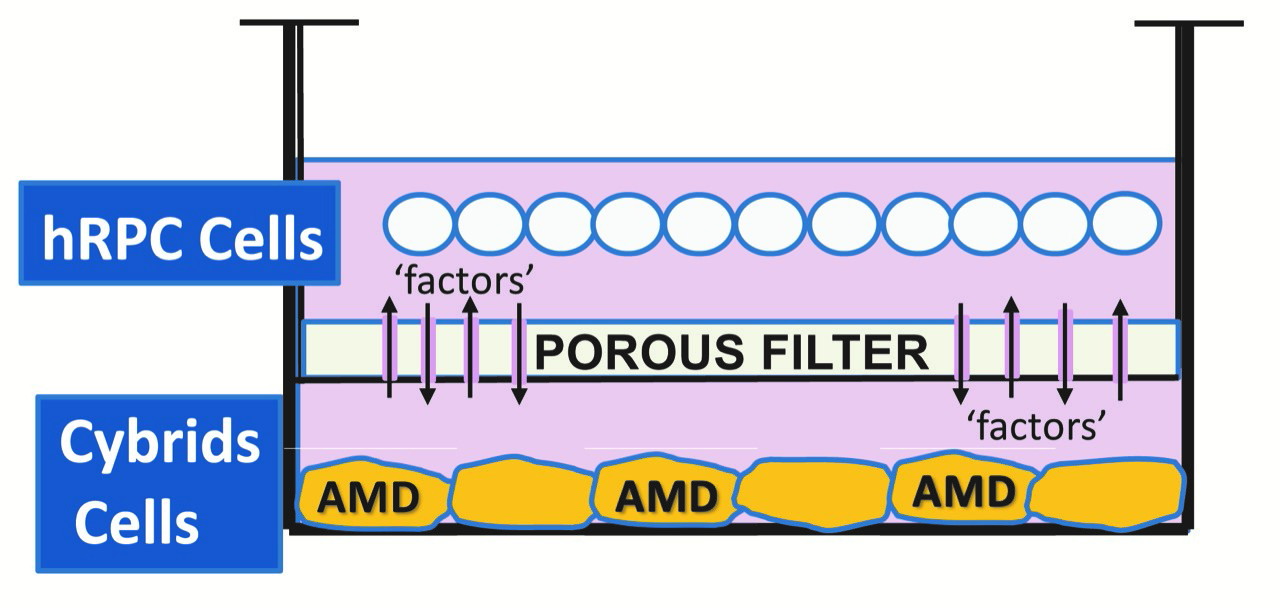
Low vision affects millions of Americans — including many older adults. People with low vision aren’t blind, but because of their vision loss, they may not be able to do everyday tasks like driving or reading even with glasses.
What is Low Vision?
When your eyesight is impaired to the degree that you struggle with daily tasks like reading or cooking – or that you have difficulty recognizing faces, you may have a medical condition referred to as low vision. Someone with low vision can’t simply put on a pair of glasses or contacts and see well; this condition is beyond the typical loss of vision that occurs with aging.
Individuals experiencing low vision can struggle with maintaining independence; hobbies, reading and even socializing may become challenging as vision loss progresses. Because of the impact low vision can have on your life, it is important to have your eyes checked by a low vision specialist if you have any concerns. Since it is unusual to be able to restore vision once it is lost, screenings can help preserve the vision you have and help you access adaptive lenses and devices if you need them. While there is not a cure for low vision, a low vision specialist can help you adapt and if needed, create a vision rehabilitation program designed to meet your specific needs.
If you are experiencing trouble seeing even with prescription eye glasses, ask your optometrist or ophthalmologist for a low vision evaluation. If your practitioner does not perform this evaluation, request a referral to a low vision specialist in a private practice, at a Braille Institute or a University Eye Care Institute.
Low vision is often caused by one of these conditions:
- Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) –AMD is a progressive eye condition affecting as many as 15 million Americans. The disease attacks the macula of the eye, where our sharpest central vision occurs, affecting reading, driving, identifying faces, watching television, safely navigating stairs and performing other daily tasks. Although it rarely results in complete blindness, it robs the individual of all but the outermost, peripheral vision, leaving only dim images or black holes at the center of vision. Read more

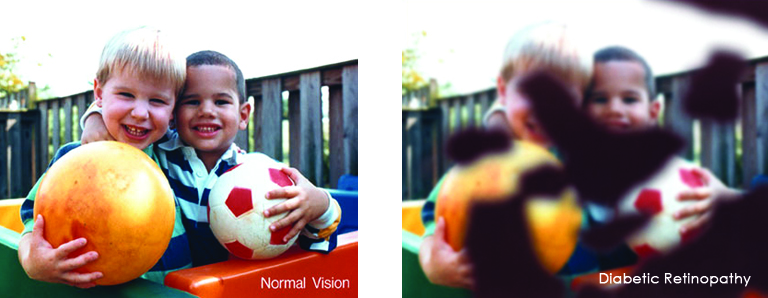
- Diabetes– Diabetic retinopathy is the most common diabetic eye disease and a leading cause of blindness in American adults caused by changes in the blood vessels of the retina.
