 Healthy Aging Month is an annual health observance designed to focus national attention on the positive aspects of growing older. Aging is a process that brings many changes. Vision loss and blindness, however, do not have to be one of them. There are several simple steps you can take to help keep your eyes healthy for the rest of your life.
Healthy Aging Month is an annual health observance designed to focus national attention on the positive aspects of growing older. Aging is a process that brings many changes. Vision loss and blindness, however, do not have to be one of them. There are several simple steps you can take to help keep your eyes healthy for the rest of your life.
Eye diseases often have no early symptoms, but can be detected during a comprehensive dilated eye exam. A comprehensive dilated eye exam is different from the basic eye exam or screening you have for glasses or contacts. By dilating the pupils and examining the back of the eyes, your eye care professional can detect eye diseases in their early stages, before vision loss occurs. By performing a comprehensive eye exam, your eye care professional can check for early signs of –
Here are some other tips to maintain healthy vision now and as you age:

- Eat a healthy, balanced diet. Fruits and vegetables can help keep your eyes healthy. Visit our website for healthy eye recipes, click here Eye Cook.
 Maintain a healthy weight. Being overweight increases your risk for diabetes. By exercising regularly, you can help keep your body healthy and prevent vision loss.
Maintain a healthy weight. Being overweight increases your risk for diabetes. By exercising regularly, you can help keep your body healthy and prevent vision loss.
 Don’t smoke. Smoking increases your risk for age-related macular degeneration, cataract, and other eye diseases and conditions that can damage the optic nerve.
Don’t smoke. Smoking increases your risk for age-related macular degeneration, cataract, and other eye diseases and conditions that can damage the optic nerve.
 Wear protective eyewear when outdoors. Protecting your eyes from the sun’s ultraviolet rays when you are outdoors is vital for your eye health. Wearing sunglasses that block 99 to 100 percent of both UV-A and UV-B radiation.
Wear protective eyewear when outdoors. Protecting your eyes from the sun’s ultraviolet rays when you are outdoors is vital for your eye health. Wearing sunglasses that block 99 to 100 percent of both UV-A and UV-B radiation.
 Know your family history. Talk to your family members about their eye health history. It’s important to know if anyone has been diagnosed with a disease or condition since many are hereditary, such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetes . This will help determine if you are at higher risk for developing an eye disease or condition.
Know your family history. Talk to your family members about their eye health history. It’s important to know if anyone has been diagnosed with a disease or condition since many are hereditary, such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetes . This will help determine if you are at higher risk for developing an eye disease or condition.
 Consider a multivitamin. Vitamins C, E and the mineral zinc have been shown to promote eye health. Vitamins with Lutein and Zeaxanthin have been known to help patients with moderate to severe age-related macular degeneration.
Consider a multivitamin. Vitamins C, E and the mineral zinc have been shown to promote eye health. Vitamins with Lutein and Zeaxanthin have been known to help patients with moderate to severe age-related macular degeneration.
