Why Lutein & Zeaxanthin are vital for healthy vision.
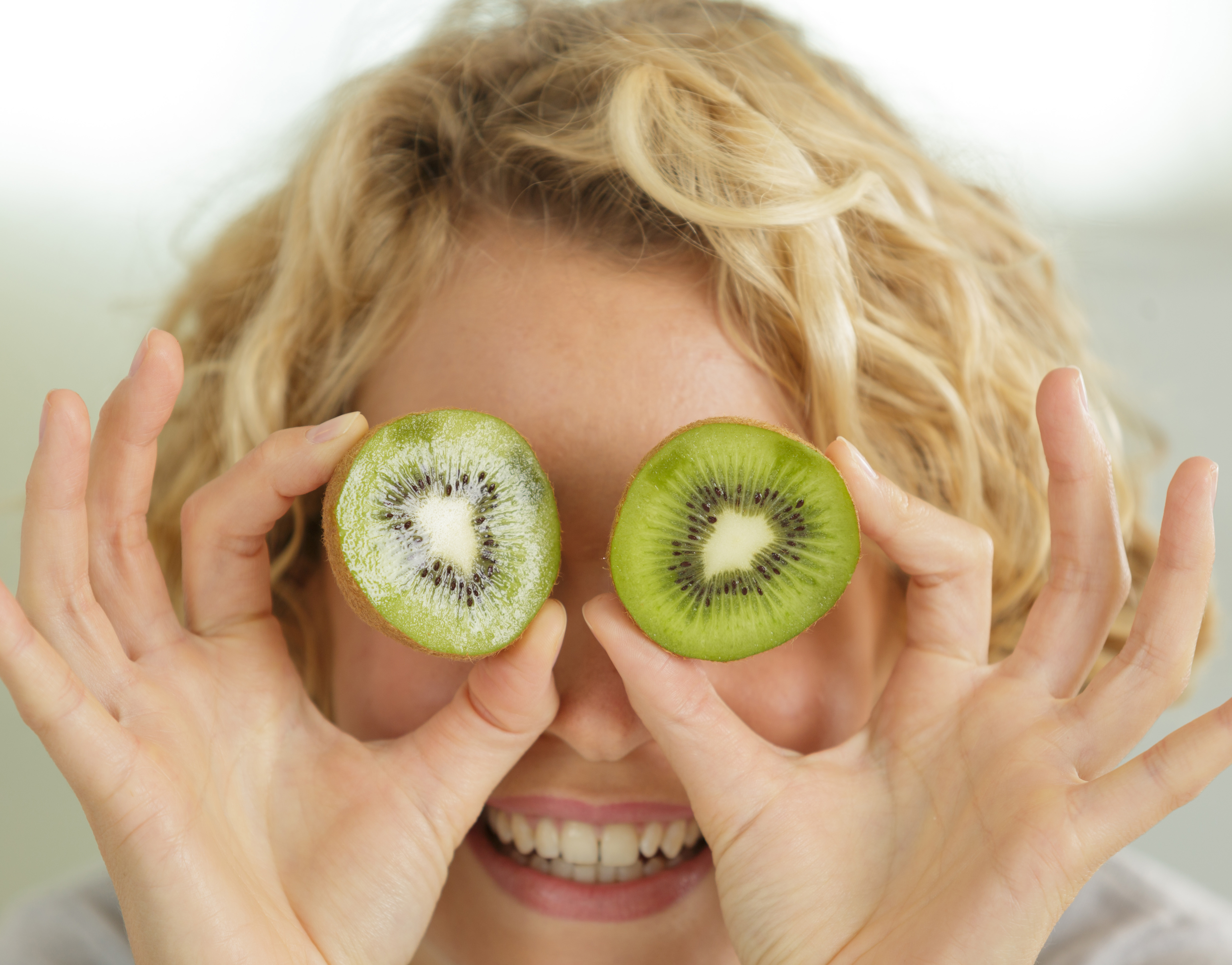 Good nutrition is important to keep your eyes healthy. Researchers have linked two very important eye nutrients that play a key role in healthy vision. Lutein (LOO-teen) and Zeaxanthin (zee-ah-ZAN-thin), both are potent antioxidants and are best known for protecting your eyes and may reduce your risk for macular degeneration and cataracts.
