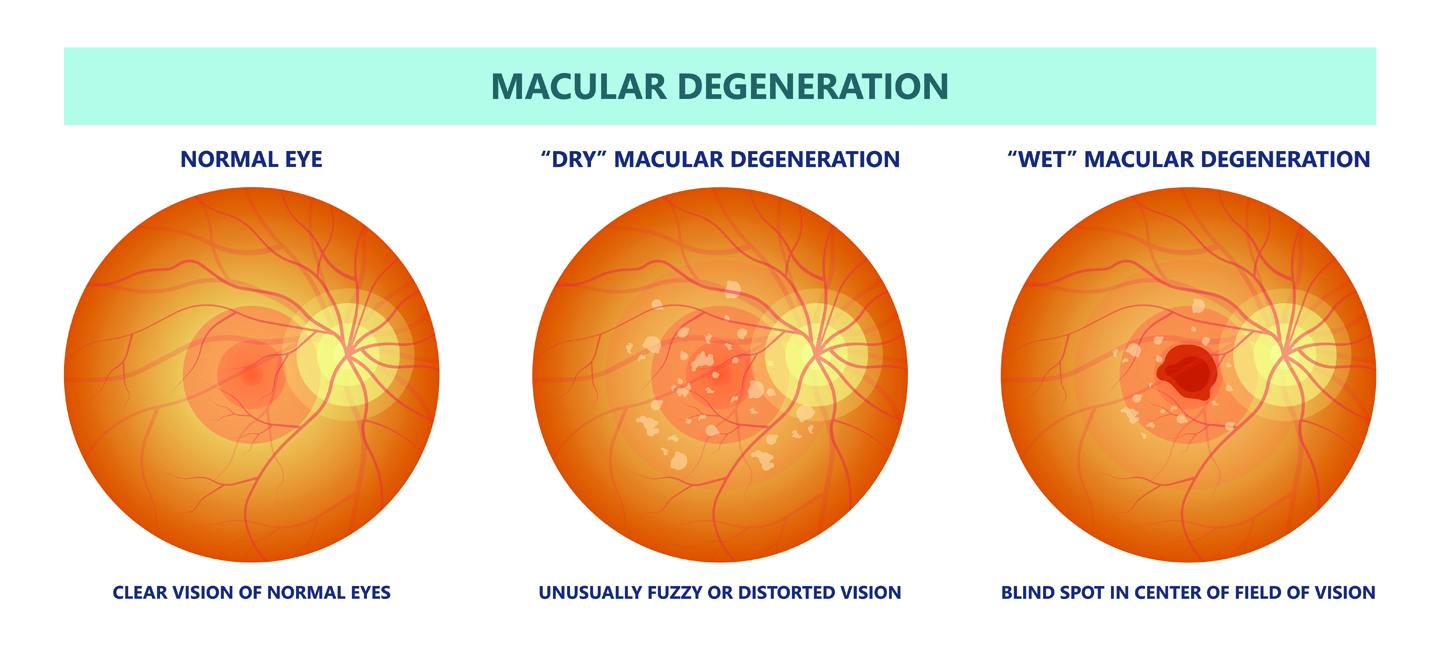
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) is a progressive eye condition that affects the macula — the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, detailed vision. The macula allows us to read, recognize faces, drive, and see fine detail.
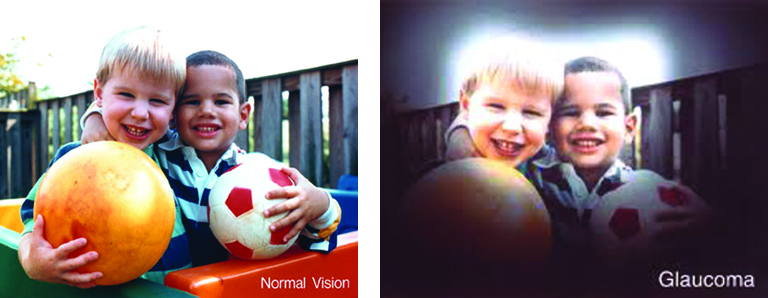
AMD does not cause complete blindness, but it can significantly impact central vision, making everyday tasks more and more difficult.
There are two main types:
Dry AMD
The most common form, accounting for about 80–90% of cases. It progresses gradually and may not show noticeable symptoms in early stages. But as time moves on the patients experience loss of central clear vision read, recognize faces, drive, and see fine detail.