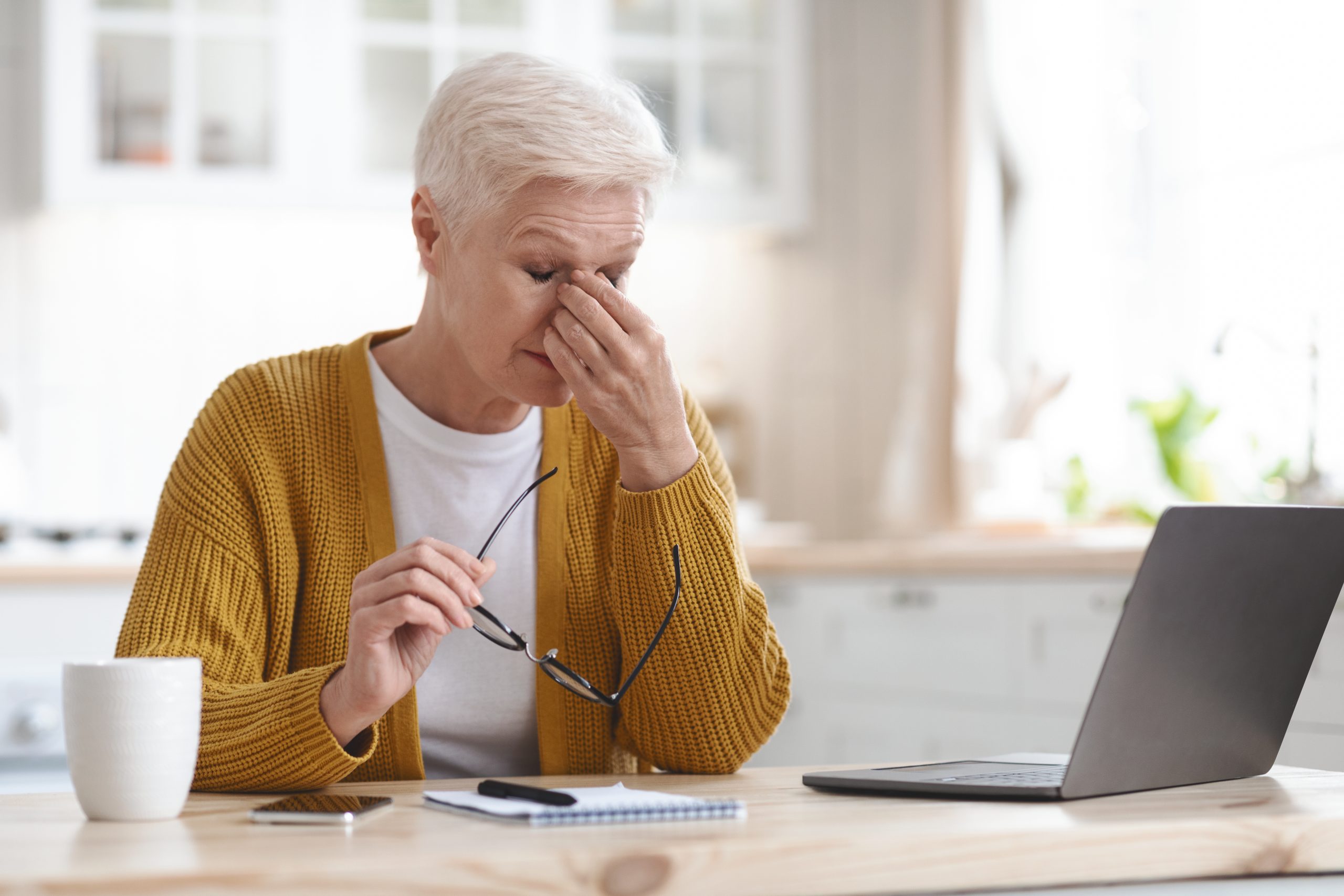 Give your eyes a rest. If you spend a lot of time at the computer or focusing at any one distance, you sometimes forget to blink, resulting in dryness and eye fatigue. Every 20 minutes, look away about 20 feet in front of you for 20 seconds. This can help reduce eyestrain. Consider using a lubricant eye drop during long periods of intense eye use and rest your eyes for 5 minutes.
Give your eyes a rest. If you spend a lot of time at the computer or focusing at any one distance, you sometimes forget to blink, resulting in dryness and eye fatigue. Every 20 minutes, look away about 20 feet in front of you for 20 seconds. This can help reduce eyestrain. Consider using a lubricant eye drop during long periods of intense eye use and rest your eyes for 5 minutes.
You can’t stop time, but you can take care of your eyes so that they remain healthy as you age. Having a healthy vision can be possible at any age! Even if you are not experiencing vision problems, visiting an eye care professional regularly for a comprehensive dilated eye exam is the most important thing you can do to reduce your risk of vision loss as you age.