Good nutrition is important to keep your eyes healthy. Researchers have linked two very important eye nutrients that play a key role in healthy vision. Lutein (LOO-teen) and Zeaxanthin (zee-ah-ZAN-thin), both are potent antioxidants and are best known for protecting your eyes and may reduce your risk for macular degeneration and cataracts.
Lutein and zeaxanthin are two types of carotenoids (kuh-RAH-teh-noids), which are yellow to red pigments found widely in vegetables and other plants and lutein is a yellow pigment, in high concentrations it appears orange-red.
Both lutein and zeaxanthin can also be found in high concentrations in the macula of the human eye. The macula is essential for vision. Lutein and zeaxanthin work as important antioxidants in this area by protecting your eyes from harmful free radicals. It’s thought that a reduction of these antioxidants over time can impair eye health. Along with other natural antioxidants, including vitamin C, beta-carotene (vitamin A) and vitamin E, these important pigments guard the body from damaging effects of free radicals, which are reactive molecules that can destroy cells and play a role in many diseases. It is also believed that lutein and zeaxanthin in the macula block blue light from reaching the underlying structures in the retina, thereby reducing the risk of light-induced oxidative damage that could lead to macular degeneration (AMD).
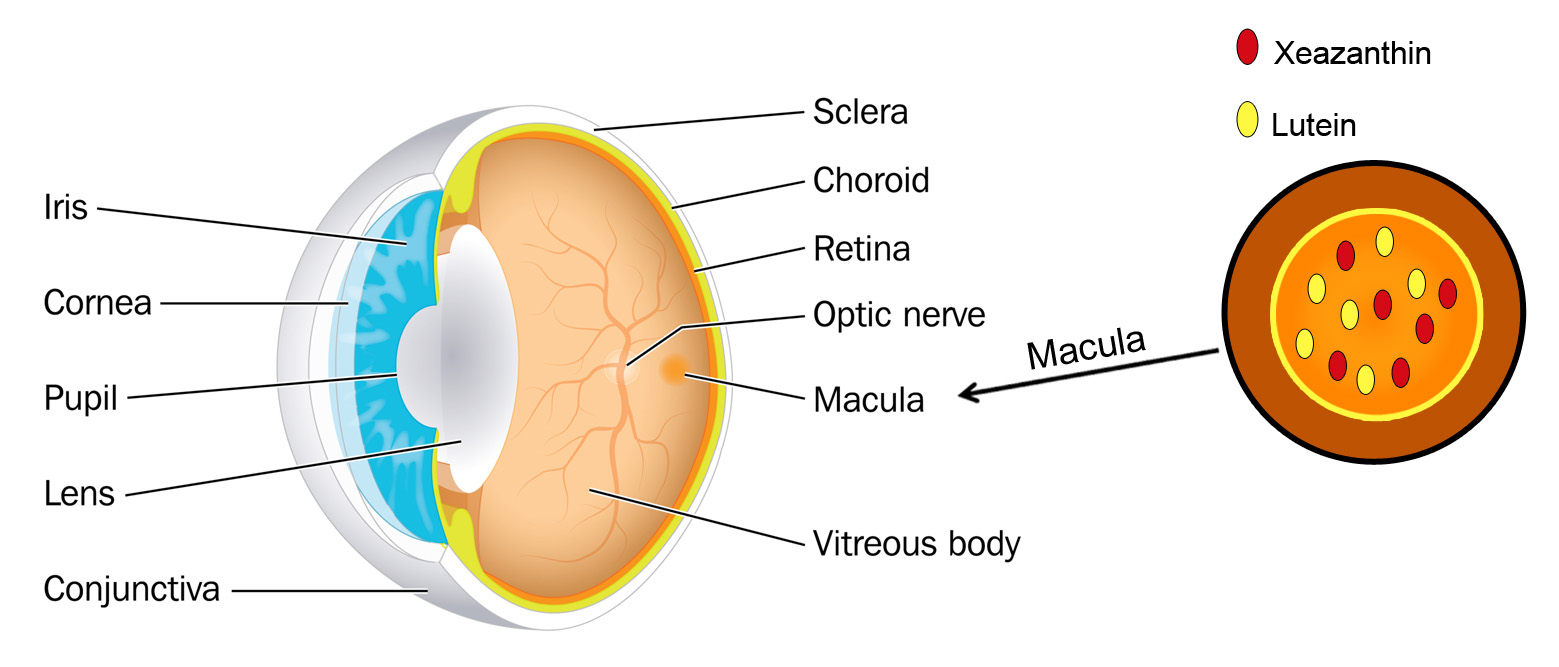
Unfortunately, the human body does not naturally make the lutein and zeaxanthin it needs. This is why getting daily amounts of lutein and zeaxanthin through your diet or nutritional supplements can help maintain good eye health.
