The inner workings of the human eye are complex, but at the same time, fascinating. Have you wondered how exactly they do work or what are the major parts of the eyeball involved in creating vision? Let’s find out.
These tiny cameras spend every day processing millions of pieces of information at lightning fast speeds, and turn them into the simple images we see almost instantly.
In reality, this process is anything but simple. The eye has several distinct parts, each of which has specific responsibilities that work together like a machine.
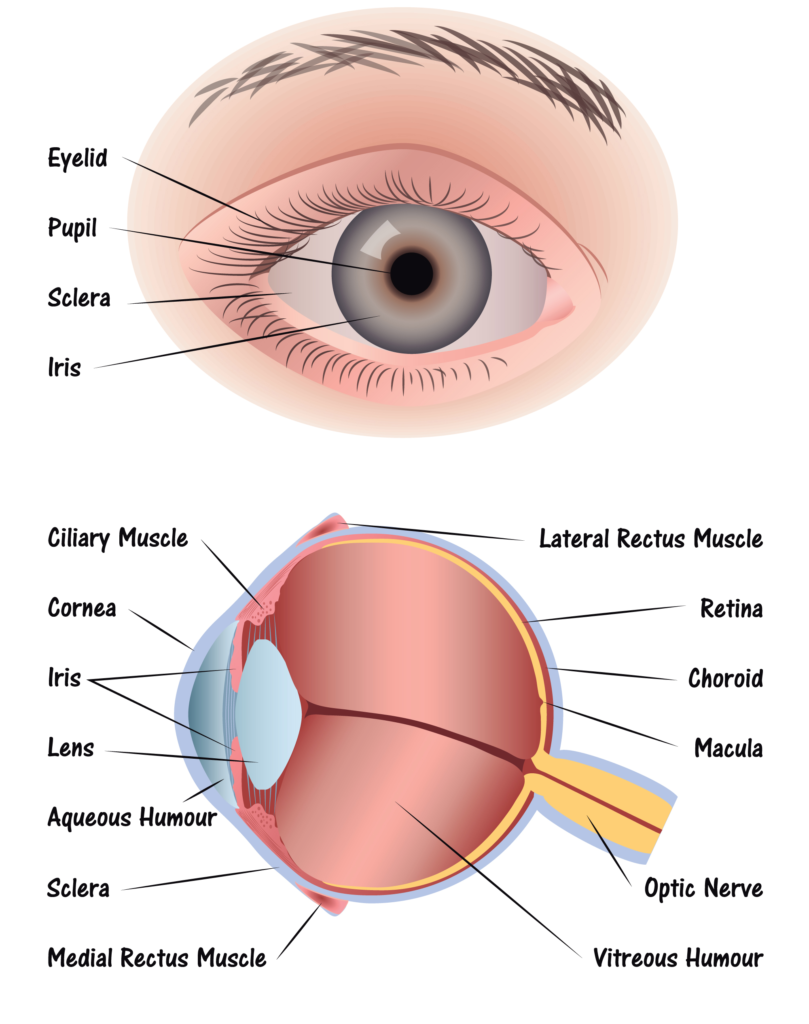
The eyeball is just like a camera. In fact, human eyes are part of a classification known as “camera-type eyes.” And just like a camera, it can’t function without the presence of light. As light hits the eyes, it’s focused by the eye in a way similar to a camera lens. This process allows the images we see to appear clear and sharp rather than blurry.
There are specific parts of the eye that make this focusing process possible. Each beam of light that hits the eye goes through a series of steps:
 Step 1: Light passes through a thin layer of moisture
Step 1: Light passes through a thin layer of moisture
Step 2: Light hits the cornea. The cornea is transparent, and is the first layer to begin focusing light within the eye. The cornea is connected to the sclera, which is a tough fiber on the outside of the eye that acts as protection.
Step 3: Behind the cornea is another liquid layer known as the aqueous humor, and its job is to maintain pressure levels in the front of the eye as light is passing through.
Step 4: Once light has passed through the aqueous humor, it has finally reached the pupil. The pupil is the round entryway of the colored iris.
Step 5: Once the pupil determines how much light it will let inside your eye, the job passes to the lens. The lens factors in the amount of light the pupil lets in, and figures out how far away you are from the object that the light is reflecting off of, or the object you’re trying to see. From there, the lens focuses your image into an accurate view of what you’re looking at. Part of this process is controlled by muscles in the lens called ciliary muscles, which expand and contract to pull on the lens and allow it to focus properly.
