Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) Awareness Month is observed annually every February. It’s an awareness month targeted at spreading information about AMD and other sight threatening diseases that could lead to visual impairment.
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) Awareness Month is observed annually every February. It’s an awareness month targeted at spreading information about AMD and other sight threatening diseases that could lead to visual impairment.
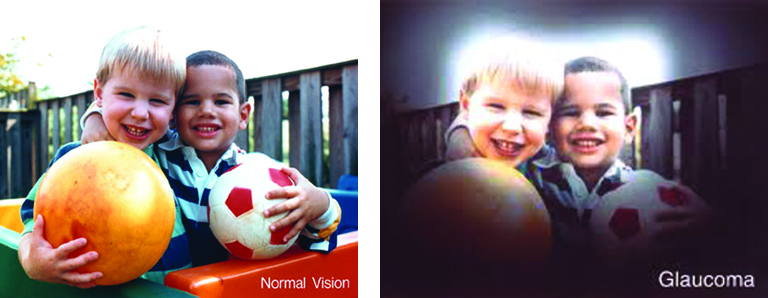
AMD is a disease that is a leading cause of low vision in Americans older than 50 years of age. The macula is the part of the eye affected by this disease, a pigmented, oval-shaped part of the retina. About 5mm in diameter, it is responsible for the central vision required for driving, reading, and fine detail. AMD, is a progressive disease that causes retinal cells to slowly die, though it causes no physical pain.
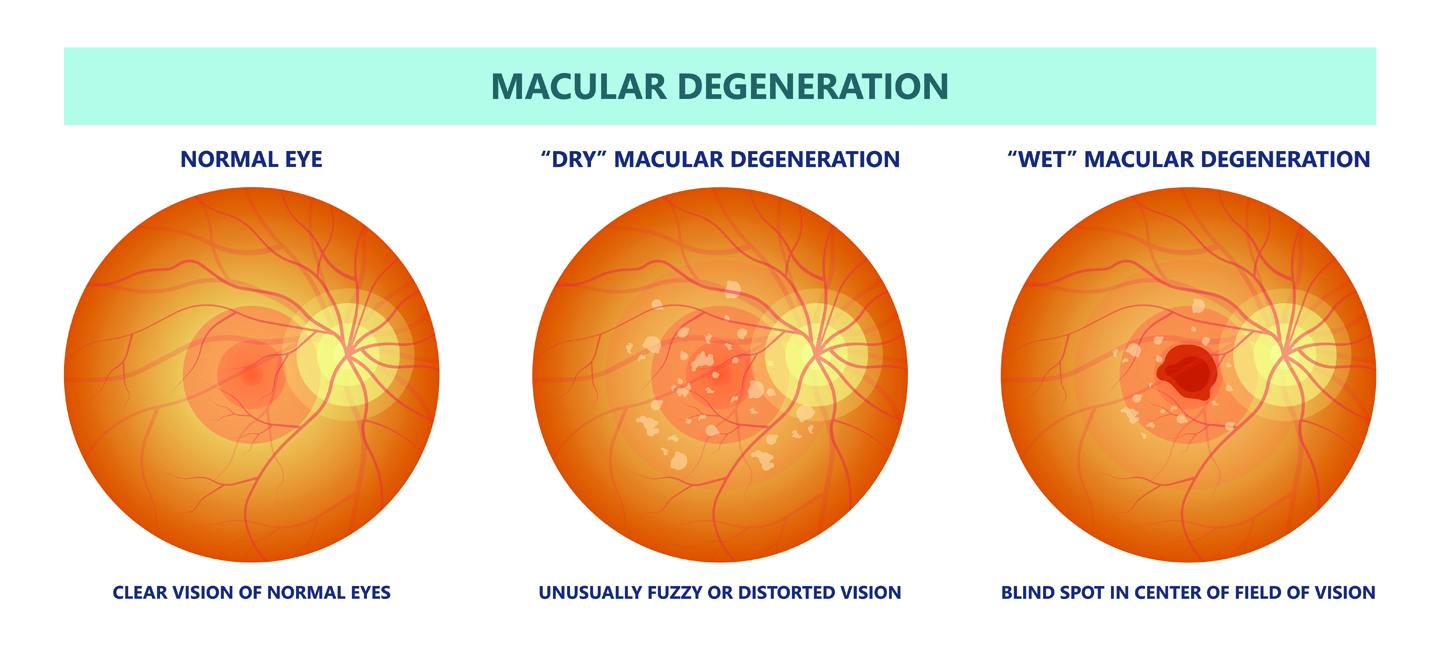
Medical experts have been able to identify some risk factors that might lead to the onset of AMD, including high blood pressure, high levels of blood cholesterol, obesity, and smoking. Other risk factors that a person has no control over are age, heredity, race, and gender. Symptoms of the disease include blurry vision, blind spots, straight lines appearing wavy, doorways seeming crooked, and objects appearing farther away or smaller. When any of these symptoms present themselves, the concerned individual is advised to immediately visit an ophthalmologist.
Watch the video below to learn more about AMD presented by M. Cristina Kenney, MD, PhD
For more information on AMD and other visual impairments – EYE CONDITIONS
The Discovery Eye Foundation is committed to finding a treatment for Dry AMD which makes up 85% of AMD cases and for which there is no FDA approved treatment as yet. This could preserve the vision of millions of people. Luckily, there are treatments for Wet AMD. Right now, research supported by DEF at the Gavin Herbert Eye Institute, University of California Irvine, Medical School is on the cutting edge of promising breakthroughs that could make the difference in the lives of so many.