Wet AMD
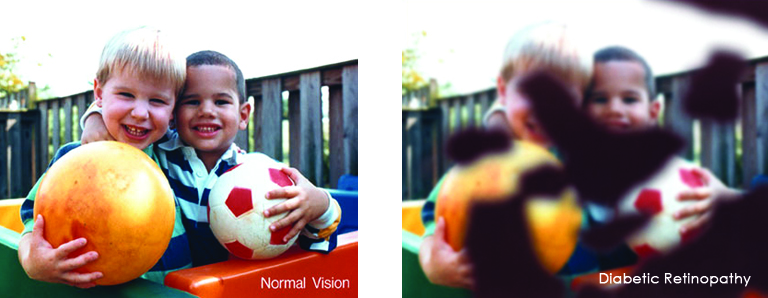
The less common form, with more sudden loss of vision. It occurs when abnormal blood vessels grow under the retina and leak fluid or blood, leading to rapid vision changes. People with a sudden drop in their vision should see an ophthalmologist promptly because early treatment can help prevent further vision loss.
Why Awareness Matters
One of the greatest challenges with AMD is that early stages often have no noticeable symptoms. By the time vision changes occur, damage may already be underway.
Early detection through comprehensive dilated eye exams can:
- Help establish the cause
- Allow timely treatment for wet AMD
- Slow progression
- Preserve independence and quality of life
If you are over 50, have a family history of AMD, smoke, or have cardiovascular disease, your risk may be higher.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
- Blurred or fuzzy central vision
- Straight lines appearing wavy
- Dark or empty areas in the center of vision
- Difficulty recognizing faces
- Increased need for brighter light when reading
- Use the amsler grid test to check your vision at home
If you notice any of these symptoms, schedule an eye exam promptly.
Taking Steps to Protect Your Vision
While there is currently no cure for AMD, lifestyle choices can play a role in delaying its onset or slowing progression:
- Schedule regular comprehensive eye exams
- Quit smoking
- Eat leafy greens and foods rich in antioxidants
- Maintain healthy blood pressure and cholesterol
- Protect your eyes from UV light
Research continues to advance, offering hope for improved treatments and, one day, prevention.
How You Can Make a Difference During AMD Awareness Month
Awareness leads to action. Here are ways to get involved:
- Support vision research by donating to the Discovery Eye Foundation, click here to donate
- Share educational resources with family and friends
- Encourage loved ones over 50 to schedule eye exams
- Learn about clinical trials and emerging therapies
Together, we can reduce the impact of AMD and ensure more people preserve their sight and independence.
A Message of Hope
AMD can be life-changing, but it does not have to mean losing independence or hope. With early detection, proper care, and continued research, we are making meaningful strides in protecting vision.
This February, let’s commit to prioritizing eye health — for ourselves and for those we love.
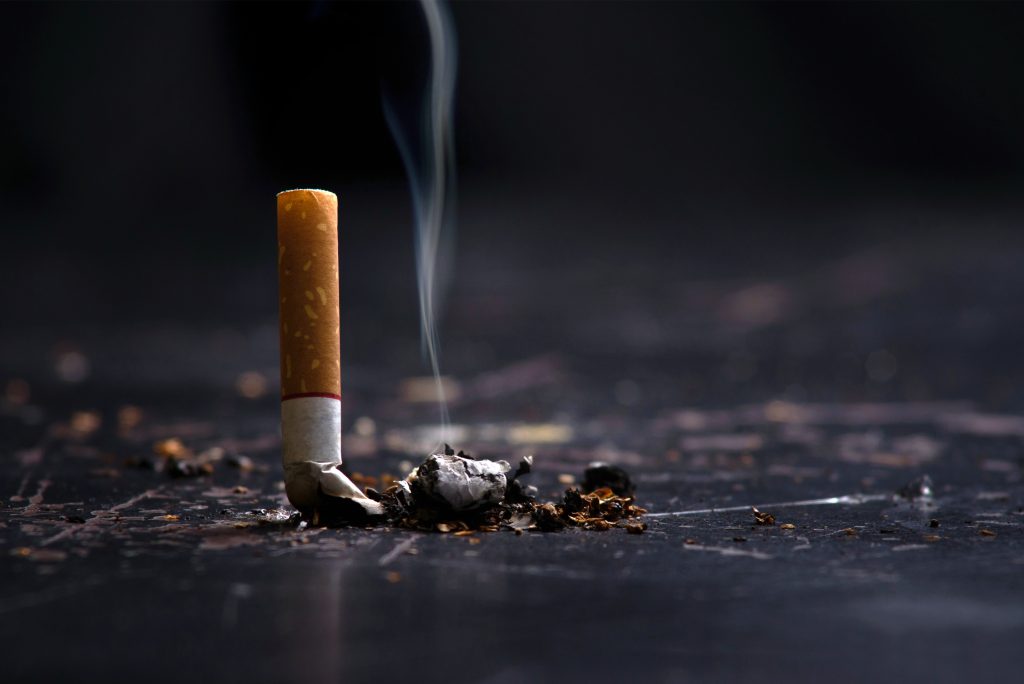










 Don’t smoke. Smoking increases your risk for age-related macular degeneration, cataract, and other eye diseases and conditions that can damage the optic nerve.
