People afflicted with keratoconus (KC) are often obligated to wear contact lenses in order to obtain functional vision. Unfortunately, wearing contact lenses can have detrimental effects on the ocular surface and tear film layers over the course of decades, ultimately reducing lens tolerance. Therefore, any intervention prolonging the comfortable wear time of contact lenses should be aggressively pursued. The tear film covers the surface of the eye, provides lubrication and is the primary defense against foreign bodies and infection. Without a robust and healthy tear film, safe and comfortable contact lens wear is not possible. This article will describe the structure of the tear film and review simple remedies that can keep it healthy throughout life.
Tear Film Layers
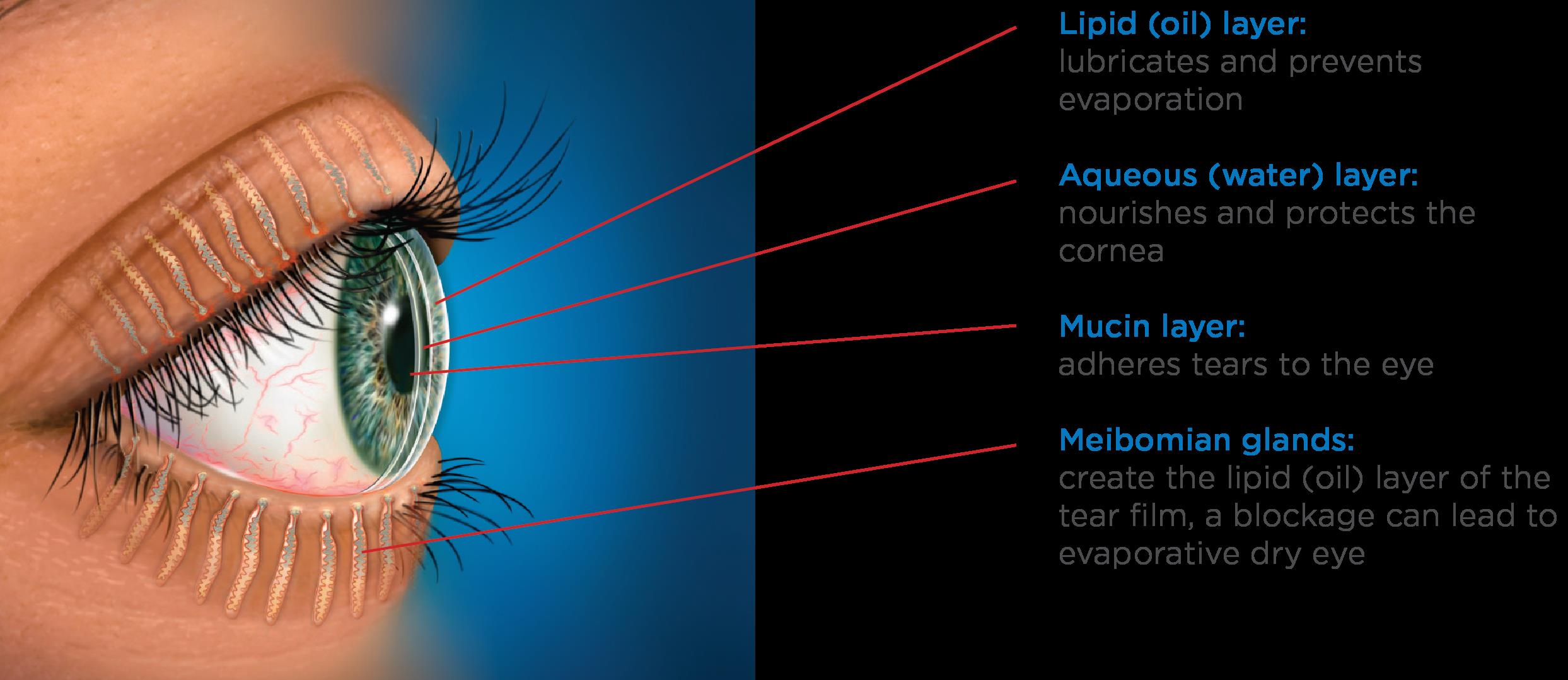
The tear film is a complex, triple layered structure comprised of mucus, water and oil. The surface of the cornea and conjunctiva contain cells specialized to secrete a sticky mucoid substance. These so called goblet cells produce the mucin layer of the tears, which creates a “Velcro” type interface and allows the overlying watery component to stick to the ocular surface without washing away.