Download “Everyone’s vision can change with age”
A handout with explanation on how vision can change with age.







 Be sure to start your holiday meal with a salad, it’s an excellent way to ensure that you and your guests get plenty of zeaxanthin and lutein, two nutrients that help protect your central vision. Adding kale, spinach, or romaine lettuce to salads helps your eyes absorb damaging blue light, combats the effects of cigarette smoke and pollution, and also decreases your risk of developing
Be sure to start your holiday meal with a salad, it’s an excellent way to ensure that you and your guests get plenty of zeaxanthin and lutein, two nutrients that help protect your central vision. Adding kale, spinach, or romaine lettuce to salads helps your eyes absorb damaging blue light, combats the effects of cigarette smoke and pollution, and also decreases your risk of developing  Turkey and lean beef, two of the main ingredients in many holiday meals, keep your eyes strong and healthy. Both foods are high in zinc, a nutrient important to the retina and the choroid layer under the retina.
Turkey and lean beef, two of the main ingredients in many holiday meals, keep your eyes strong and healthy. Both foods are high in zinc, a nutrient important to the retina and the choroid layer under the retina.  Zinc is essential for good night vision. Eating foods that are high in the nutrient can also reduce your risk of cataracts and AMD. Other foods that contain zinc include pork, dairy products, chick peas, black-eyed peas, crab, oysters, beans, spinach, mushrooms, cashews, and almonds.
Zinc is essential for good night vision. Eating foods that are high in the nutrient can also reduce your risk of cataracts and AMD. Other foods that contain zinc include pork, dairy products, chick peas, black-eyed peas, crab, oysters, beans, spinach, mushrooms, cashews, and almonds.  It wasn’t an old wives tale, it is true Carrots are good for your eyes! They contain beta carotene, a substance that turns into vitamin A when eaten. Eating carrots can benefit your night vision and could possibly reduce your risk of cataracts, AMD, and dry eyes. Other foods that contain beta carotene include pumpkin, sweet potatoes, and butternut squash. All great ingredients to include into your holiday feast.
It wasn’t an old wives tale, it is true Carrots are good for your eyes! They contain beta carotene, a substance that turns into vitamin A when eaten. Eating carrots can benefit your night vision and could possibly reduce your risk of cataracts, AMD, and dry eyes. Other foods that contain beta carotene include pumpkin, sweet potatoes, and butternut squash. All great ingredients to include into your holiday feast.  Fish contain omega-3 fatty acids, which can reduce your risk of developing AMD, dry eye, and glaucoma. Salmon, mackerel, flounder, tuna, halibut, herring, and sardines would be a great addition to your holiday meals.
Fish contain omega-3 fatty acids, which can reduce your risk of developing AMD, dry eye, and glaucoma. Salmon, mackerel, flounder, tuna, halibut, herring, and sardines would be a great addition to your holiday meals. Whole grains reduce your risk of heart disease, obesity, and type 2 diabetes and can also decrease your risk of AMD. Substituting whole grain flour for white flour in holiday breads and muffins is a simple way to boost your whole grain intake. Other good whole grain sources include wild rice, brown rice, popcorn, oatmeal, bulgur, barley, buckwheat, and couscous.
Whole grains reduce your risk of heart disease, obesity, and type 2 diabetes and can also decrease your risk of AMD. Substituting whole grain flour for white flour in holiday breads and muffins is a simple way to boost your whole grain intake. Other good whole grain sources include wild rice, brown rice, popcorn, oatmeal, bulgur, barley, buckwheat, and couscous.  Fruits high in vitamin C, such as strawberries and oranges, also offer important vision benefits. Vitamin C is an antioxidant, a substance that can prevent cell damage caused by free radicals. Vitamin C-rich foods help keep the collagen in your cornea healthy and reduce the risk of cataracts and AMD. You can also find vitamin C in grapefruit, kiwi, blueberries, peas, broccoli, and tomatoes.