Foods that Contain Lutein and Zeaxanthin
 Diets rich in these two nutrients may help hold off age-related eye diseases. The best natural food sources of lutein and zeaxanthin are green leafy vegetables and other green or yellow vegetables. Among these, cooked kale and cooked spinach top the list.
Diets rich in these two nutrients may help hold off age-related eye diseases. The best natural food sources of lutein and zeaxanthin are green leafy vegetables and other green or yellow vegetables. Among these, cooked kale and cooked spinach top the list.
Key sources of these carotenoids include kale, parsley, spinach, broccoli and peas. Orange juice, honeydew melon, kiwis, red peppers, squash and grapes are also good sources of lutein and zeaxanthin.
In addition, egg yolk may be an important source of lutein and zeaxanthin, as the high fat content of the yolk may improve the absorption of these nutrients.
For eye healthy recipes visit Eye Cook
Lutein and Zeaxanthin Supplements
Because of the benefits of lutein and zeaxanthin, many nutritional companies have added these carotenoids to their multiple vitamin formulas. Others have introduced special eye vitamins that are predominantly lutein and zeaxanthin supplements.
Some popular lutein and zeaxanthin supplements include:
- MacuHealth with LMZ3 (MacuHealth LLC)
- EyePromise Zeaxanthin (Zeavision)
- ICaps Eye Vitamin Lutein & Zeaxanthin Formula (Alcon)
- Macula Complete (Biosyntrx)
- MacularProtect Complete (ScienceBased Health)
- MaxiVision Ocular Formula (MedOp)
- OcuGuard Plus (TwinLab)
- Ocuvite (Bausch + Lomb
The source of lutein in many lutein supplements is marigold flowers, while for zeaxanthin it is often red peppers. If you choose a lutein and zeaxanthin supplement, make sure it’s a high quality product from a reputable dietary supplement company.