The bulk of the tear film is comprised of the watery, or “aqueous” layer which is secreted primarily by the lacrimal gland. This specialized structure is located near the eyebrow. This gland continuously releases small amounts of watery fluid that also contains enzymes and antibodies to help fight infection and wash away contaminants.
The lipid layer is the final, outermost layer of the tears. If the tear film is the first line of defense for the ocular surface, then the lipid layer is the first line of defense for the entire tear film and the ocular surface combined. Because of that role, it is extremely important and helps stabilize the tear film by preventing evaporation. This thin, lipid based layer is released by the meibomian glands, which are modified sebaceous glands that reside in the upper and lower lids. In each lid there are 20-30 glands. These glands open up onto the lid margin and through the action of a complete blink, release the lipid secretion to ocular surface which gets spread with the upward motion of the upper eyelid.
Each one of these layers contributes to the structure of the tear film, and a problem with any one of these structures (goblet cells, lacrimal gland or meibomian glands) will negatively impact the corresponding tear layer.
Tear Film Issues
Because the tear film is so thin, each individual component is necessary to maintain the integrity of the tears as a whole. When any layer of the tear film is deficient, the tear film becomes unstable and the ocular surface becomes irritated and can progress to developing classic symptoms of dry eye. This includes burning, stinging, redness, tearing, fatigue and contact lens intolerance.
Deficiencies in the mucin layer are uncommon, and are typically the result of chemical or thermal insult, or scarring. An aqueous deficiency, primarily from a lacrimal gland related etiology, is also relatively uncommon, and can arise from autoimmune and inflammatory causes such as Sjögren’s Syndrome. The most common reason for a poor tear film is linked with excessive evaporation of our tears due to a lack of sufficient lipid secretions from non-functioning or obstructed meibomian glands. It is understood that many factors contribute to why these glands stop performing optimally.
One factor has been linked to our habitual working environments. The compressive force exerted by the muscles of our eyelids that control blinking are essential for lipid secretion. However, the use of computers or wearing contact lenses has been shown to negatively impact our blinking habits, both by reducing the number of blinks and making blinks less complete. With an incomplete blink, the upper and lower lids do not make contact. The negative consequences of this are 1) the meibomian glands do not release their lipid contents, 2) the lower part of the eye is chronically exposed to the air, increasing evaporative stress and 3) dead skin cells accumulate on the lid margin which can clog the meibomian gland openings.
When increased evaporation of the tear film occurs chronically, the integrity of the entire ocular system becomes compromised over time and problems to the health of the eye become permanent attributes. This condition is known as Meibomian Gland Dysfunction or MGD and is linked with 86% of all dry eye sufferers.
The characteristics of the post lens tear film can differ depending on the type of lens that is worn. For example, soft lenses and scleral lenses have very little turnover of this post-lens tear film. This can cause issues related to the build up of toxic waste and bacterial elements that ultimately aggravate the corneal surface. Conversely, rigid gas permeable lenses are designed to have substantial tear turnover behind the contact lens with every blink.
The pre-lens tear film is also greatly affected by the type of lens material, as well as the interaction between the lid and the contact lens surfaces. Eye doctors know that without a healthy tear film, chances for contact lens intolerance increases. The rate of contact lens intolerance substantially increases as patients enter their fourth decade of life, primarily because of MGD caused by years of poor blinking habits.
