 Harsh weather conditions can reduce the natural moisture in your eyes and the irritation usually results in a burning or itching sensation that often leads to rubbing or scratching your eyes which can worsen the symptoms. Sometimes it feels like there is a foreign object in your eye and for some, dry eyes can even cause excessive tearing, as your eyes try to overcompensate for their lack of protective tears. Prolonged, untreated dry eyes can lead to blurred vision as well. Between the harsh winter winds outside and the dry heat radiating inside, our eyes are very quickly irritated and dried in the winter months. The result is itchy, dry eyes that may cause pain, blurred vision, a burning sensation, or even watery vision as our eyes try to compensate for the dryness.
Harsh weather conditions can reduce the natural moisture in your eyes and the irritation usually results in a burning or itching sensation that often leads to rubbing or scratching your eyes which can worsen the symptoms. Sometimes it feels like there is a foreign object in your eye and for some, dry eyes can even cause excessive tearing, as your eyes try to overcompensate for their lack of protective tears. Prolonged, untreated dry eyes can lead to blurred vision as well. Between the harsh winter winds outside and the dry heat radiating inside, our eyes are very quickly irritated and dried in the winter months. The result is itchy, dry eyes that may cause pain, blurred vision, a burning sensation, or even watery vision as our eyes try to compensate for the dryness.
What Are The Symptoms?
- Uncomfortable, stingy, burning or scratchy feeling.
- Stringy mucus in or around your eyes
- Increased eye irritation from smoke or wind
- Eye fatigue
- Sensitivity to light
- Eye redness
- A sensation of having something in your eyes
- Difficulty wearing contact lenses
- Periods of excessive tearing
- Blurred vision, often worsening at the end of the day or after focusing for a prolonged period
10 TIPS TO KEEP YOUR EYES COMFORTABLE DURING THE WINTER MONTHS
Whatever the symptoms, dry eyes can cause significant discomfort during the long winters and relief can seriously improve your quality of life.
- To keep eyes moist, apply artificial tears/eye drops a few times a day. If you have chronic dry eyes, speak to your eye doctor about the best product for your condition.
- Drink a lot of fluids – keeping your body hydrated will also help maintain the moisture in your eyes.
- If you spend a lot of time indoors in heated environments, use a humidifier to add some moisture back into the air.
- Try to situate yourself away from sources of heat, especially if they are blowing. While a nice cozy fire can add to the perfect winter evening, make sure to keep your distance so dry eyes don’t ruin it.
- Staring at a computer or digital device for extended amounts of time can further dry out your eyes. If you spend a lot of time staring at the screen, make sure you blink often and practice the 20/20/20 rule – every 20 minutes, look 20 feet away for 20 seconds. Use artificial tears often to lubricate eyes during long periods of using your eyes.
- Avoid air blowing in your eyes. Don’t direct hair dryers, car heaters, air conditioners or fans toward your eyes. In your car, direct heat to floor vents and away from your eyes once your windshield is defrosted.
- Stop smoking and avoid smoky environments.
- Don’t rub your eyes! This will only increase irritation and can also lead to infections if your hands are not clean.
- Give your eyes a break and break out your glasses. If your contact lenses are causing further irritation, take a break and wear your glasses for a few hours or days. Also talk to your optometrist about switching to contacts that are better for dry eyes.
- Protect your eyes. If you know you are going to be venturing into harsh weather conditions, such as extreme cold or wind, make sure you wear protection. Try large, 100% UV protective eyeglasses and a hat with a visor to keep the wind and particles from getting near your eyes. If you are a winter sports enthusiast, make sure you wear well-fitted ski goggles.
If you find that after following these tips you continue to suffer, contact your eye doctor.

 Most people have eye problems at one time or another. Some are minor and will go away on their own, or are easy to treat at home. Others need a specialist’s care. Some eye issues come with age while others may be a serious condition.
Most people have eye problems at one time or another. Some are minor and will go away on their own, or are easy to treat at home. Others need a specialist’s care. Some eye issues come with age while others may be a serious condition. Dry eye is a common condition that occurs when your tears aren’t able to provide adequate lubrication for your eyes. Tears can be inadequate for many reasons. For example, dry eyes may occur if you don’t produce enough tears or if you produce poor-quality tears. Dry eyes can also feel very uncomfortable.
Dry eye is a common condition that occurs when your tears aren’t able to provide adequate lubrication for your eyes. Tears can be inadequate for many reasons. For example, dry eyes may occur if you don’t produce enough tears or if you produce poor-quality tears. Dry eyes can also feel very uncomfortable.
