When it comes to our health, we may visit our doctors and nurses regularly to make sure our bodies are healthy. But what about our eyes? They’re not always top of mind, but they’re just as important! May is Healthy Vision Month, an observance coordinated by the National Eye Institute to motivate Americans to make their eye health a priority and educate them about steps they can take to protect their vision.
When it comes to our health, we may visit our doctors and nurses regularly to make sure our bodies are healthy. But what about our eyes? They’re not always top of mind, but they’re just as important! May is Healthy Vision Month, an observance coordinated by the National Eye Institute to motivate Americans to make their eye health a priority and educate them about steps they can take to protect their vision.
Here are a few ways you can help protect your vision
- Get an annual comprehensive dilated eye exam.
- Know your family’s eye health history. It’s important to know if anyone has been diagnosed with an eye disease or condition, since some are hereditary.
- Eat right to protect your sight: In particular, eat plenty of dark leafy greens such as spinach, kale, or collard greens, and fish that is high in omega-3 fatty acids such as salmon, albacore tuna, trout, and halibut. Visit Eye Cook for eye healthy recipes.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Wear protective eyewear when playing sports or doing activities around the home, such as painting, yard work, and home repairs.
- Quit smoking or never start.
- Wear sunglasses that block 99 -100 percent of ultraviolet A (UVA) and ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation.
- Wash your hands before taking out your contacts and cleanse your contact lenses properly to avoid infection.
- Practice workplace eye safety.

Taking care of your eyes also may benefit your overall health. People with vision problems are more likely than those with good vision to have diabetes, poor hearing, heart problems, high blood pressure, lower back pain and strokes, as well as have increased risk for falls, injury and depression.
In addition to your comprehensive dilated eye exams, visit an eye care professional if you have
- Decreased vision.
- Eye pain
- Drainage or redness of the eye
- Double vision
- Diabetes
- Floaters (tiny specks that appear to float before your eyes)
- Circles (halos) around light sources or if you see flashes of light
For this Healthy Vision Month, take care of your eyes to make them last a lifetime.
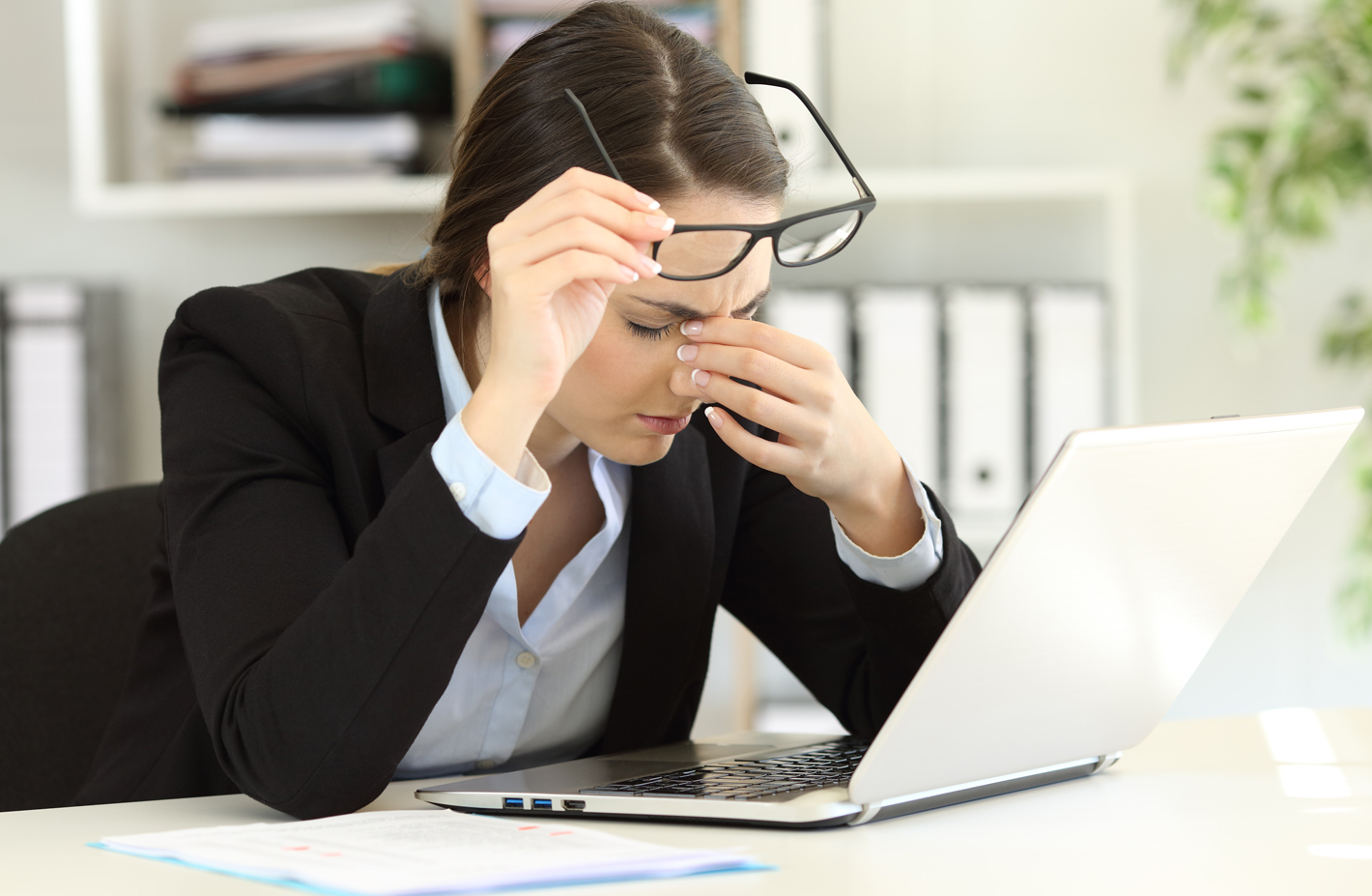