Be sure to keep in mind that individuals sometimes react differently to certain supplements, which can have unintended effects such as adverse reactions with medications. Consult with your physician or eye doctor before trying any vision supplements.
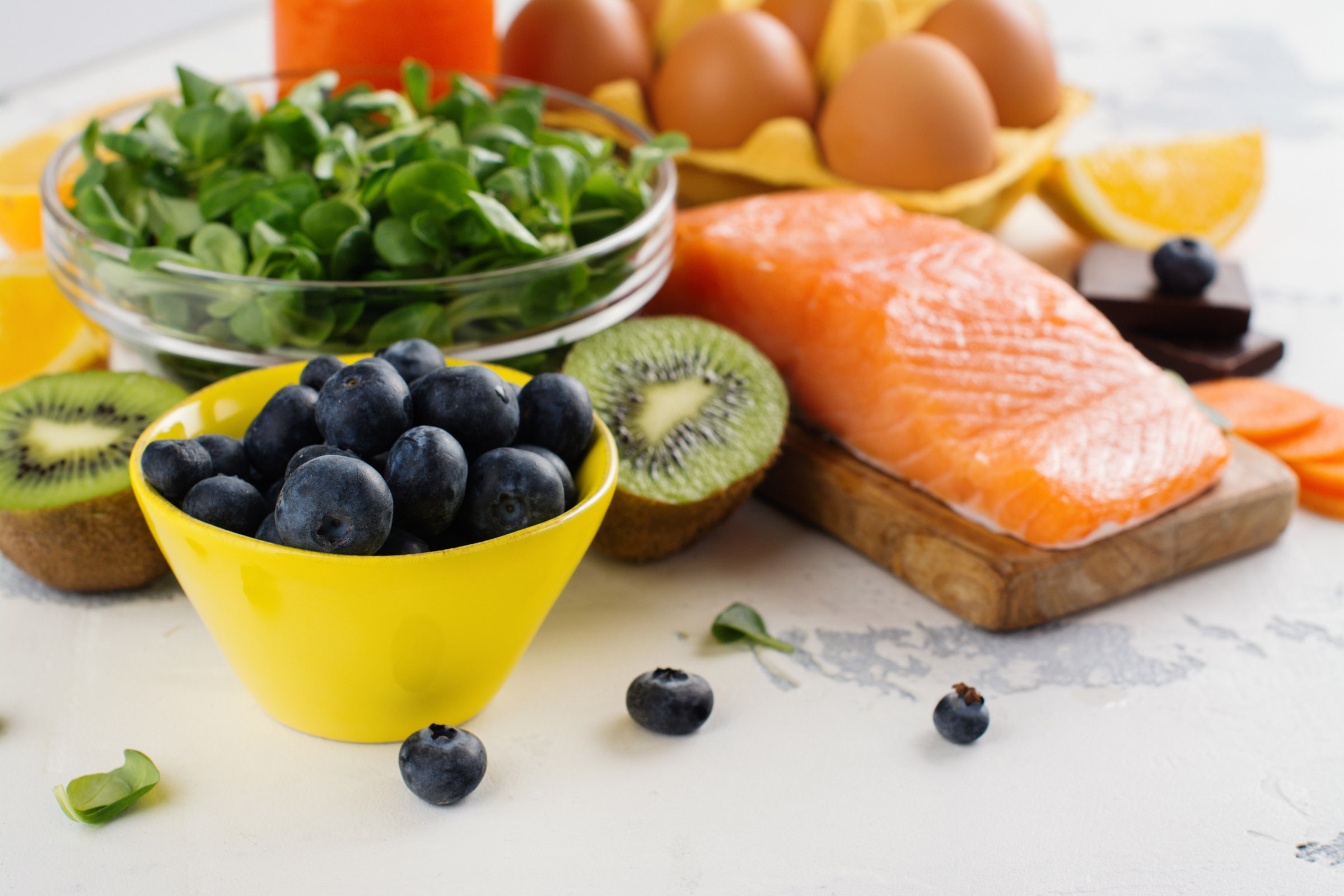

Remember that taking dietary supplements does not replace a healthy diet. Eating a well-balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits and vegetables usually is the best way to get the important eye nutrients you need.



 Lauren Hauptman
Lauren Hauptman The other day my daughter Blythe asked me which Christmas I consider to be my favorite. I had to think a minute, because as a family, the Sullivan’s have had some great ones. I was about to say the first time you and your brother Tom were old enough to really get into Santa, being absolutely sure that the fat man brought your presents right down the chimney. I was about to say that, and then I remembered.
The other day my daughter Blythe asked me which Christmas I consider to be my favorite. I had to think a minute, because as a family, the Sullivan’s have had some great ones. I was about to say the first time you and your brother Tom were old enough to really get into Santa, being absolutely sure that the fat man brought your presents right down the chimney. I was about to say that, and then I remembered.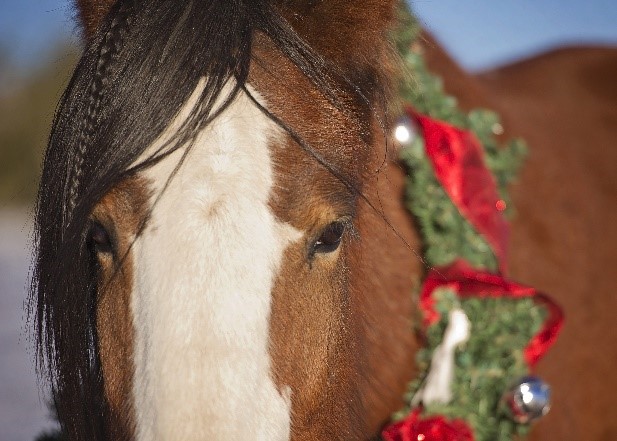  Colorado, when our children were teenagers and our friend, the marvelous Betty White, joined us for a Christmas Eve sleigh ride none of us will ever forget. The night was perfect. It had snowed earlier that day, and the air had a feeling of Christmas that you could almost taste. Oh, sure, it was cold, but we were bundled up under tons of blankets as two beautiful Clydesdale horses with bells jingling took us through the woods to a magical barn where dinner would be served and carols sung.
