6/17/14
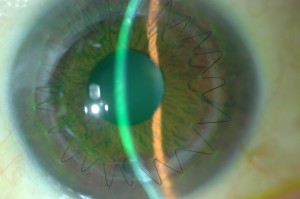
In the United States, more than 40,000 corneal transplants are performed each year with a high success rate in comparison to other types of organ transplants. According to the Eye Bank Association of America (EBAA), keratoconus was the leading cause of anterior lamellar keratoplasty (DALK/ALK partial thickness transplant) and was the fourth most common indication for penetrating keratoplasty surgery in 2012 (their last reporting period).
Advances in technology have led to increasingly successful outcomes for all who need corneal transplants. New long-term research of corneal transplant patients have shown that the age of corneal donors is no longer as important as once thought by eye health providers. According to a study funded by the National Institutes of Health, ten years after a transplant, a cornea from a 71-year-old donor is likely to remain as healthy as a cornea from a donor half that age.
The Cornea Donor Study (see www.ClinicalTrials.gov), funded by NIH’s National Eye Institute (NEI), was designed to compare graft survival rates for corneas from two donor age groups, aged 12-65 and aged 66-75. It was coordinated by the Jaeb Center for Health Research in Tampa, Fla., and involved 80 clinical sites across the United States. The study enrolled 1,090 people eligible for transplants, ages 40-80. Donor corneas were provided by 43 eye banks, and met the quality standards of the Eye Bank Association of America. The study found that 10-year success rates remained steady at 75 percent for corneal transplants from donors 34-71 years old. In the United States, three-fourths of cornea donors are within this age range, and one-third of donors are at the upper end of the range, from 61-70 years old.
Prior to this study, many surgeons would not accept corneas from donors over 65. Since the supply of young donor corneas is limited, these study results are encouraging for those who face a corneal transplant . The high level of success rates using corneas from older donors (over age 60) greatly increases the pool of donated corneas and corneal tissue available for transplant. In 2012, corneal donors under age 31 comprised less than 10 percent of the U.S. donor pool. “Our study supports continued expansion of the corneal donor pool beyond age 65,” said study co-chair Edward J. Holland, M.D., professor of ophthalmology at the University of Cincinnati and director of the Cornea Service at the Cincinnati Eye Institute. “We found that transplant success rates were similar across a broad range of donor ages.”
“Overall, the findings clearly demonstrate that most corneal transplants have remarkable longevity regardless of donor age,” said Mark Mannis, M.D., chair of ophthalmology at the University of California, Davis, and co-chair of the study. “The majority of patients continued to do well after 10 years, even those who received corneas from the oldest donors.”
SOURCE: National Eye Institute Press Releases
For information about Eye Bank Association of America
 Cathy Warren, RN
Cathy Warren, RN
Executive Director
National Keratoconus Foundation