 Rest and blink your eyes – Researchers found that over 30% of people using digital devices rarely take time to rest their eyes. Just over 10% say they never take a break, even when working from home. The eye muscles get overworked and don’t get a chance to relax and recover. Experts suggest the 20-20-20 rule; every 20 minutes, focus your eyes and attention on something 20 feet away for 20 seconds. You can also get up and walk around for a few minutes.
Rest and blink your eyes – Researchers found that over 30% of people using digital devices rarely take time to rest their eyes. Just over 10% say they never take a break, even when working from home. The eye muscles get overworked and don’t get a chance to relax and recover. Experts suggest the 20-20-20 rule; every 20 minutes, focus your eyes and attention on something 20 feet away for 20 seconds. You can also get up and walk around for a few minutes. Reduce exposure to blue light – In the spectrum of light, blue is more high energy and close to ultraviolet light. So, if you use screens throughout the day, ask your eye doctor about the value of computer glasses that block blue light. Reducing exposure to blue light may help lessen vision problems. At home, using digital devices until bedtime can overstimulate your brain and make it more difficult to fall asleep. Eye doctors recommend no screen time at least one to two hours before going to sleep.
Reduce exposure to blue light – In the spectrum of light, blue is more high energy and close to ultraviolet light. So, if you use screens throughout the day, ask your eye doctor about the value of computer glasses that block blue light. Reducing exposure to blue light may help lessen vision problems. At home, using digital devices until bedtime can overstimulate your brain and make it more difficult to fall asleep. Eye doctors recommend no screen time at least one to two hours before going to sleep.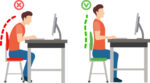 Sit up straight – Proper posture is important. Your back should be straight and your feet on the floor while you work. Elevate your wrists slightly instead of resting them on the keyboard.
Sit up straight – Proper posture is important. Your back should be straight and your feet on the floor while you work. Elevate your wrists slightly instead of resting them on the keyboard. Set up monitor properly – Make sure your computer screen is about 25 inches, or an arm’s length, away from your face. The center of the screen should be about 10-15 degrees below eye level. Cut glare by using a matte screen filter. You can find them for all types of computers, phones, and tablets. Increase font size or set the magnification of the documents you are reading to a comfortable size.