Colorado, when our children were teenagers and our friend, the marvelous Betty White, joined us for a Christmas Eve sleigh ride none of us will ever forget. The night was perfect. It had snowed earlier that day, and the air had a feeling of Christmas that you could almost taste. Oh, sure, it was cold, but we were bundled up under tons of blankets as two beautiful Clydesdale horses with bells jingling took us through the woods to a magical barn where dinner would be served and carols sung.  Tom Sullivan
Tom Sullivan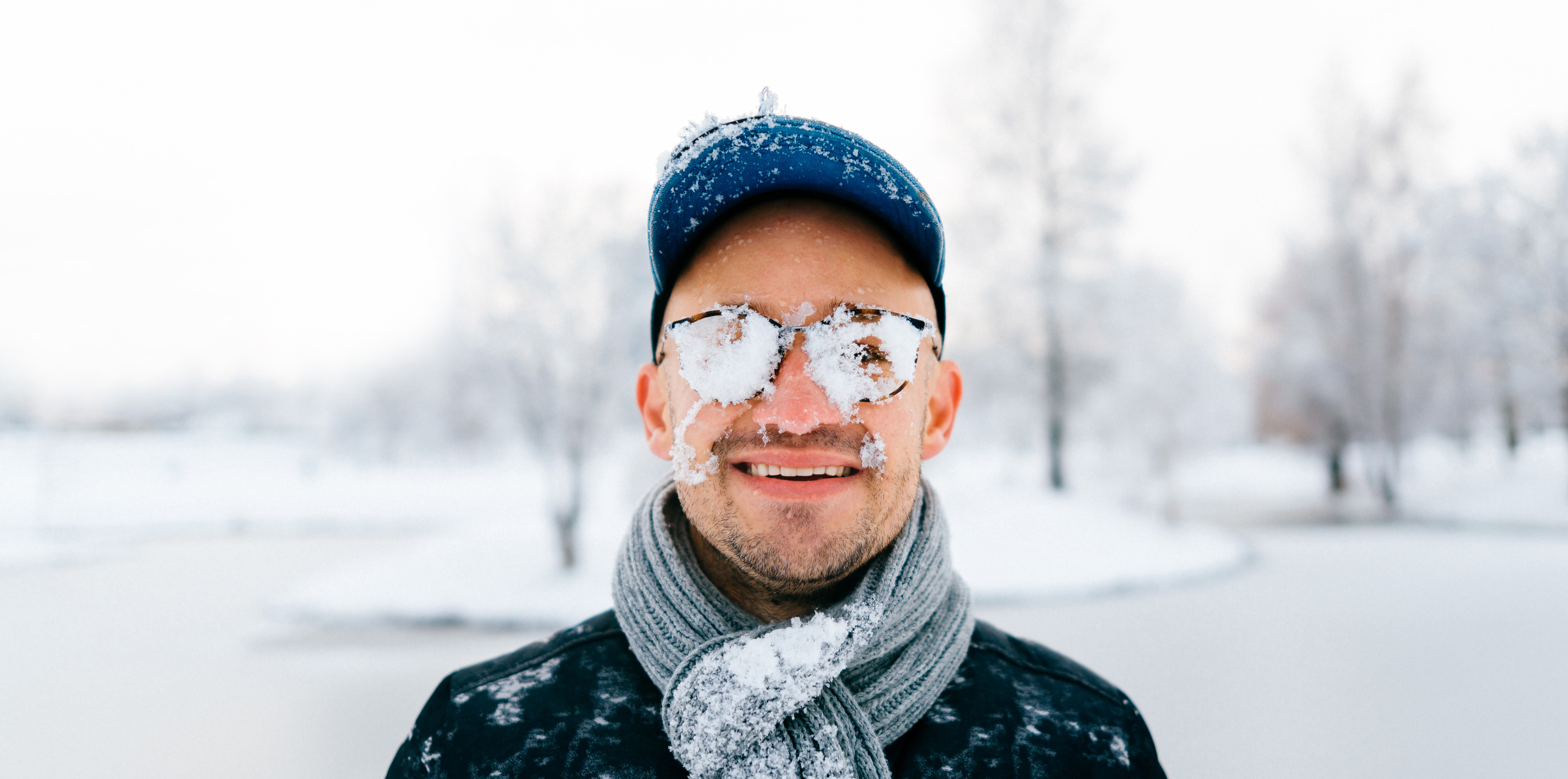 Harsh weather conditions can reduce the natural moisture in your eyes and the irritation usually results in a burning or itching sensation that often leads to rubbing or scratching your eyes which can worsen the symptoms. Sometimes it feels like there is a foreign object in your eye and for some, dry eyes can even cause excessive tearing, as your eyes try to overcompensate for their lack of protective tears. Prolonged, untreated dry eyes can lead to blurred vision as well. Between the harsh winter winds outside and the dry heat radiating inside, our eyes are very quickly irritated and dried in the winter months. The result is itchy, dry eyes that may cause pain, blurred vision, a burning sensation, or even watery vision as our eyes try to compensate for the dryness.