Fruits high in vitamin C, such as strawberries and oranges, also offer important vision benefits. Vitamin C is an antioxidant, a substance that can prevent cell damage caused by free radicals. Vitamin C-rich foods help keep the collagen in your cornea healthy and reduce the risk of cataracts and AMD. You can also find vitamin C in grapefruit, kiwi, blueberries, peas, broccoli, and tomatoes.
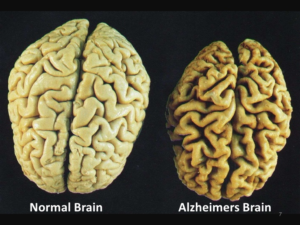
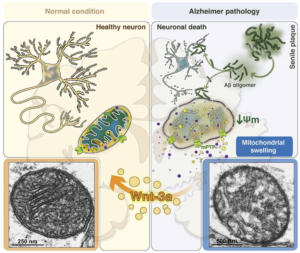
 For example, lutein and zeaxanthin are important antioxidants that help prevent degeneration in the lens and retina. Eating a diet rich in these carotenoids helps reduce the risk of AMD by fighting oxidation in the retinal cells of the eye.
For example, lutein and zeaxanthin are important antioxidants that help prevent degeneration in the lens and retina. Eating a diet rich in these carotenoids helps reduce the risk of AMD by fighting oxidation in the retinal cells of the eye. Eating fatty fish, such as salmon, tuna, mackerel, and sardines, that are rich in omega-3 fatty acids also helps lower the risk of AMD. Omega-3 fatty acids are rich in docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), which is important for eye health and visual function. People with dry eye syndrome (i.e., low tear production) can benefit from a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids because dry eye is linked to low levels of DHA.
Eating fatty fish, such as salmon, tuna, mackerel, and sardines, that are rich in omega-3 fatty acids also helps lower the risk of AMD. Omega-3 fatty acids are rich in docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), which is important for eye health and visual function. People with dry eye syndrome (i.e., low tear production) can benefit from a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids because dry eye is linked to low levels of DHA.

 The National Eye Institute has recommended that people who are high-risk for developing AMD eat diets rich in green leafy vegetables, whole fruits, any type of nuts and omega 3 fatty acids. Many of these foods have anti-oxidant properties that help to “turn off” genes involved with inflammation, an important factor of retinal diseases. Salmon, mackerel and sardines have the highest levels of omega-3 fatty acids. An analysis that combined the data from 9 different studies showed that fish intake at least twice a week was associated with reduced risk of early and late AMD. Other studies show that Omega-3 fatty acids improve mitochondrial function, decreases production of reactive oxygen species (free radicals that damage cells) and leads to less fat accumulation in the body. The green leafy vegetables contain important protective macular pigments (carotenoids) called lutein and zeaxanthin that reduce the risk of AMD by 43%. High levels of lipid or fat deposits in the body (obesity) can “soak-up” the lutein and zeaxanthin so that they are not available to protect the retina.
The National Eye Institute has recommended that people who are high-risk for developing AMD eat diets rich in green leafy vegetables, whole fruits, any type of nuts and omega 3 fatty acids. Many of these foods have anti-oxidant properties that help to “turn off” genes involved with inflammation, an important factor of retinal diseases. Salmon, mackerel and sardines have the highest levels of omega-3 fatty acids. An analysis that combined the data from 9 different studies showed that fish intake at least twice a week was associated with reduced risk of early and late AMD. Other studies show that Omega-3 fatty acids improve mitochondrial function, decreases production of reactive oxygen species (free radicals that damage cells) and leads to less fat accumulation in the body. The green leafy vegetables contain important protective macular pigments (carotenoids) called lutein and zeaxanthin that reduce the risk of AMD by 43%. High levels of lipid or fat deposits in the body (obesity) can “soak-up” the lutein and zeaxanthin so that they are not available to protect the retina.