Step 6: As light reaches the center of the eye passes through another layer of moisture, called the vitreous, or vitreous humor. Then, it reaches the final stop in the process: The Retina.
The retina is the back of the eye. If the lens in your eye is most like a camera, the retina is most like its film – this is where the final product is projected. The retina has several parts:
- Macula: The center of the retina. The center point of the macula is called the fovea, and it has the most photoreceptors and nerve endings of any part of the eye.
- Photoreceptors: Split into two designations – rods and cones.
- Cones are in the macula. When there is bright light, cones provide clear, sharp central vision and detect colors and fine details.
-
- Rods are located outside the macula and extend all the way to the outer edge of the retina. They provide peripheral or side vision. Rods also allow the eyes to detect motion and help us see in dim light and at night.
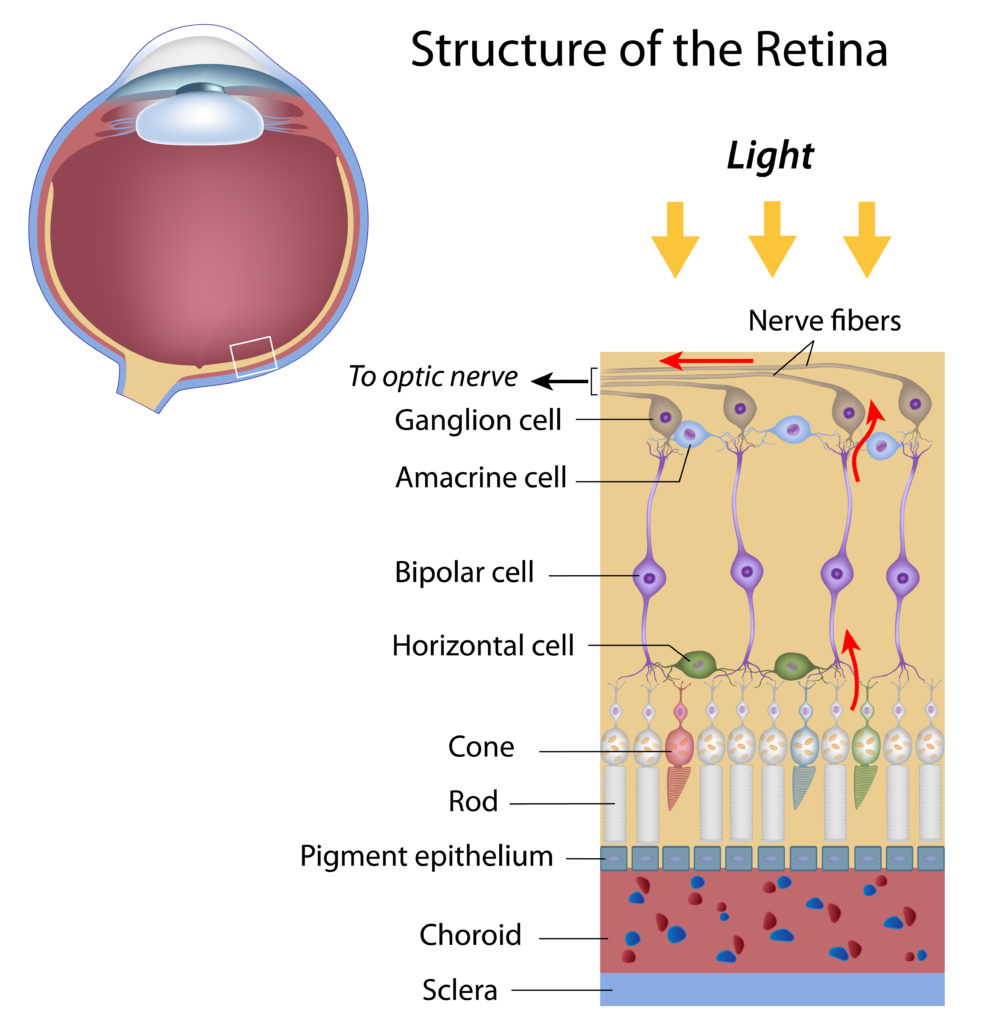
- Retinal pigment epithelium: Abbreviated RPE, this is a tissue layer below the rods and cones which absorbs any extra, unneeded light.
- Choroid: The choroid is behind the retina, and is in charge of making sure the retina and RPE have enough nutrition flowing from small blood vessels.
Once the photoreceptors have converted light into an electronic signal, they send a signal to the brain’s visual command center and you have vision. It’s amazing what even small parts of our bodies can do.
How the Eye Works