Set up monitor properly – Make sure your computer screen is about 25 inches, or an arm’s length, away from your face. The center of the screen should be about 10-15 degrees below eye level. Cut glare by using a matte screen filter. You can find them for all types of computers, phones, and tablets. Increase font size or set the magnification of the documents you are reading to a comfortable size. Consider computer glasses –For the greatest comfort at your computer, you might benefit from having your eye doctor modify your eyeglasses prescription to create customized computer glasses. This is especially true if you normally wear distance contact lenses, which may also become dry and uncomfortable during extended screen time. Computer glasses also are a good choice if you wear bifocals or progressive lenses, because these lenses generally are not optimal for the distance to your computer screen.
Consider computer glasses –For the greatest comfort at your computer, you might benefit from having your eye doctor modify your eyeglasses prescription to create customized computer glasses. This is especially true if you normally wear distance contact lenses, which may also become dry and uncomfortable during extended screen time. Computer glasses also are a good choice if you wear bifocals or progressive lenses, because these lenses generally are not optimal for the distance to your computer screen. Get an Eye Exam – If you have tried all these tips and eye strain is still an issue, it might be time to see an eye care professional to schedule an eye exam. The exam may even detect underlying issues before they becomes worse.
Get an Eye Exam – If you have tried all these tips and eye strain is still an issue, it might be time to see an eye care professional to schedule an eye exam. The exam may even detect underlying issues before they becomes worse.