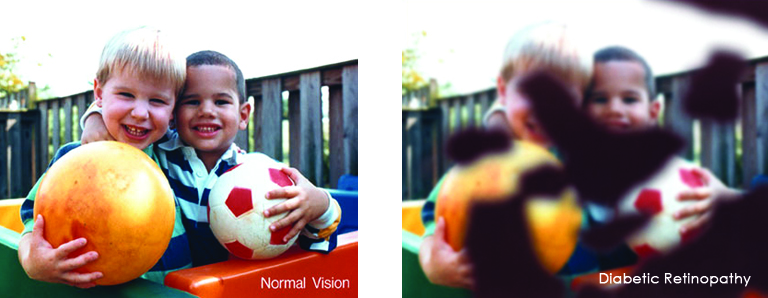
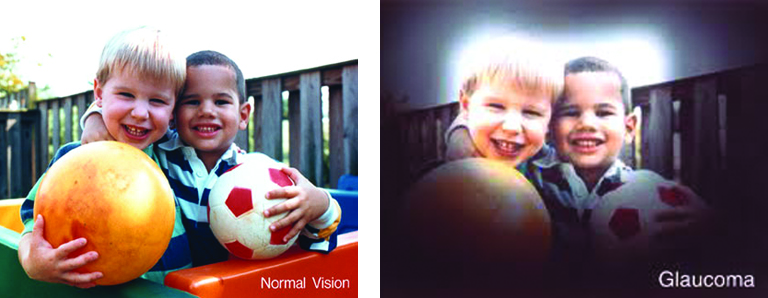
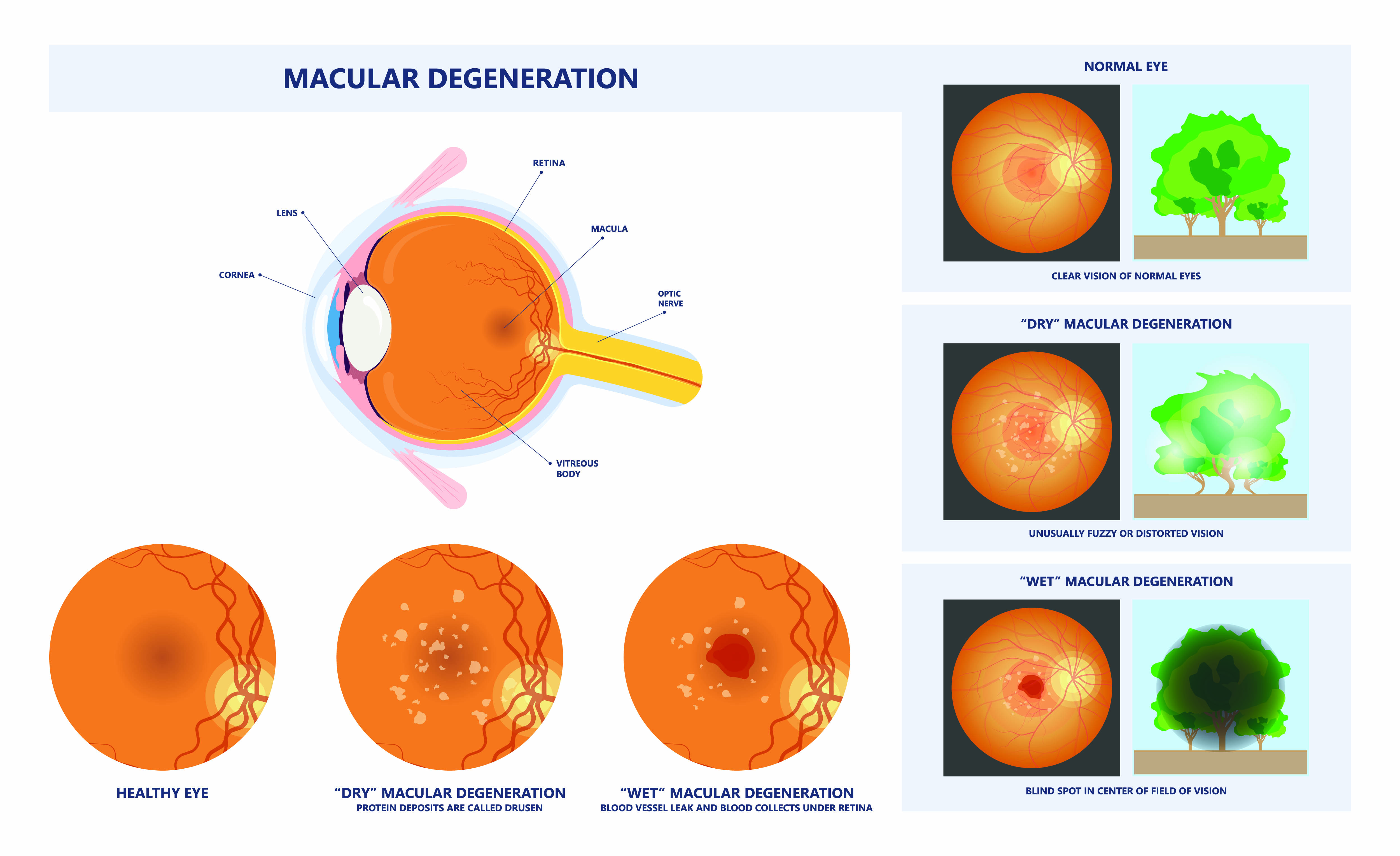
 As winter shifts to spring, and flowers, grasses and trees begin to bloom, spring can take a toll on your eyes if you suffer from seasonal allergies. The spring season has a marked an increase in pollen and allergens in the air, that leave you with congestion, headaches, and itchy, swollen eyes, known as eye allergies.