Harsh weather conditions can reduce the natural moisture in your eyes and the irritation usually results in a burning or itching sensation that often leads to rubbing or scratching your eyes which can worsen the symptoms. Sometimes it feels like there is a foreign object in your eye and for some, dry eyes can even cause excessive tearing, as your eyes try to overcompensate for their lack of protective tears. Prolonged, untreated dry eyes can lead to blurred vision as well. Between the harsh winter winds outside and the dry heat radiating inside, our eyes are very quickly irritated and dried in the winter months. The result is itchy, dry eyes that may cause pain, blurred vision, a burning sensation, or even watery vision as our eyes try to compensate for the dryness. I could hear Charlie rubbing his wife’s shoulders and telling her that everything would be alright. But, Rose kept saying “I know we’ll have to sell the house and move into something smaller, and I am going to be blind Charlie. Blind.”
I could hear Charlie rubbing his wife’s shoulders and telling her that everything would be alright. But, Rose kept saying “I know we’ll have to sell the house and move into something smaller, and I am going to be blind Charlie. Blind.” Today, people are living longer than ever before so it’s important to be proactive and take responsibility for your health as you age.
Today, people are living longer than ever before so it’s important to be proactive and take responsibility for your health as you age.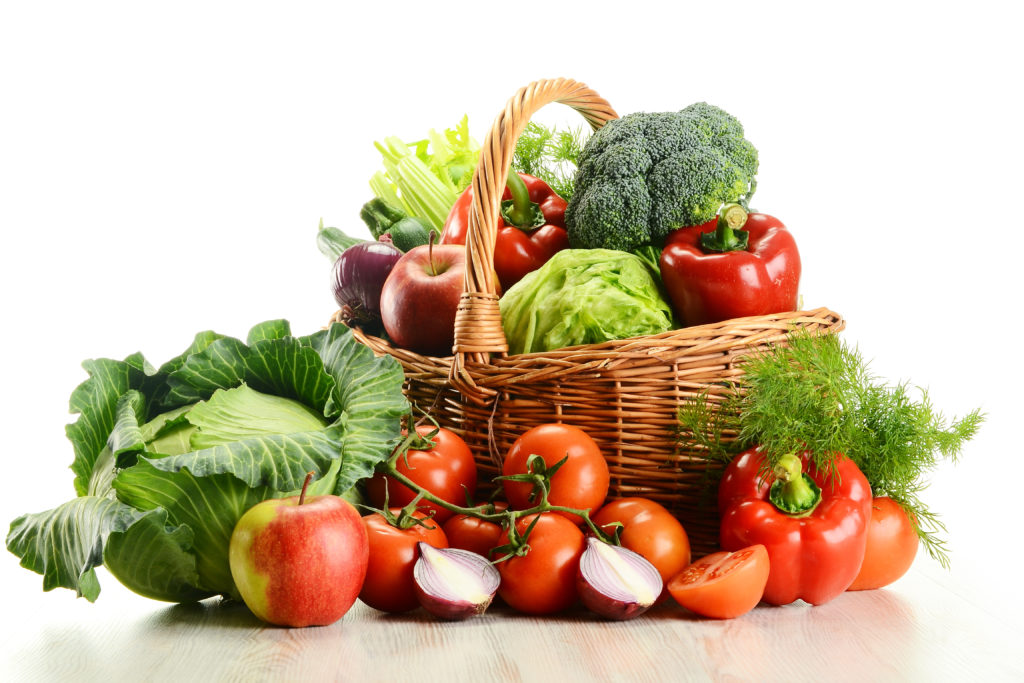 
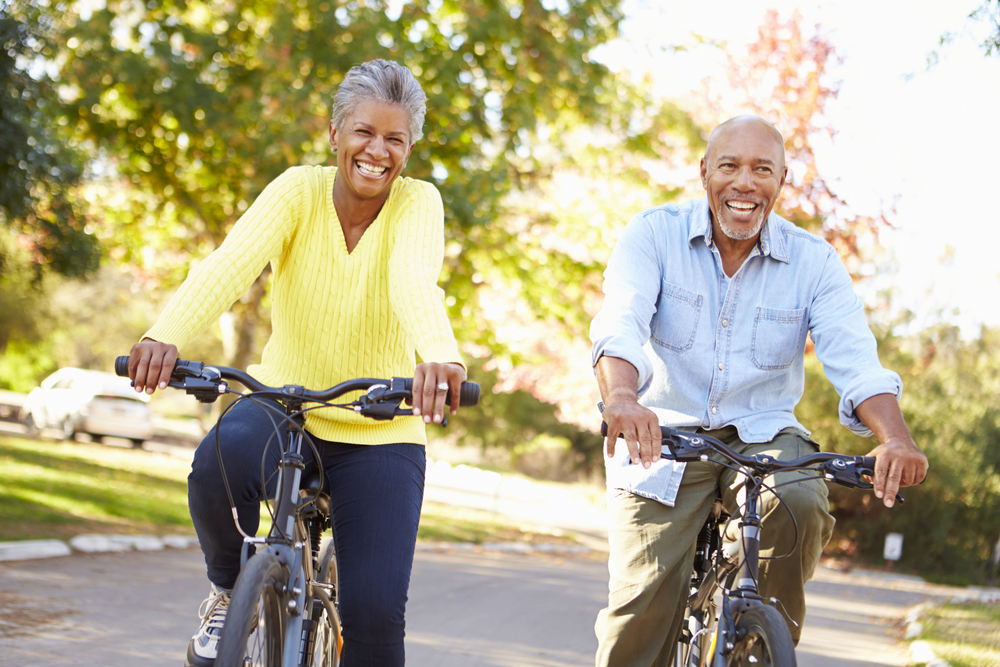 Maintain a healthy weight. Being overweight increases your risk for diabetes. By exercising regularly, you can help keep your body healthy and prevent vision loss.
Maintain a healthy weight. Being overweight increases your risk for diabetes. By exercising regularly, you can help keep your body healthy and prevent vision loss.  Don’t smoke. Smoking increases your risk for age-related macular degeneration, cataract, and other eye diseases and conditions that can damage the optic nerve.
Don’t smoke. Smoking increases your risk for age-related macular degeneration, cataract, and other eye diseases and conditions that can damage the optic nerve. Wear protective eyewear when outdoors. Protecting your eyes from the sun’s ultraviolet rays when you are outdoors is vital for your eye health. Wearing sunglasses that block 99 to 100 percent of both UV-A and UV-B radiation.