 Thanksgiving is almost here; a meal that nourishes the family bonds and traditions. It’s the one time of the year where you can guarantee your eyes will be bigger than your stomach.
Thanksgiving is almost here; a meal that nourishes the family bonds and traditions. It’s the one time of the year where you can guarantee your eyes will be bigger than your stomach. 


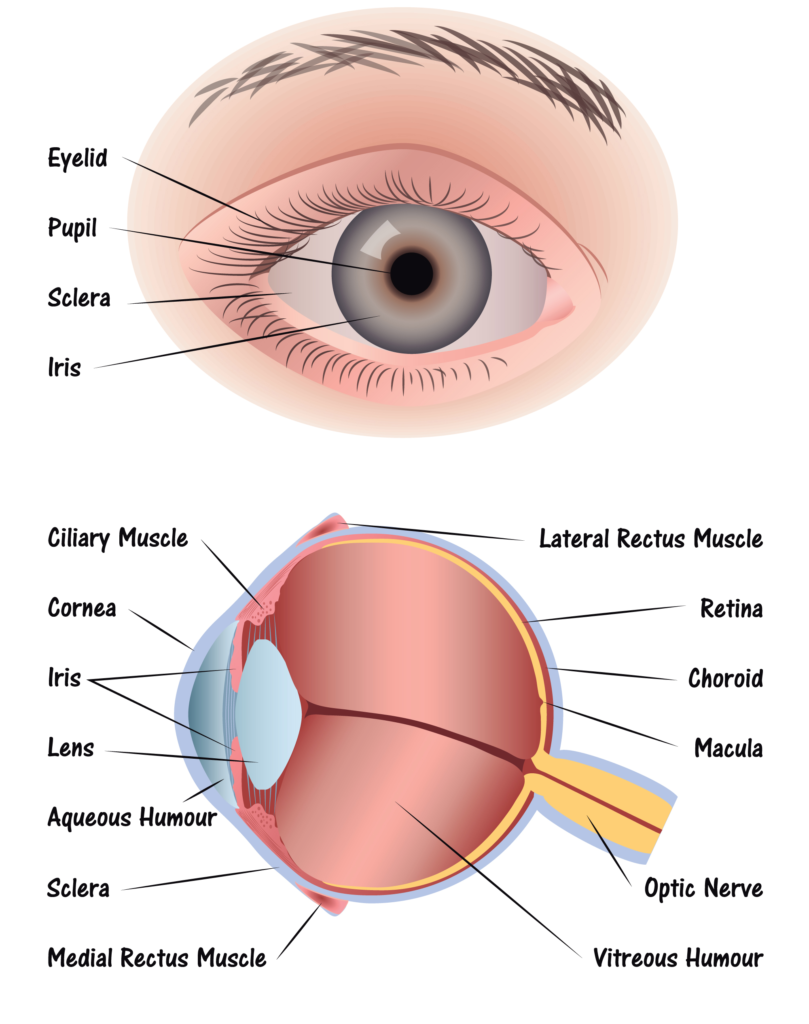 Step 1: Light passes through a thin layer of moisture
Step 1: Light passes through a thin layer of moisture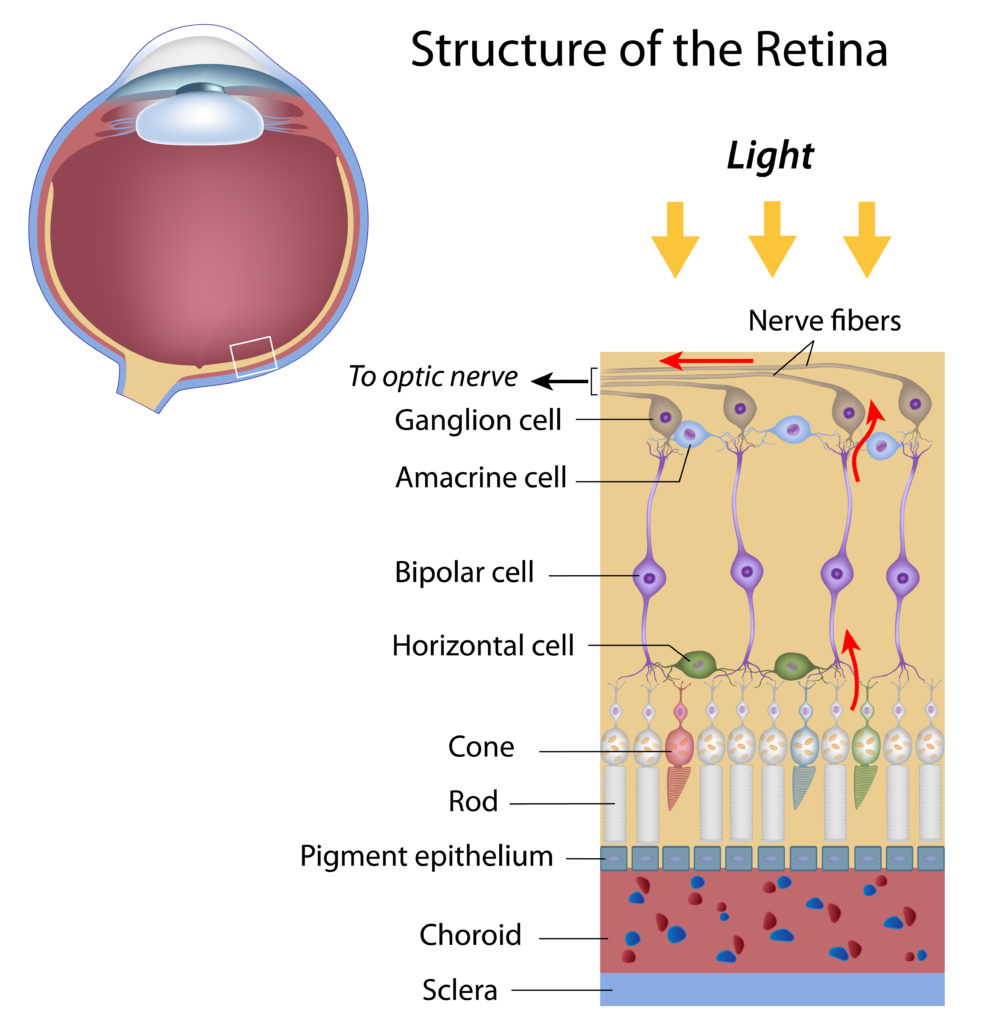
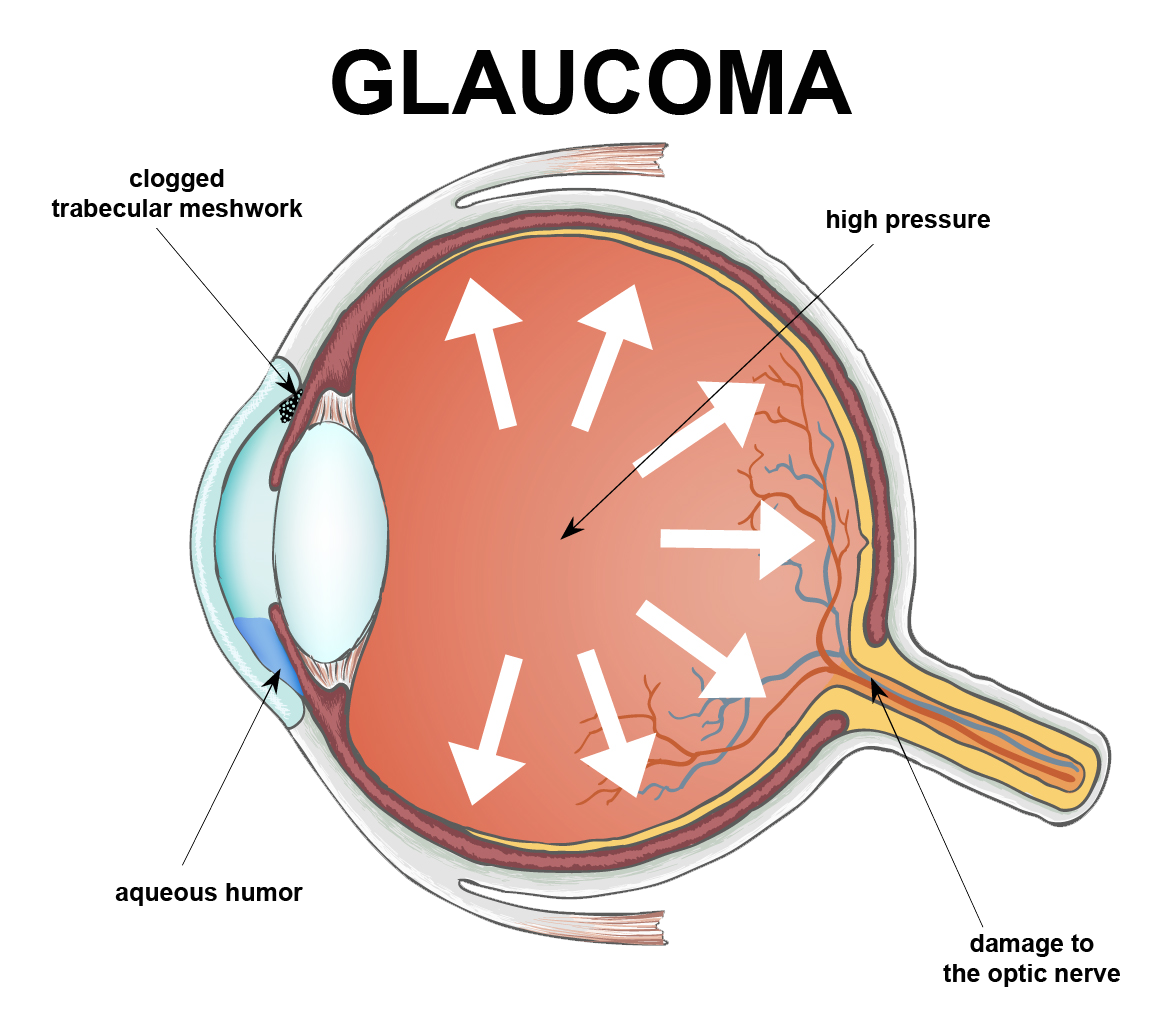
 National Glaucoma Awareness Month reminds all of us to get regular eye exams and show support for those suffering from this condition.
National Glaucoma Awareness Month reminds all of us to get regular eye exams and show support for those suffering from this condition.