Why You Need An Eye Exam
The end of the year is fast approaching – when was the last time you had an eye exam? Was it a comprehensive eye exam?

To keep your eyes healthy and maintain your vision, the American Optometric Association (AOA) recommends a comprehensive eye exam every two years for adults ages 18 to 60, and annual exams for people age 61 and older. However, if you have a family history of eye disease (glaucoma, macular degeneration, etc.), diabetes or high blood pressure, or have had an eye injury or surgery, you should have a comprehensive exam every year, unless otherwise indicated by your doctor.
Also, adults who wear contact lenses should have annual eye exams.
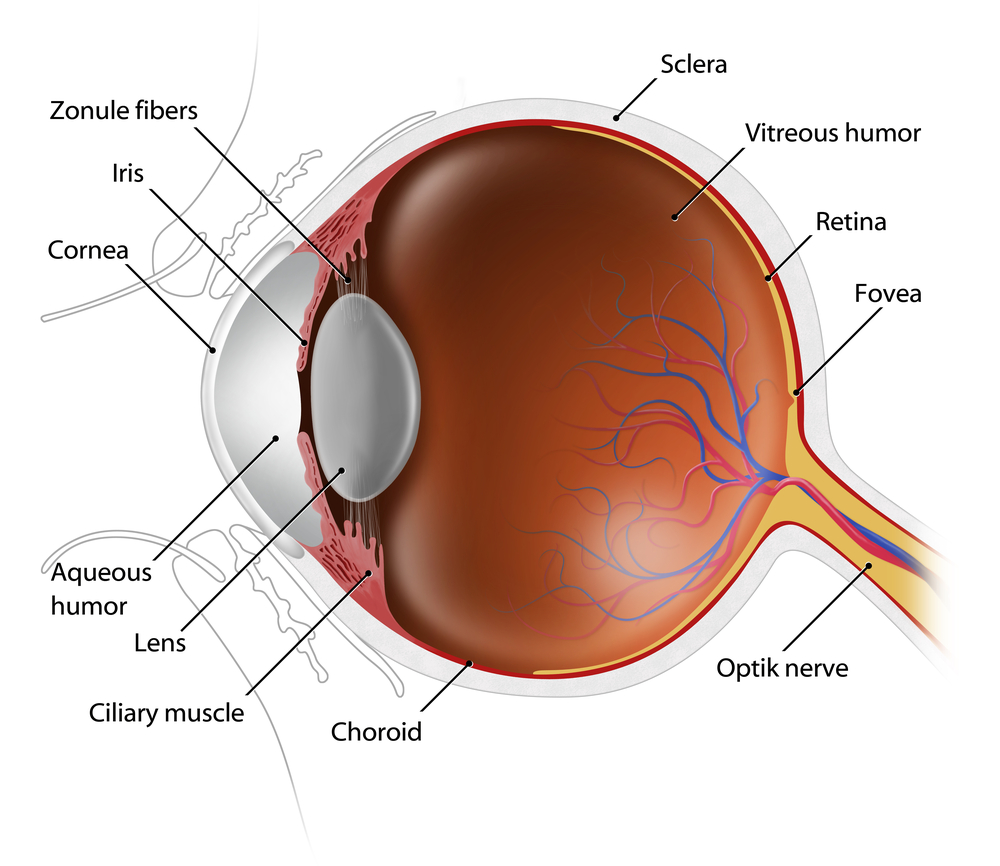
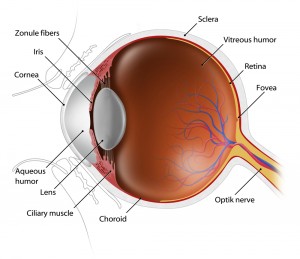
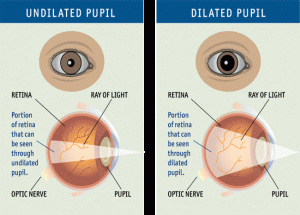
An important part of the comprehensive eye exam is the dilated eye exam to look inside your eye. Drops are placed in each eye to widen the pupil and allow more light to enter the eye. This gives your doctor a clear view of important tissues at the back of the eye, including the retina, the macula, and the optic nerve. This allows for early diagnosis of sight-threatening eye diseases like age-related macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, etc.
To better understand the importance of the dilated eye exam, here is a video from the National Eye Institute (NE) that explains what to expect.
At the end of your comprehensive eye exam your doctor should raise any concerns he has with you. But it is up to you to be prepared to react and ask questions for peace of mind and to help save your vision.
Questions To Ask After Your Eye Exam
It is always important to know if anything about your eyes have changed since your last visit. If the doctor says no, then the only thing you need to know is when they want to see you again.
If the doctor says the have been some minor changes, you need to know what questions to ask, such as:
- Is my condition stable, or can I lose more sight?
- What new symptoms should I watch out for?
- Is there anything I can do to improve or help my vision?
- When is the next time you want to see me?
If the doctor sees a marked change in your vision or give you a diagnosis of eye disease, you would want to ask:
- Are there treatments for my eye disease?
- When should I start treatment and how long will it last?
- What are the benefits of this treatment and how successful is it?
- What are the risks and possible side effects associated with this treatment?
- Are there any foods, medications, or activities I should avoid while I am undergoing this treatment?
- If I need to take medication, what should I do if I miss a dose or have a reaction?
- Are there any other treatments available?
- Will I need more tests necessary later?
- How often should I schedule follow-up visits? Should I be monitored on a regular basis?
- Am I still safe to drive?
Your vision is a terrible thing to lose, but with proper diet, exercise and no smoking, along with regularly scheduled eye exams, you improve your chances of maintaining your sight.
11/5/15