As winter shifts to spring, and flowers, grasses and trees begin to bloom, spring can take a toll on your eyes if you suffer from seasonal allergies. The spring season has a marked an increase in pollen and allergens in the air, that leave you with congestion, headaches, and itchy, swollen eyes, known as eye allergies. Costume Contact Lenses such as cat eyes or zombie may make your Halloween costume a bit more frightful although wearing those lenses without a prescription can be more terrifying, as it could result in vision loss or even blindness.
Costume Contact Lenses such as cat eyes or zombie may make your Halloween costume a bit more frightful although wearing those lenses without a prescription can be more terrifying, as it could result in vision loss or even blindness.
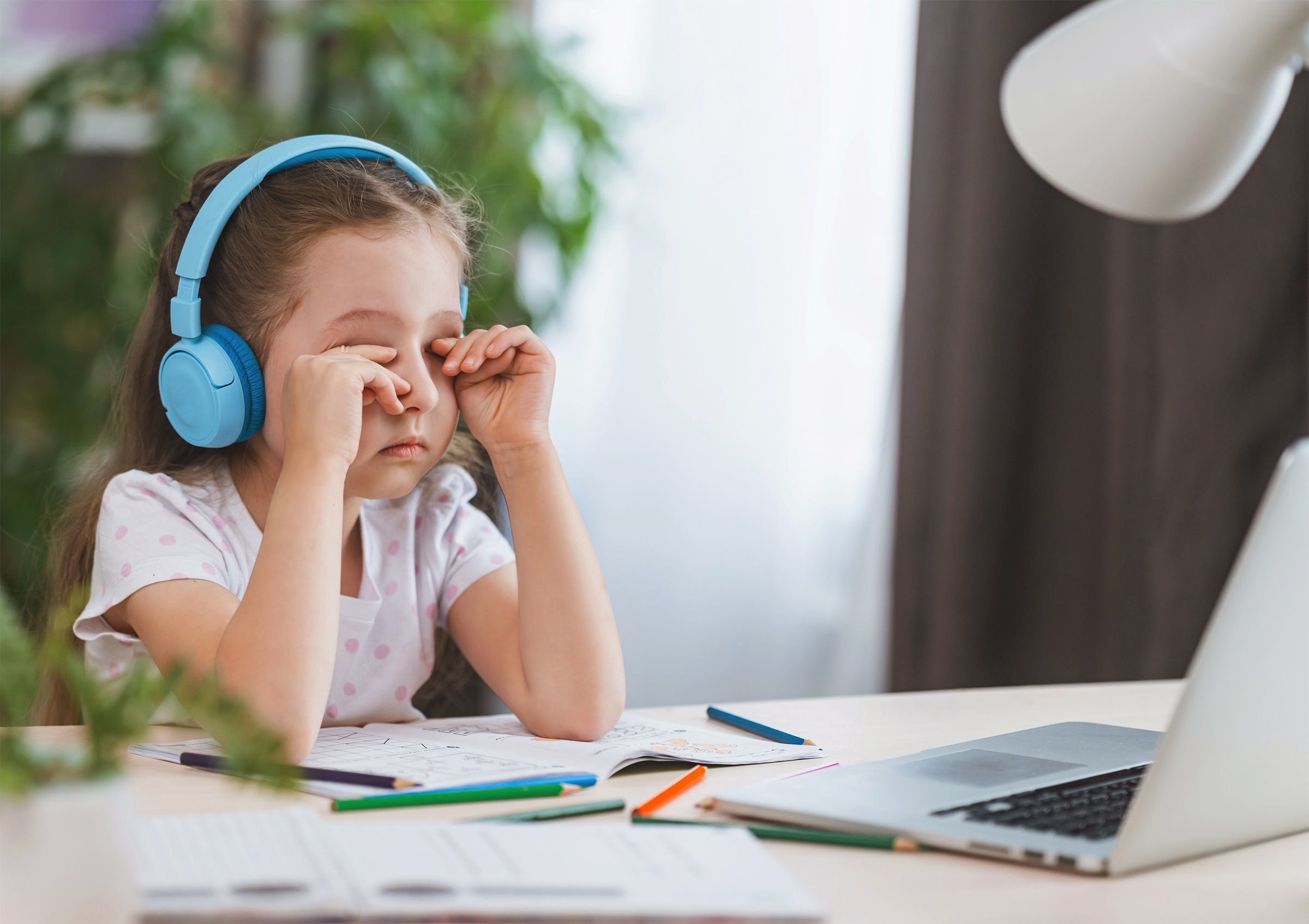
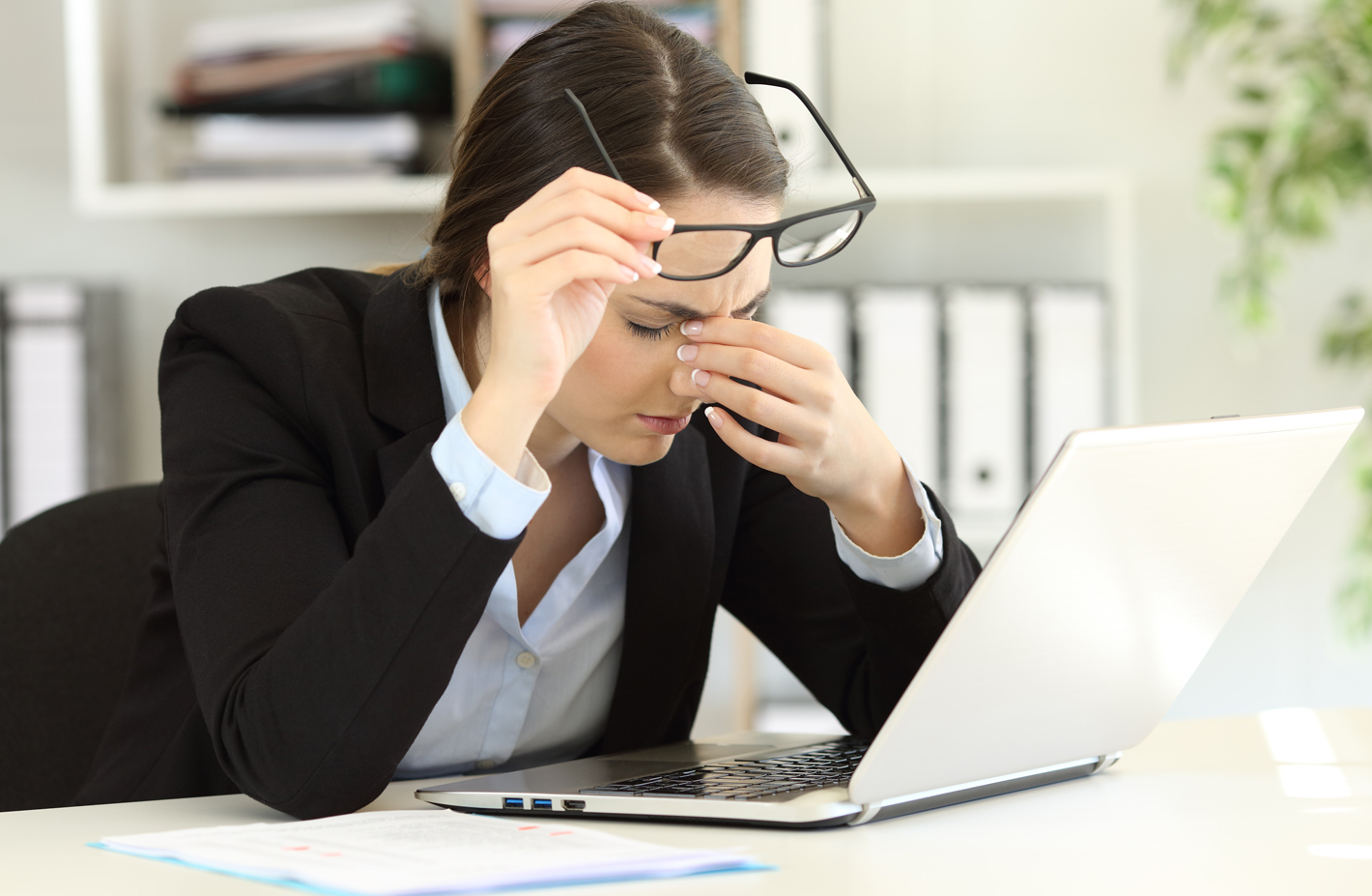













 Rest and blink your eyes – Researchers found that over 30% of people using digital devices rarely take time to rest their eyes. Just over 10% say they never take a break, even when working from home. The eye muscles get overworked and don’t get a chance to relax and recover. Experts suggest the 20-20-20 rule; every 20 minutes, focus your eyes and attention on something 20 feet away for 20 seconds. You can also get up and walk around for a few minutes.