Wear protective eyewear when outdoors. Protecting your eyes from the sun’s ultraviolet rays when you are outdoors is vital for your eye health. Wearing sunglasses that block 99 to 100 percent of both UV-A and UV-B radiation. Know your family history. Talk to your family members about their eye health history. It’s important to know if anyone has been diagnosed with a disease or condition since many are hereditary, such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetes . This will help determine if you are at higher risk for developing an eye disease or condition.
Know your family history. Talk to your family members about their eye health history. It’s important to know if anyone has been diagnosed with a disease or condition since many are hereditary, such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetes . This will help determine if you are at higher risk for developing an eye disease or condition. Consider a multivitamin. Vitamins C, E and the mineral zinc have been shown to promote eye health. Vitamins with Lutein and Zeaxanthin have been known to help patients with moderate to severe age-related macular degeneration.
Consider a multivitamin. Vitamins C, E and the mineral zinc have been shown to promote eye health. Vitamins with Lutein and Zeaxanthin have been known to help patients with moderate to severe age-related macular degeneration. Give your eyes a rest. If you spend a lot of time at the computer or focusing at any one distance, you sometimes forget to blink, resulting in dryness and eye fatigue. Every 20 minutes, look away about 20 feet in front of you for 20 seconds. This can help reduce eyestrain. Consider using a lubricant eye drop during long periods of intense eye use and rest your eyes for 5 minutes.
Give your eyes a rest. If you spend a lot of time at the computer or focusing at any one distance, you sometimes forget to blink, resulting in dryness and eye fatigue. Every 20 minutes, look away about 20 feet in front of you for 20 seconds. This can help reduce eyestrain. Consider using a lubricant eye drop during long periods of intense eye use and rest your eyes for 5 minutes.
 Tom Sullivan
Tom Sullivan





 The Difference Between an
The Difference Between an