In some people with diabetic retinopathy, blood vessels may swell and leak fluid or blood inside the eye. In other people, abnormal new blood vessels grow on the surface of the retina. The retina is the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. A healthy retina is necessary for good vision. Read More
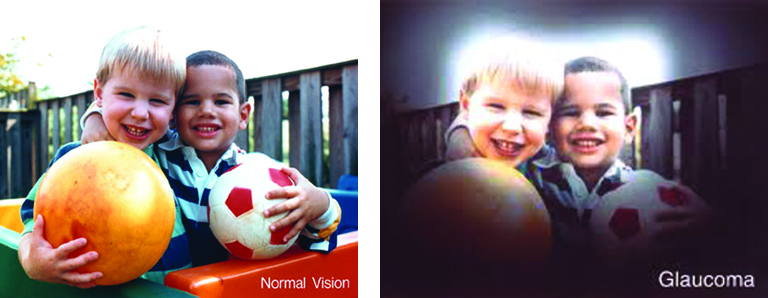
- Glaucoma– Glaucoma is a disease that causes damage to the major nerve of the eye called the optic nerve, a part of the central nervous system that carries visual information from the eye to the brain
The eye experiences a gradual increase of intraocular pressure (IOP) due to an imbalance of the fluid produced in the eye and the amount of fluid drained. Over time, elevated IOP can cause vision loss. The most common form of glaucoma is primary open angle glaucoma which affects about 3 million Americans. However, there are other types including narrow angle, congenital, normal tension, and secondary glaucoma. Read more
Reducing your risk for Low Vision
Practicing healthy daily lifestyle habits can reduce your risk for low vision. A healthy diet, not smoking and maintaining healthy blood pressure are important first steps. Other healthy habits that can lower the risk include:
- Eat a diet with plenty of green, leafy vegetables such as kale, spinach, and collard greens, and fresh fruit.
- Fish that is high in omega-3 fatty acids is good for eye health. Try to include it in your diet at least once or twice a week. Types of fish that are high in omega-3 fatty acids include salmon, sardines, mackerel, herring, and albacore tuna.
- It’s important to keep your body healthy. Maintain a healthy weight, exercise regularly, maintain healthy blood pressure and cholesterol levels. The healthier your body, the more it can foster good eye health. Visit our website for eye healthy recipes Eye Cook.
- Protect your eyes. Wear sunglasses and a hat with a visor in bright sunlight to protect your eyes from potentially harmful ultra-violet (UV) light and blue light.
Low Vision Reading Apps on Your Smartphone
Reading often is one of the most difficult challenges for visually impaired people. Many people with low vision give up reading altogether, because what used to be an enjoyable, effortless activity now requires thought, preparation and a lot of adjustment. In short, reading is just no fun anymore.
The American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO) has listed some of the top apps, devices and resources for people with low vision, below are a few listed for reading app, for more apps visit American Academy of Ophthalmology.
Reading
- KNFB Reader (Android and iOS, $99.99) – This voice-to-text tool lets you take a picture of any text—books, recipes, product labels—and have it read back to you or converted to braille.
- Audible (Android and iOS, $14.95 per month plus downloads) – Provides downloadable audiobooks, periodicals, newspapers and more. Their collection currently includes 200,000+ books.
- Kindle app (Android, iOS, PC and Mac, free) – An e-reader app that allows you to download books. Books can be purchased and directly downloaded from Amazon, or downloaded from your library app into the Kindle app. The free Kindle app can be downloaded onto many iOS and Android devices.
- Bookshare (Android and iOS, $50 per year) – An online library for people with low vision. Currently, the Bookshare collection contains nearly 850,000 titles, downloadable in a choice of formats including ebooks, audio, braille, and large font. Membership requires verification of your print disability, and includes free downloads.
- BARD Mobile (Android and iOS, free) – A talking book library that offers access to tens of thousands of titles. You must first enroll in the National Library Service (NLS) for the Blind and Print Disabled at the Library of Congress. Note that this program may only be available in the United States.
Regular eye exams are essential for all adults; it is recommended that adults over the age of 60 have eye exams each year. If your vision can not be improved to the point that you are able to see the things you need to see or read, your eye care professional can refer you to a low vision specialist. This specialist differs from a conventional optometrist and is trained to evaluate your low vision problem and offer solutions to help you retain or regain independence and the ability to do things you enjoy again.
More Low Vision resources




 Costume Contact Lenses such as cat eyes or zombie may make your Halloween costume a bit more frightful although wearing those lenses without a prescription can be more terrifying, as it could result in vision loss or even blindness.
Costume Contact Lenses such as cat eyes or zombie may make your Halloween costume a bit more frightful although wearing those lenses without a prescription can be more terrifying, as it could result in vision loss or even blindness.