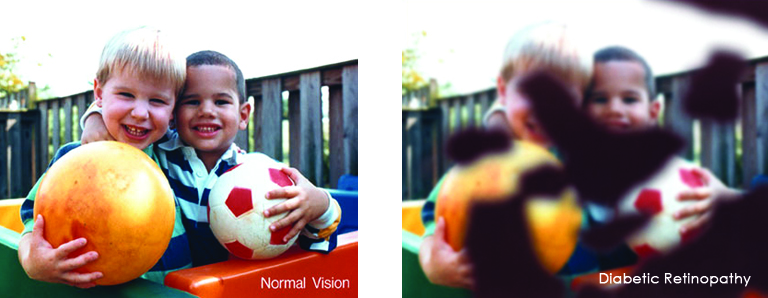
 Harsh weather conditions can reduce the natural moisture in your eyes and the irritation usually results in a burning or itching sensation that often leads to rubbing or scratching your eyes which can worsen the symptoms. Sometimes it feels like there is a foreign object in your eye and for some, dry eyes can even cause excessive tearing, as your eyes try to overcompensate for their lack of protective tears. Prolonged, untreated dry eyes can lead to blurred vision as well. Between the harsh winter winds outside and the dry heat radiating inside, our eyes are very quickly irritated and dried in the winter months. The result is itchy, dry eyes that may cause pain, blurred vision, a burning sensation, or even watery vision as our eyes try to compensate for the dryness.
Harsh weather conditions can reduce the natural moisture in your eyes and the irritation usually results in a burning or itching sensation that often leads to rubbing or scratching your eyes which can worsen the symptoms. Sometimes it feels like there is a foreign object in your eye and for some, dry eyes can even cause excessive tearing, as your eyes try to overcompensate for their lack of protective tears. Prolonged, untreated dry eyes can lead to blurred vision as well. Between the harsh winter winds outside and the dry heat radiating inside, our eyes are very quickly irritated and dried in the winter months. The result is itchy, dry eyes that may cause pain, blurred vision, a burning sensation, or even watery vision as our eyes try to compensate for the dryness.








 Rest and blink your eyes – Researchers found that over 30% of people using digital devices rarely take time to rest their eyes. Just over 10% say they never take a break, even when working from home. The eye muscles get overworked and don’t get a chance to relax and recover. Experts suggest the 20-20-20 rule; every 20 minutes, focus your eyes and attention on something 20 feet away for 20 seconds. You can also get up and walk around for a few minutes.
Rest and blink your eyes – Researchers found that over 30% of people using digital devices rarely take time to rest their eyes. Just over 10% say they never take a break, even when working from home. The eye muscles get overworked and don’t get a chance to relax and recover. Experts suggest the 20-20-20 rule; every 20 minutes, focus your eyes and attention on something 20 feet away for 20 seconds. You can also get up and walk around for a few minutes. Reduce exposure to blue light – In the spectrum of light, blue is more high energy and close to ultraviolet light. So, if you use screens throughout the day, ask your eye doctor about the value of computer glasses that block blue light. Reducing exposure to blue light may help lessen vision problems. At home, using digital devices until bedtime can overstimulate your brain and make it more difficult to fall asleep. Eye doctors recommend no screen time at least one to two hours before going to sleep.
Reduce exposure to blue light – In the spectrum of light, blue is more high energy and close to ultraviolet light. So, if you use screens throughout the day, ask your eye doctor about the value of computer glasses that block blue light. Reducing exposure to blue light may help lessen vision problems. At home, using digital devices until bedtime can overstimulate your brain and make it more difficult to fall asleep. Eye doctors recommend no screen time at least one to two hours before going to sleep.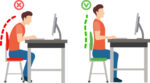 Sit up straight – Proper posture is important. Your back should be straight and your feet on the floor while you work. Elevate your wrists slightly instead of resting them on the keyboard.
Sit up straight – Proper posture is important. Your back should be straight and your feet on the floor while you work. Elevate your wrists slightly instead of resting them on the keyboard. Set up monitor properly – Make sure your computer screen is about 25 inches, or an arm’s length, away from your face. The center of the screen should be about 10-15 degrees below eye level. Cut glare by using a matte screen filter. You can find them for all types of computers, phones, and tablets. Increase font size or set the magnification of the documents you are reading to a comfortable size.
Set up monitor properly – Make sure your computer screen is about 25 inches, or an arm’s length, away from your face. The center of the screen should be about 10-15 degrees below eye level. Cut glare by using a matte screen filter. You can find them for all types of computers, phones, and tablets. Increase font size or set the magnification of the documents you are reading to a comfortable size. Consider computer glasses –For the greatest comfort at your computer, you might benefit from having your eye doctor modify your eyeglasses prescription to create customized computer glasses. This is especially true if you normally wear distance contact lenses, which may also become dry and uncomfortable during extended screen time. Computer glasses also are a good choice if you wear bifocals or progressive lenses, because these lenses generally are not optimal for the distance to your computer screen.
Consider computer glasses –For the greatest comfort at your computer, you might benefit from having your eye doctor modify your eyeglasses prescription to create customized computer glasses. This is especially true if you normally wear distance contact lenses, which may also become dry and uncomfortable during extended screen time. Computer glasses also are a good choice if you wear bifocals or progressive lenses, because these lenses generally are not optimal for the distance to your computer screen. Get an Eye Exam – If you have tried all these tips and eye strain is still an issue, it might be time to see an eye care professional to schedule an eye exam. The exam may even detect underlying issues before they becomes worse.
Get an Eye Exam – If you have tried all these tips and eye strain is still an issue, it might be time to see an eye care professional to schedule an eye exam. The exam may even detect underlying issues before they becomes worse.