Don’t smoke. Smoking increases your risk for age-related macular degeneration, cataract, and other eye diseases and conditions that can damage the optic nerve. Wear protective eyewear when outdoors. Protecting your eyes from the sun’s ultraviolet rays when you are outdoors is vital for your eye health. Wearing sunglasses that block 99 to 100 percent of both UV-A and UV-B radiation.
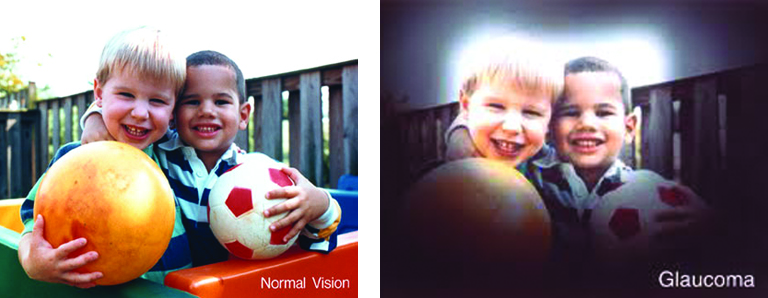
Wear protective eyewear when outdoors. Protecting your eyes from the sun’s ultraviolet rays when you are outdoors is vital for your eye health. Wearing sunglasses that block 99 to 100 percent of both UV-A and UV-B radiation. Know your family history. Talk to your family members about their eye health history. It’s important to know if anyone has been diagnosed with a disease or condition since many are hereditary, such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetes . This will help determine if you are at higher risk for developing an eye disease or condition.
Know your family history. Talk to your family members about their eye health history. It’s important to know if anyone has been diagnosed with a disease or condition since many are hereditary, such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetes . This will help determine if you are at higher risk for developing an eye disease or condition. Consider a multivitamin. Vitamins C, E and the mineral zinc have been shown to promote eye health. Vitamins with Lutein and Zeaxanthin have been known to help patients with moderate to severe age-related macular degeneration.
Consider a multivitamin. Vitamins C, E and the mineral zinc have been shown to promote eye health. Vitamins with Lutein and Zeaxanthin have been known to help patients with moderate to severe age-related macular degeneration. Give your eyes a rest. If you spend a lot of time at the computer or focusing at any one distance, you sometimes forget to blink, resulting in dryness and eye fatigue. Every 20 minutes, look away about 20 feet in front of you for 20 seconds. This can help reduce eyestrain. Consider using a lubricant eye drop during long periods of intense eye use and rest your eyes for 5 minutes.
Give your eyes a rest. If you spend a lot of time at the computer or focusing at any one distance, you sometimes forget to blink, resulting in dryness and eye fatigue. Every 20 minutes, look away about 20 feet in front of you for 20 seconds. This can help reduce eyestrain. Consider using a lubricant eye drop during long periods of intense eye use and rest your eyes for 5 minutes.
 Most people have eye problems at one time or another. Some are minor and will go away on their own, or are easy to treat at home. Others need a specialist’s care. Some eye issues come with age while others may be a serious condition.
Most people have eye problems at one time or another. Some are minor and will go away on their own, or are easy to treat at home. Others need a specialist’s care. Some eye issues come with age while others may be a serious condition. Dry eye is a common condition that occurs when your tears aren’t able to provide adequate lubrication for your eyes. Tears can be inadequate for many reasons. For example, dry eyes may occur if you don’t produce enough tears or if you produce poor-quality tears. Dry eyes can also feel very uncomfortable.
Dry eye is a common condition that occurs when your tears aren’t able to provide adequate lubrication for your eyes. Tears can be inadequate for many reasons. For example, dry eyes may occur if you don’t produce enough tears or if you produce poor-quality tears. Dry eyes can also feel very uncomfortable.