Rest and blink your eyes – Researchers found that over 30% of people using digital devices rarely take time to rest their eyes. Just over 10% say they never take a break, even when working from home. The eye muscles get overworked and don’t get a chance to relax and recover. Experts suggest the 20-20-20 rule; every 20 minutes, focus your eyes and attention on something 20 feet away for 20 seconds. You can also get up and walk around for a few minutes. Reduce exposure to blue light – In the spectrum of light, blue is more high energy and close to ultraviolet light. So, if you use screens throughout the day, ask your eye doctor about the value of computer glasses that block blue light. Reducing exposure to blue light may help lessen vision problems. At home, using digital devices until bedtime can overstimulate your brain and make it more difficult to fall asleep. Eye doctors recommend no screen time at least one to two hours before going to sleep.
Reduce exposure to blue light – In the spectrum of light, blue is more high energy and close to ultraviolet light. So, if you use screens throughout the day, ask your eye doctor about the value of computer glasses that block blue light. Reducing exposure to blue light may help lessen vision problems. At home, using digital devices until bedtime can overstimulate your brain and make it more difficult to fall asleep. Eye doctors recommend no screen time at least one to two hours before going to sleep.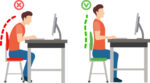 Sit up straight – Proper posture is important. Your back should be straight and your feet on the floor while you work. Elevate your wrists slightly instead of resting them on the keyboard.
Sit up straight – Proper posture is important. Your back should be straight and your feet on the floor while you work. Elevate your wrists slightly instead of resting them on the keyboard. Set up monitor properly – Make sure your computer screen is about 25 inches, or an arm’s length, away from your face. The center of the screen should be about 10-15 degrees below eye level. Cut glare by using a matte screen filter. You can find them for all types of computers, phones, and tablets. Increase font size or set the magnification of the documents you are reading to a comfortable size.
Set up monitor properly – Make sure your computer screen is about 25 inches, or an arm’s length, away from your face. The center of the screen should be about 10-15 degrees below eye level. Cut glare by using a matte screen filter. You can find them for all types of computers, phones, and tablets. Increase font size or set the magnification of the documents you are reading to a comfortable size. Consider computer glasses –For the greatest comfort at your computer, you might benefit from having your eye doctor modify your eyeglasses prescription to create customized computer glasses. This is especially true if you normally wear distance contact lenses, which may also become dry and uncomfortable during extended screen time. Computer glasses also are a good choice if you wear bifocals or progressive lenses, because these lenses generally are not optimal for the distance to your computer screen.
Consider computer glasses –For the greatest comfort at your computer, you might benefit from having your eye doctor modify your eyeglasses prescription to create customized computer glasses. This is especially true if you normally wear distance contact lenses, which may also become dry and uncomfortable during extended screen time. Computer glasses also are a good choice if you wear bifocals or progressive lenses, because these lenses generally are not optimal for the distance to your computer screen. Get an Eye Exam – If you have tried all these tips and eye strain is still an issue, it might be time to see an eye care professional to schedule an eye exam. The exam may even detect underlying issues before they becomes worse.
Get an Eye Exam – If you have tried all these tips and eye strain is still an issue, it might be time to see an eye care professional to schedule an eye exam. The exam may even detect underlying issues before they becomes worse.