Tear Film Care
Fortunately, simple interventions can prevent and/or limit the severity of MGD altogether or help to manage it once it occurs. Just like brushing and flossing one’s teeth can prevent gum disease, attention to complete blinking and lid margin hygiene can improve the tear film and prevent contact lens intolerance problems.
Because partial blinking is strongly linked with developing MGD, it is vitally important that the two lids touch when blinking. It is best to practice this several times throughout the day as well as when you are reading or using the computer.
Akin to flossing the teeth, it is also important to clean the lid margins with a Q-tip soaked in saline solution or a bit of mineral oil by gently brushing the Q-tip across the lid margin 10-20 times each night. It is easiest to get the lower lid.
Finally, performing warm compresses daily can provide heat to the Meibomian glands to soften the hardened oil that can plug the meibomian gland ducts. Warm compresses need to be done continuously for at least 10 minutes with consistent heat in order to attain a temperature that is sufficient to melt the oil that clogs the glands. We recommend folding 5-6 small towels or facecloths into a rectangular shape and wrapped together into a circular bundle, similar to the appearance of a cinnamon roll. The towels should be damp and moist, placed in a microwaveable safe dish with a lid and heated for approximately 1 minute and 50 seconds. After removal, wait a minute or two and then proceed to use the outermost cloth and cover the rest. Replace the first cloth after two minutes and grab the next outer most towel from the bundle, continuing this until all towels are used. In this way, the temperature can be adequately maintained for the full 10 minutes. The high temperatures applied to the lid are transferred to the cornea and very often cause temporary deformation, a phenomenon characterized by transient visual blur immediately following compress application. Therefore, it is vitally important, especially for patients with keratoconus, that pressure never be exerted onto the globe of the eye with a compress or massage administered to the lids of closed eyes after a compress.
It is becoming apparent that MGD is developing in patients at earlier ages. Because of this, the condition has likely been present for decades by the time the patient becomes symptomatic. It may take significant time and effort to rehabilitate not only the glands themselves, but also to reduce the resulting inflammation of the ocular surface.
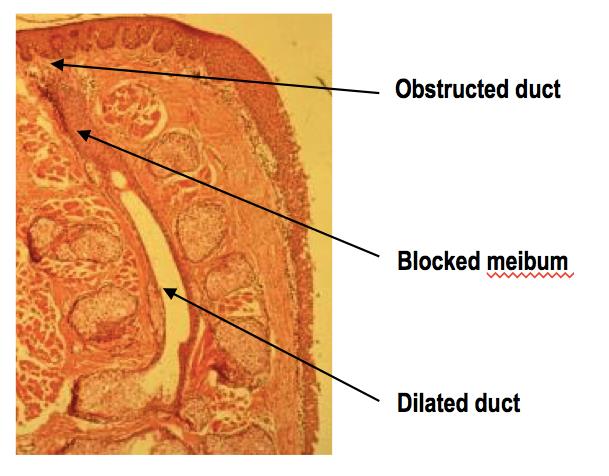
Meibography is the technique used to image Meibomian glands. In chronic cases of MGD, we see abnormal changes to gland structure, in the form of atrophy or loss of gland tissue and/or dilation of glands where obstructed material causes glands to become widened. In severe cases, the prognosis for recovery is guarded.
The visual clarity that contact lenses provide for patients with keratoconus is incredibly important. But the ability to comfortably wear contact lenses is reliant on our body’s ability to provide a sufficiently thick protective tear film. Taking a small amount of time daily to attend to the lipid producing Meibomian glands by proper blinking habits, exfoliation of the lid margin with a Q-tip and warm compresses will help to extend the number of hours, and ultimately the number of years, that contact lenses can be safely and comfortably worn.
10/20/15
 Amy Nau, OD
Amy Nau, OD
Korb and Associates, Boston, MA
Contact lens fitting for keratoconus, other ocular surface disorders and dry eye
 David Murakami, MPH, OD, FAAO
David Murakami, MPH, OD, FAAO
Tear Science, Inc.
Researcher, Dry Eye

